Information Retrieval
Search engines, recommender systems, and web mining
Search engines, recommender systems, and web mining
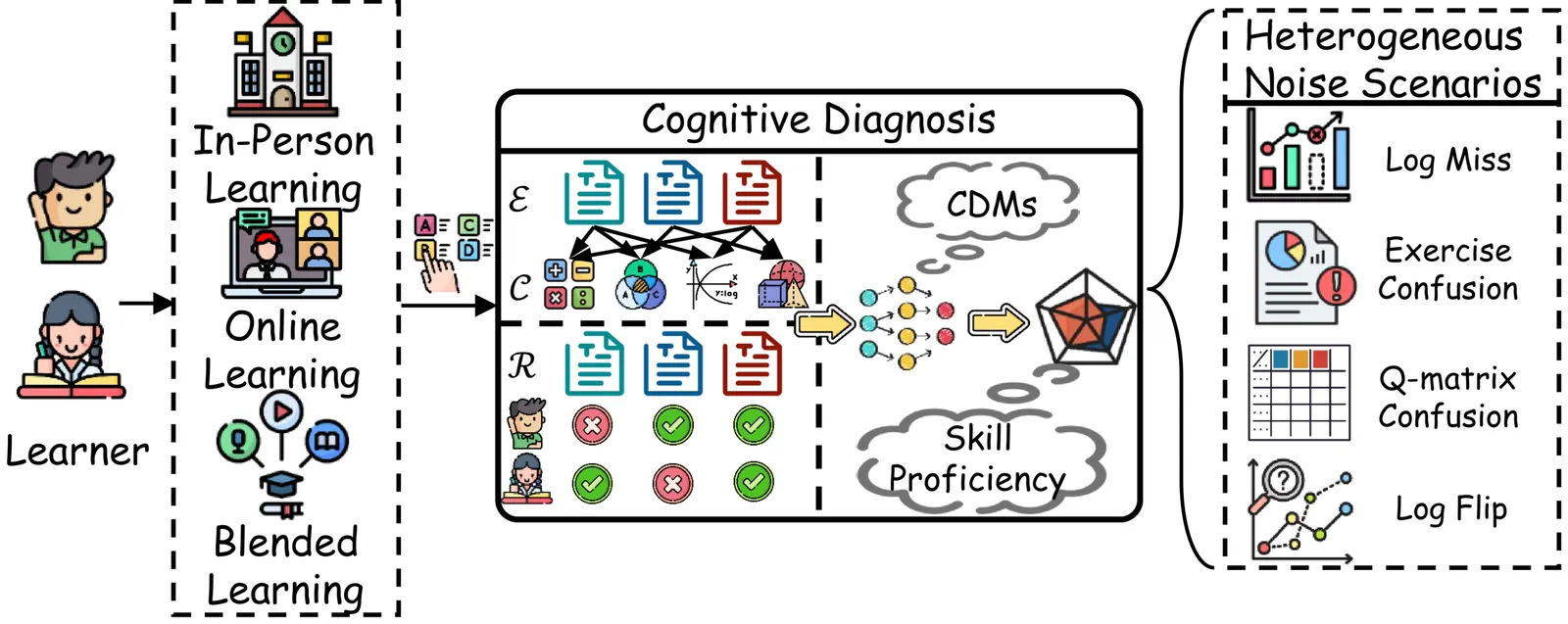
With the advancement of network technologies, intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) have emerged to deliver increasingly precise and tailored personalized learning services. Cognitive diagnosis (CD) has emerged as a core research task in ITS, aiming to infer learners' mastery of specific knowledge concepts by modeling the mapping between learning behavior data and knowledge states. However, existing research prioritizes model performance enhancement while neglecting the pervasive noise contamination in observed response data, significantly hindering practical deployment. Furthermore, current cognitive diagnosis models (CDMs) rely heavily on researchers' domain expertise for structural design, which fails to exhaustively explore architectural possibilities, thus leaving model architectures' full potential untapped. To address this issue, we propose OSCD, an evolutionary multi-objective One-Shot neural architecture search method for Cognitive Diagnosis, designed to efficiently and robustly improve the model's capability in assessing learner proficiency. Specifically, OSCD operates through two distinct stages: training and searching. During the training stage, we construct a search space encompassing diverse architectural combinations and train a weight-sharing supernet represented via the complete binary tree topology, enabling comprehensive exploration of potential architectures beyond manual design priors. In the searching stage, we formulate the optimal architecture search under heterogeneous noise scenarios as a multi-objective optimization problem (MOP), and develop an optimization framework integrating a Pareto-optimal solution search strategy with cross-scenario performance evaluation for resolution. Extensive experiments on real-world educational datasets validate the effectiveness and robustness of the optimal architectures discovered by our OSCD model for CD tasks.
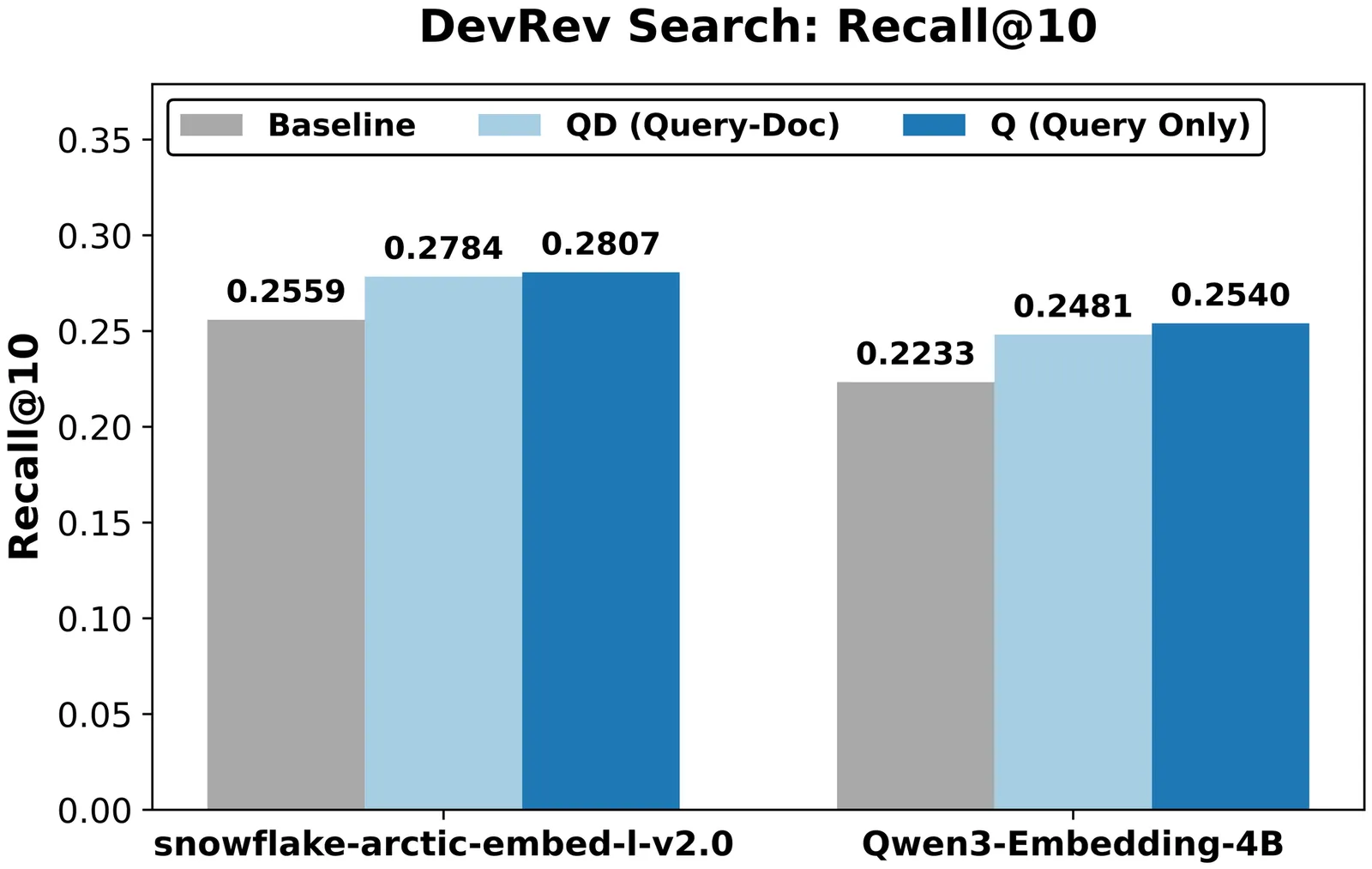
Large-scale multi-tenant retrieval systems amass vast user query logs yet critically lack the curated relevance labels required for effective domain adaptation. This "dark data" problem is exacerbated by the operational cost of model updates: jointly fine-tuning query and document encoders requires re-indexing the entire corpus, which is prohibitive in multi-tenant environments with thousands of isolated indices. To address these dual challenges, we introduce \textbf{DevRev Search}, a passage retrieval benchmark for technical customer support constructed through a fully automatic pipeline. We employ a \textbf{fusion-based candidate generation} strategy, pooling results from diverse sparse and dense retrievers, and utilize an LLM-as-a-Judge to perform rigorous \textbf{consistency filtering} and relevance assignment. We further propose a practical \textbf{Index-Preserving Adaptation} strategy: by fine-tuning only the query encoder via Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), we achieve competitive performance improvements while keeping the document index frozen. Our experiments on DevRev Search and SciFact demonstrate that targeting specific transformer layers in the query encoder yields optimal quality-efficiency trade-offs, offering a scalable path for personalized enterprise search.
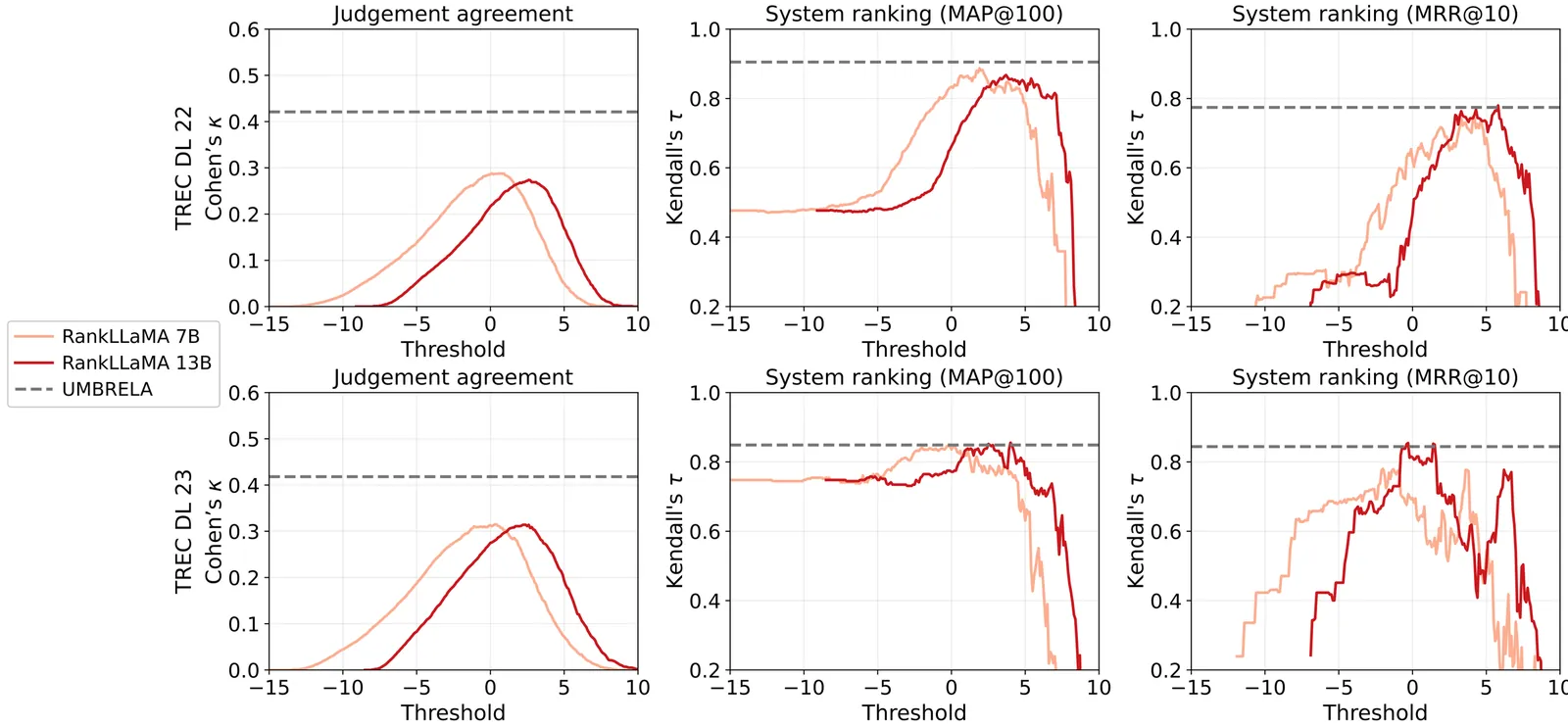
Using large language models (LLMs) to predict relevance judgments has shown promising results. Most studies treat this task as a distinct research line, e.g., focusing on prompt design for predicting relevance labels given a query and passage. However, predicting relevance judgments is essentially a form of relevance prediction, a problem extensively studied in tasks such as re-ranking. Despite this potential overlap, little research has explored reusing or adapting established re-ranking methods to predict relevance judgments, leading to potential resource waste and redundant development. To bridge this gap, we reproduce re-rankers in a re-ranker-as-relevance-judge setup. We design two adaptation strategies: (i) using binary tokens (e.g., "true" and "false") generated by a re-ranker as direct judgments, and (ii) converting continuous re-ranking scores into binary labels via thresholding. We perform extensive experiments on TREC-DL 2019 to 2023 with 8 re-rankers from 3 families, ranging from 220M to 32B, and analyse the evaluation bias exhibited by re-ranker-based judges. Results show that re-ranker-based relevance judges, under both strategies, can outperform UMBRELA, a state-of-the-art LLM-based relevance judge, in around 40% to 50% of the cases; they also exhibit strong self-preference towards their own and same-family re-rankers, as well as cross-family bias.
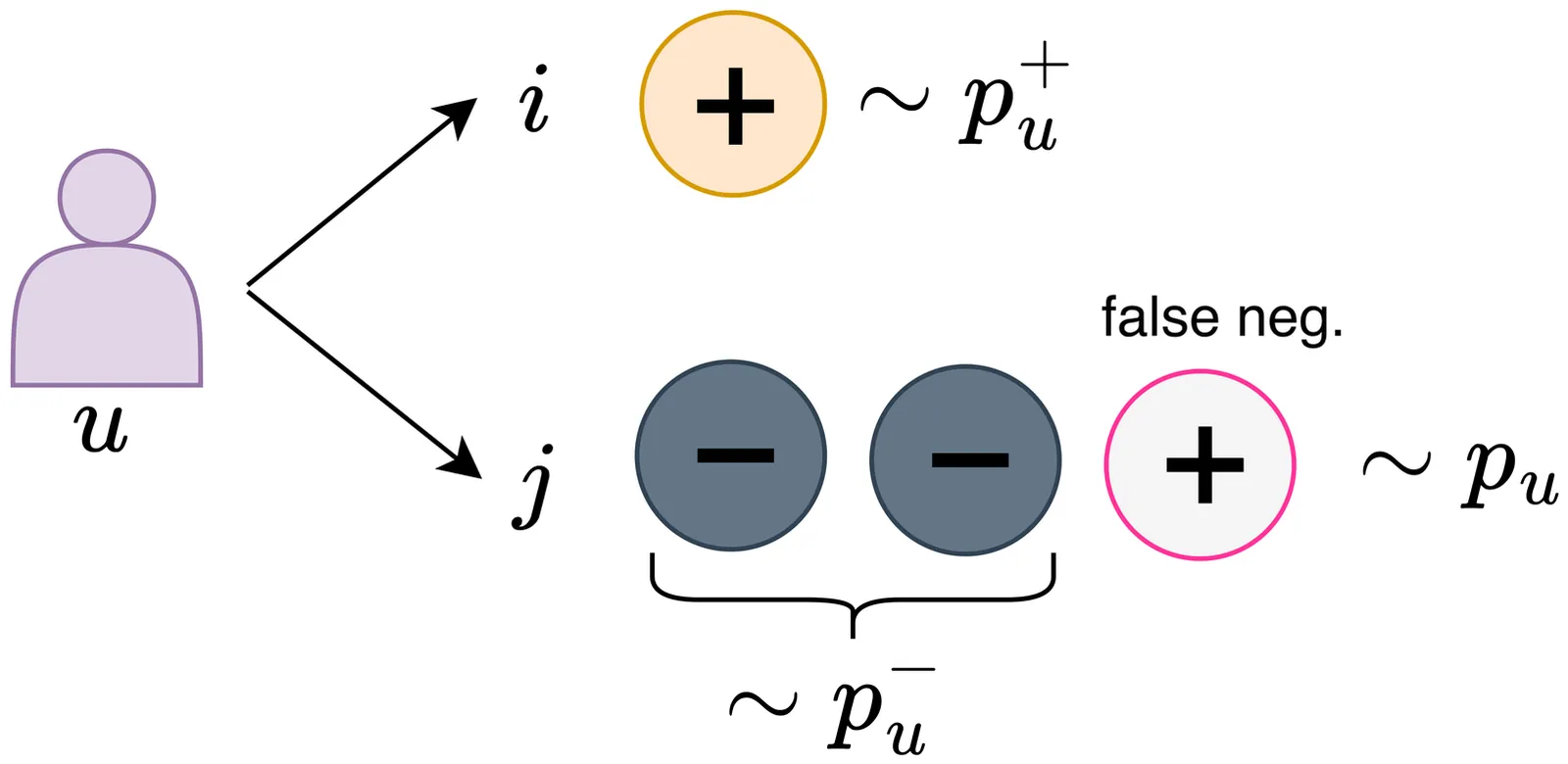
Learning from implicit feedback has become the standard paradigm for modern recommender systems. However, this setting is fraught with the persistent challenge of false negatives, where unobserved user-item interactions are not necessarily indicative of negative preference. To address this issue, this paper introduces a novel and principled loss function, named Corrected and Weighted (CW) loss, that systematically corrects for the impact of false negatives within the training objective. Our approach integrates two key techniques. First, inspired by Positive-Unlabeled learning, we debias the negative sampling process by re-calibrating the assumed negative distribution. By theoretically approximating the true negative distribution (p-) using the observable general data distribution (p) and the positive interaction distribution (p^+), our method provides a more accurate estimate of the likelihood that a sampled unlabeled item is truly negative. Second, we introduce a dynamic re-weighting mechanism that modulates the importance of each negative instance based on the model's current prediction. This scheme encourages the model to enforce a larger ranking margin between positive items and confidently predicted (i.e., easy) negative items, while simultaneously down-weighting the penalty on uncertain negatives that have a higher probability of being false negatives. A key advantage of our approach is its elegance and efficiency; it requires no complex modifications to the data sampling process or significant computational overhead, making it readily applicable to a wide array of existing recommendation models. Extensive experiments conducted on four large-scale, sparse benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed loss. The results show that our method consistently and significantly outperforms a suite of state-of-the-art loss functions across multiple ranking-oriented metrics.
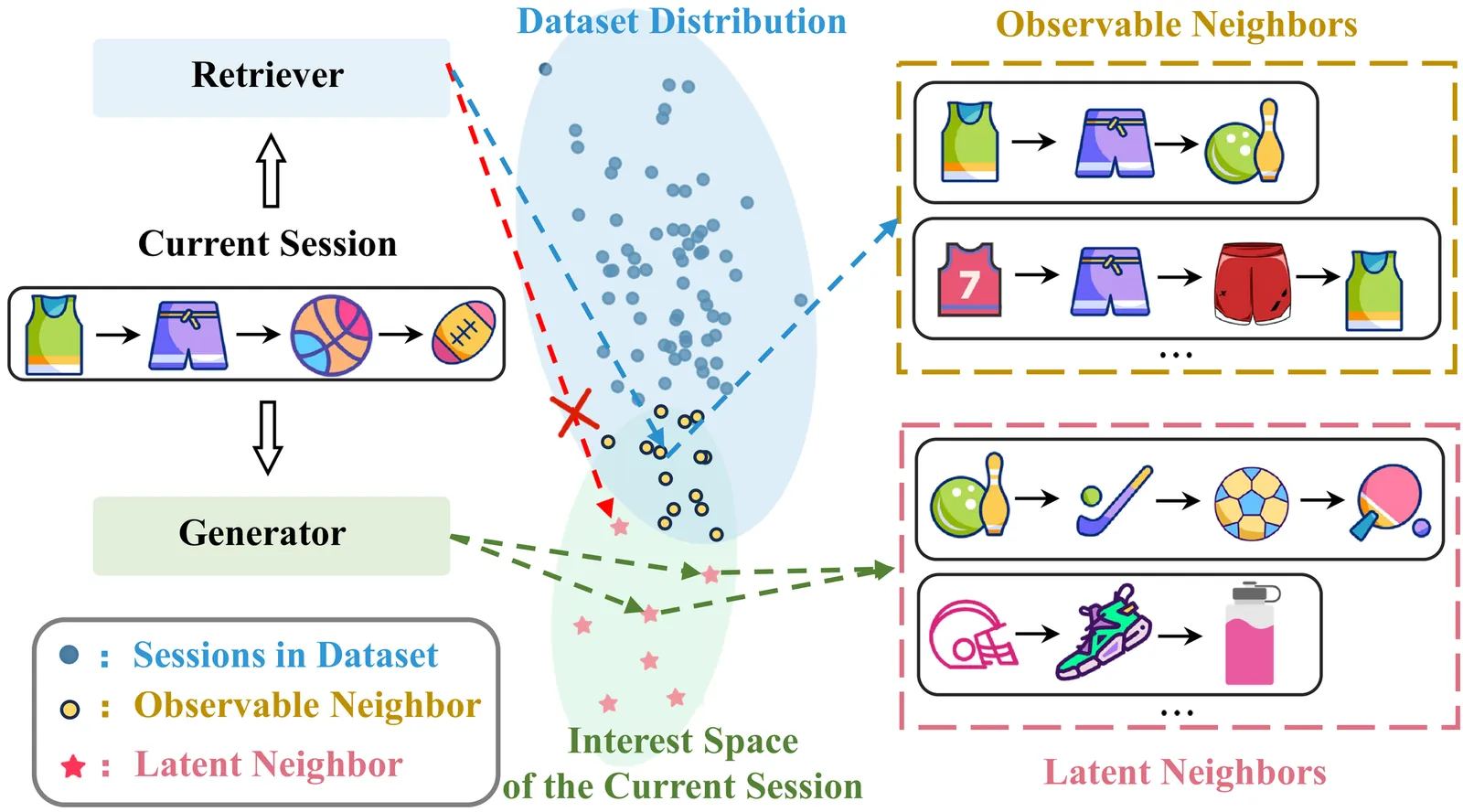
Session-based recommendation aims to predict the next item that anonymous users may be interested in, based on their current session interactions. Recent studies have demonstrated that retrieving neighbor sessions to augment the current session can effectively alleviate the data sparsity issue and improve recommendation performance. However, existing methods typically rely on explicitly observed session data, neglecting latent neighbors - not directly observed but potentially relevant within the interest space - thereby failing to fully exploit the potential of neighbor sessions in recommendation. To address the above limitation, we propose a novel model of diffusion-based latent neighbor generation for session-based recommendation, named DiffSBR. Specifically, DiffSBR leverages two diffusion modules, including retrieval-augmented diffusion and self-augmented diffusion, to generate high-quality latent neighbors. In the retrieval-augmented diffusion module, we leverage retrieved neighbors as guiding signals to constrain and reconstruct the distribution of latent neighbors. Meanwhile, we adopt a training strategy that enables the retriever to learn from the feedback provided by the generator. In the self-augmented diffusion module, we explicitly guide the generation of latent neighbors by injecting the current session's multi-modal signals through contrastive learning. After obtaining the generated latent neighbors, we utilize them to enhance session representations for improving session-based recommendation. Extensive experiments on four public datasets show that DiffSBR generates effective latent neighbors and improves recommendation performance against state-of-the-art baselines.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems are increasingly deployed on large-scale document collections, often comprising millions of documents and tens of millions of text chunks. In industrial-scale retrieval platforms, scalability is typically addressed through horizontal sharding and a combination of Approximate Nearest-Neighbor search, hybrid indexing, and optimized metadata filtering. Although effective from an efficiency perspective, these mechanisms rely on bottom-up, similarity-driven organization and lack a conceptual rationale for corpus partitioning. In this paper, we claim that the design of large-scale RAG systems may benefit from the combination of two orthogonal strategies: semantic clustering, which optimizes locality in embedding space, and multidimensional partitioning, which governs where retrieval should occur based on conceptual dimensions such as time and organizational context. Although such dimensions are already implicitly present in current systems, they are used in an ad hoc and poorly structured manner. We propose the Dimensional Fact Model (DFM) as a conceptual framework to guide the design of multidimensional partitions for RAG corpora. The DFM provides a principled way to reason about facts, dimensions, hierarchies, and granularity in retrieval-oriented settings. This framework naturally supports hierarchical routing and controlled fallback strategies, ensuring that retrieval remains robust even in the presence of incomplete metadata, while transforming the search process from a 'black-box' similarity matching into a governable and deterministic workflow. This work is intended as a position paper; its goal is to bridge the gap between OLAP-style multidimensional modeling and modern RAG architectures, and to stimulate further research on principled, explainable, and governable retrieval strategies at scale.
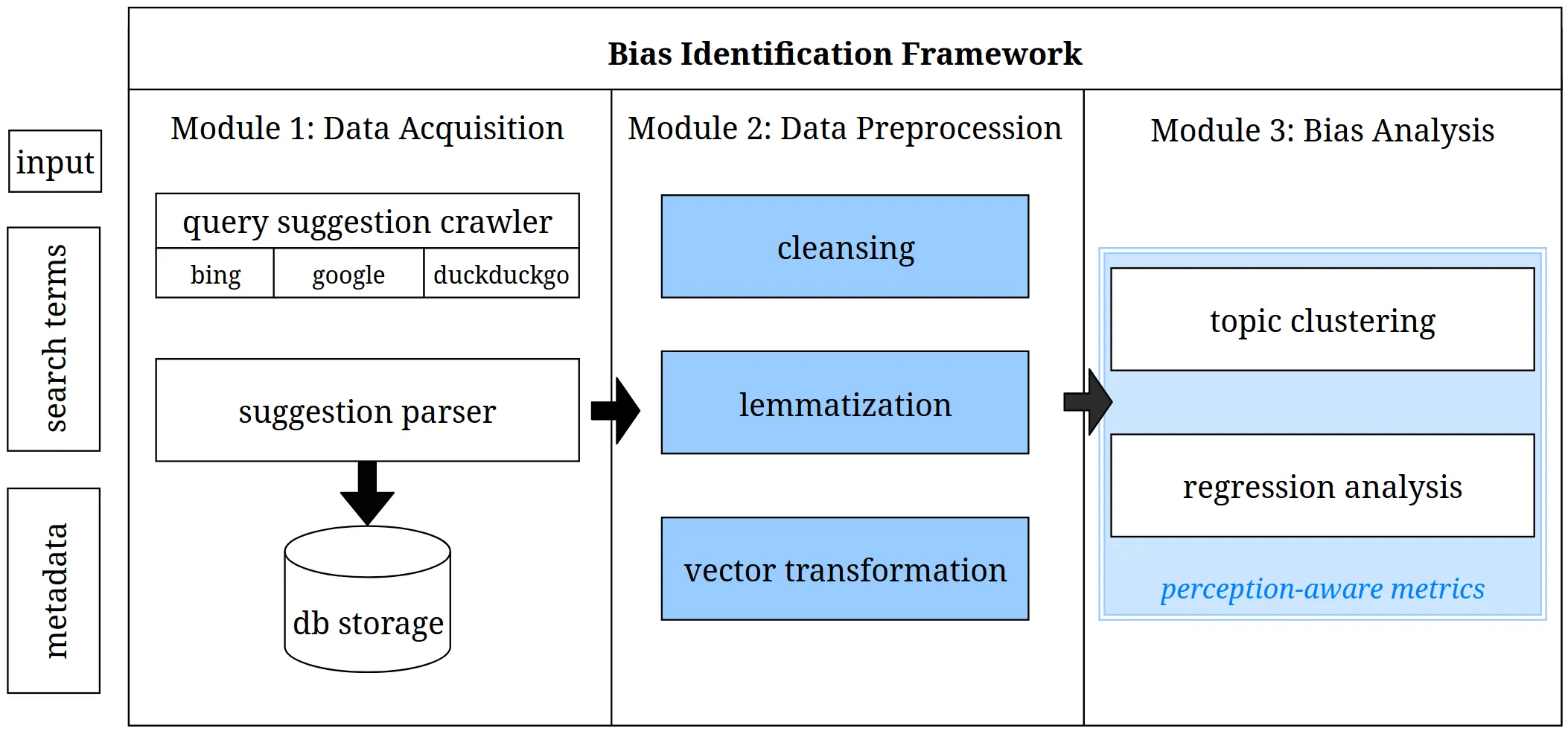
Bias in web search has been in the spotlight of bias detection research for quite a while. At the same time, little attention has been paid to query suggestions in this regard. Awareness of the problem of biased query suggestions has been raised. Likewise, there is a rising need for automatic bias detection approaches. This paper adds on the bias detection pipeline for bias detection in query suggestions of person-related search developed by Bonart et al. \cite{Bonart_2019a}. The sparseness and lack of contextual metadata of query suggestions make them a difficult subject for bias detection. Furthermore, query suggestions are perceived very briefly and subliminally. To overcome these issues, perception-aware metrics are introduced. Consequently, the enhanced pipeline is able to better detect systematic topical bias in search engine query suggestions for person-related searches. The results of an analysis performed with the developed pipeline confirm this assumption. Due to the perception-aware bias detection metrics, findings produced by the pipeline can be assumed to reflect bias that users would discern.
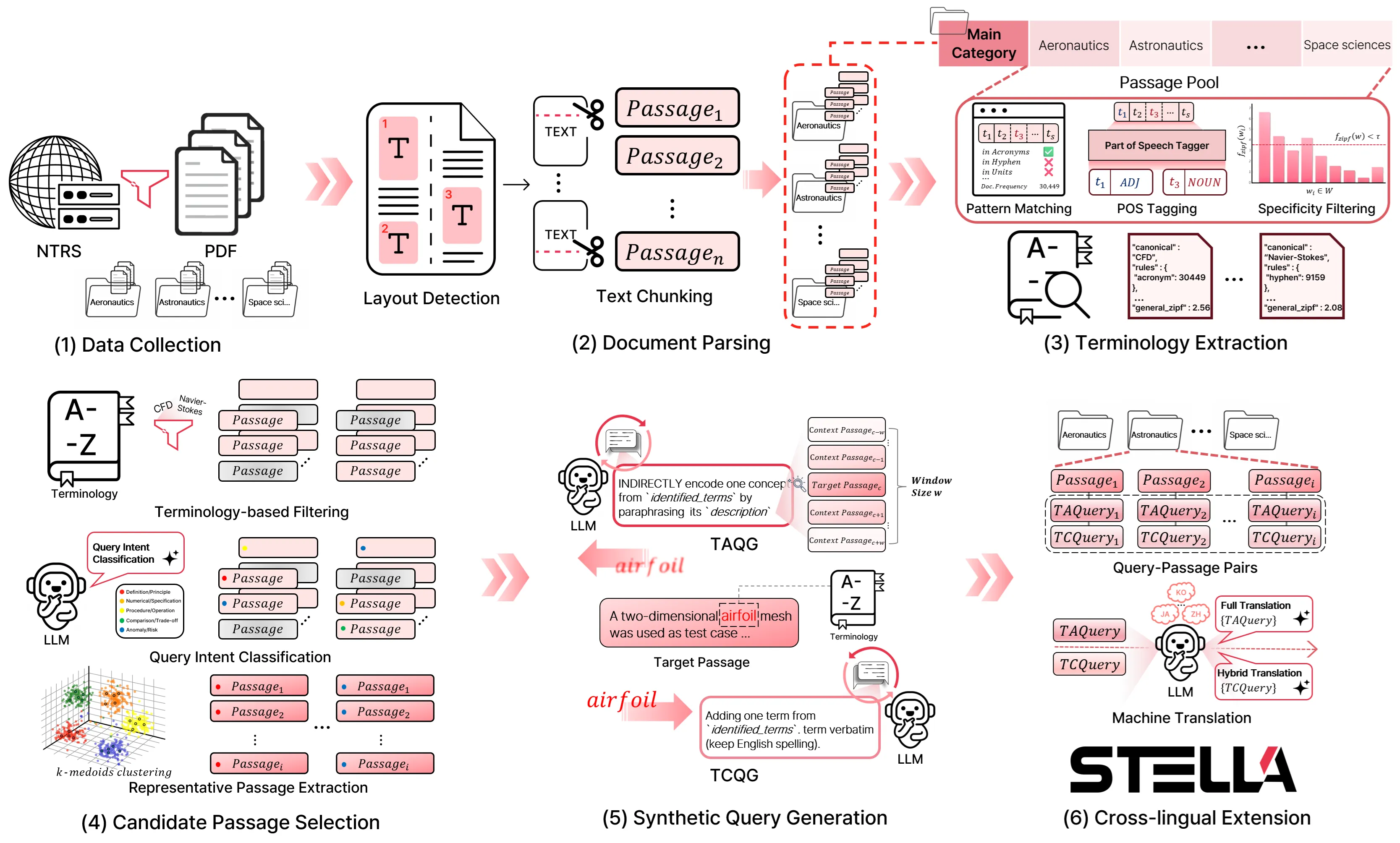
Tasks in the aerospace industry heavily rely on searching and reusing large volumes of technical documents, yet there is no public information retrieval (IR) benchmark that reflects the terminology- and query-intent characteristics of this domain. To address this gap, this paper proposes the STELLA (Self-Reflective TErminoLogy-Aware Framework for BuiLding an Aerospace Information Retrieval Benchmark) framework. Using this framework, we introduce the STELLA benchmark, an aerospace-specific IR evaluation set constructed from NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS) documents via a systematic pipeline that comprises document layout detection, passage chunking, terminology dictionary construction, synthetic query generation, and cross-lingual extension. The framework generates two types of queries: the Terminology Concordant Query (TCQ), which includes the terminology verbatim to evaluate lexical matching, and the Terminology Agnostic Query (TAQ), which utilizes the terminology's description to assess semantic matching. This enables a disentangled evaluation of the lexical and semantic matching capabilities of embedding models. In addition, we combine Chain-of-Density (CoD) and the Self-Reflection method with query generation to improve quality and implement a hybrid cross-lingual extension that reflects real user querying practices. Evaluation of seven embedding models on the STELLA benchmark shows that large decoder-based embedding models exhibit the strongest semantic understanding, while lexical matching methods such as BM25 remain highly competitive in domains where exact lexical matching technical term is crucial. The STELLA benchmark provides a reproducible foundation for reliable performance evaluation and improvement of embedding models in aerospace-domain IR tasks. The STELLA benchmark can be found in https://huggingface.co/datasets/telepix/STELLA.
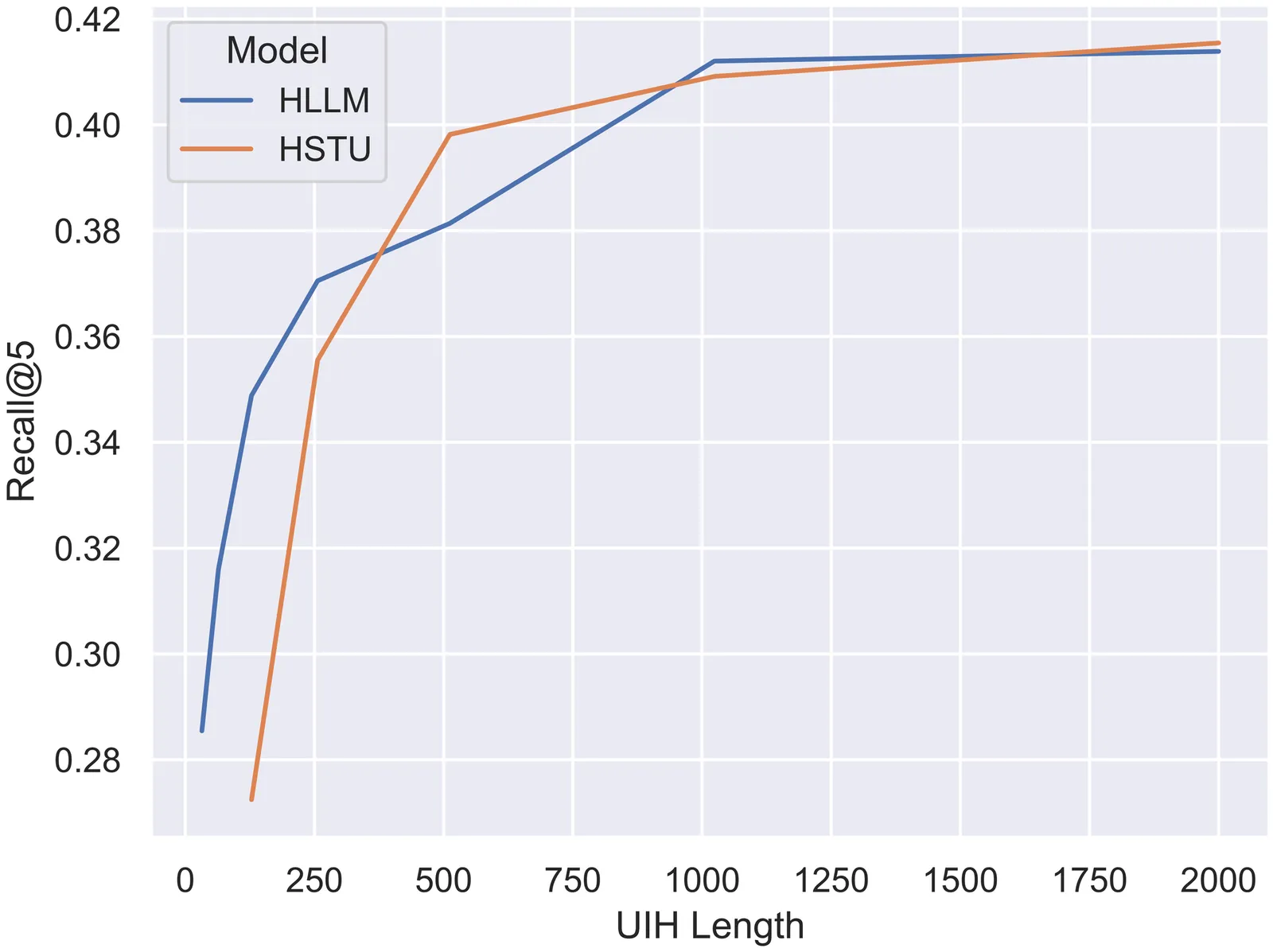
Recent years have witnessed success of sequential modeling, generative recommender, and large language model for recommendation. Though the scaling law has been validated for sequential models, it showed inefficiency in computational capacity when considering real-world applications like recommendation, due to the non-linear(quadratic) increasing nature of the transformer model. To improve the efficiency of the sequential model, we introduced a novel approach to sequential recommendation that leverages personalization techniques to enhance efficiency and performance. Our method compresses long user interaction histories into learnable tokens, which are then combined with recent interactions to generate recommendations. This approach significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining high recommendation accuracy. Our method could be applied to existing transformer based recommendation models, e.g., HSTU and HLLM. Extensive experiments on multiple sequential models demonstrate its versatility and effectiveness. Source code is available at \href{https://github.com/facebookresearch/PerSRec}{https://github.com/facebookresearch/PerSRec}.
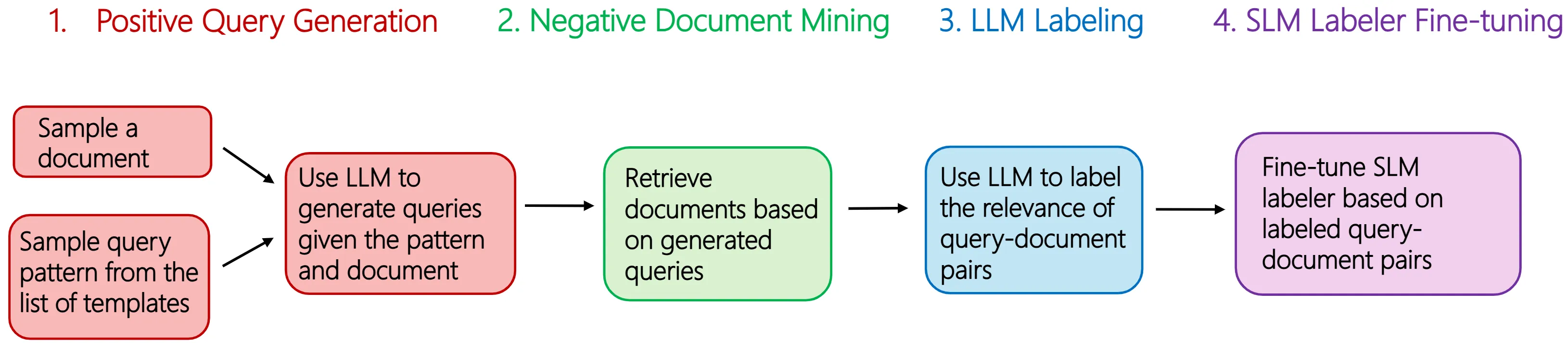
In enterprise search, building high-quality datasets at scale remains a central challenge due to the difficulty of acquiring labeled data. To resolve this challenge, we propose an efficient approach to fine-tune small language models (SLMs) for accurate relevance labeling, enabling high-throughput, domain-specific labeling comparable or even better in quality to that of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). To overcome the lack of high-quality and accessible datasets in the enterprise domain, our method leverages on synthetic data generation. Specifically, we employ an LLM to synthesize realistic enterprise queries from a seed document, apply BM25 to retrieve hard negatives, and use a teacher LLM to assign relevance scores. The resulting dataset is then distilled into an SLM, producing a compact relevance labeler. We evaluate our approach on a high-quality benchmark consisting of 923 enterprise query-document pairs annotated by trained human annotators, and show that the distilled SLM achieves agreement with human judgments on par with or better than the teacher LLM. Furthermore, our fine-tuned labeler substantially improves throughput, achieving 17 times increase while also being 19 times more cost-effective. This approach enables scalable and cost-effective relevance labeling for enterprise-scale retrieval applications, supporting rapid offline evaluation and iteration in real-world settings.
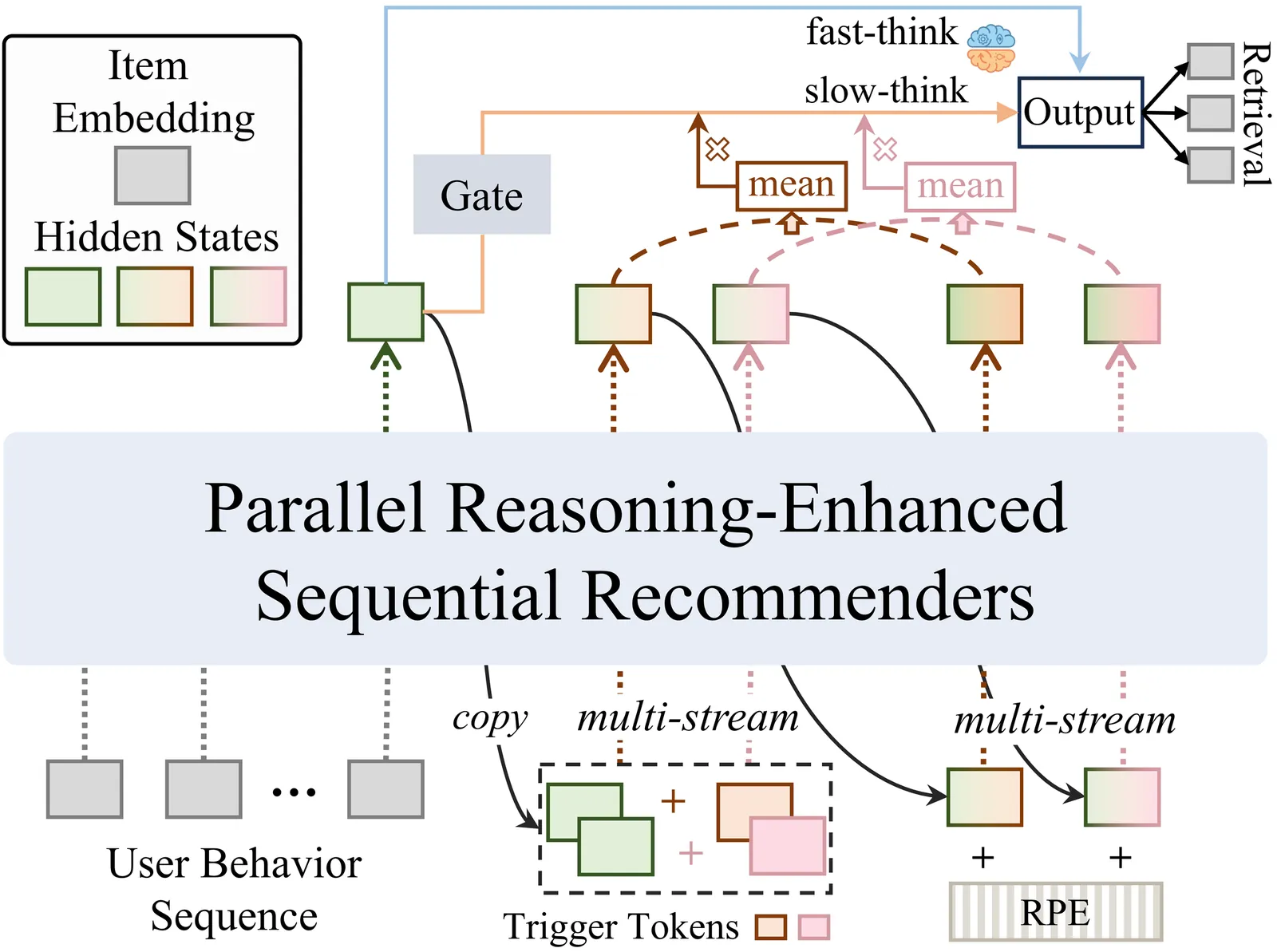
Capturing complex user preferences from sparse behavioral sequences remains a fundamental challenge in sequential recommendation. Recent latent reasoning methods have shown promise by extending test-time computation through multi-step reasoning, yet they exclusively rely on depth-level scaling along a single trajectory, suffering from diminishing returns as reasoning depth increases. To address this limitation, we propose \textbf{Parallel Latent Reasoning (PLR)}, a novel framework that pioneers width-level computational scaling by exploring multiple diverse reasoning trajectories simultaneously. PLR constructs parallel reasoning streams through learnable trigger tokens in continuous latent space, preserves diversity across streams via global reasoning regularization, and adaptively synthesizes multi-stream outputs through mixture-of-reasoning-streams aggregation. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that PLR substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining real-time inference efficiency. Theoretical analysis further validates the effectiveness of parallel reasoning in improving generalization capability. Our work opens new avenues for enhancing reasoning capacity in sequential recommendation beyond existing depth scaling.
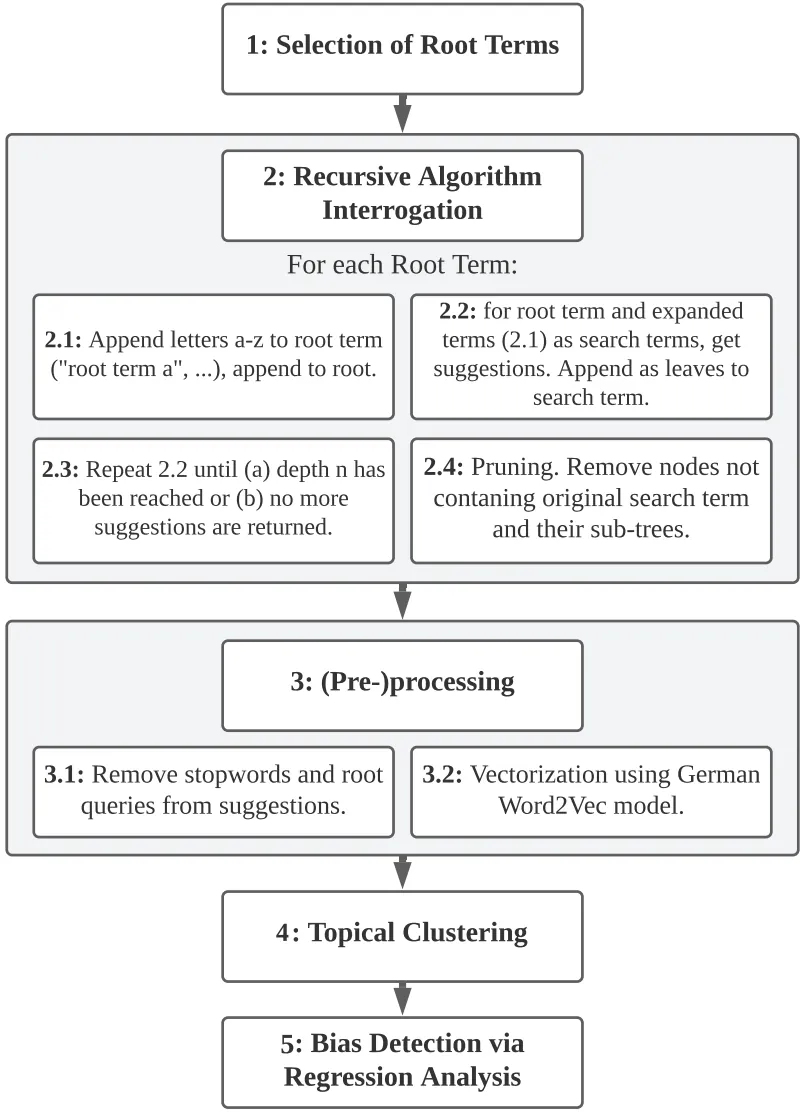
Despite their important role in online information search, search query suggestions have not been researched as much as most other aspects of search engines. Although reasons for this are multi-faceted, the sparseness of context and the limited data basis of up to ten suggestions per search query pose the most significant problem in identifying bias in search query suggestions. The most proven method to reduce sparseness and improve the validity of bias identification of search query suggestions so far is to consider suggestions from subsequent searches over time for the same query. This work presents a new, alternative approach to search query bias identification that includes less high-level suggestions to deepen the data basis of bias analyses. We employ recursive algorithm interrogation techniques and create suggestion trees that enable access to more subliminal search query suggestions. Based on these suggestions, we investigate topical group bias in person-related searches in the political domain.
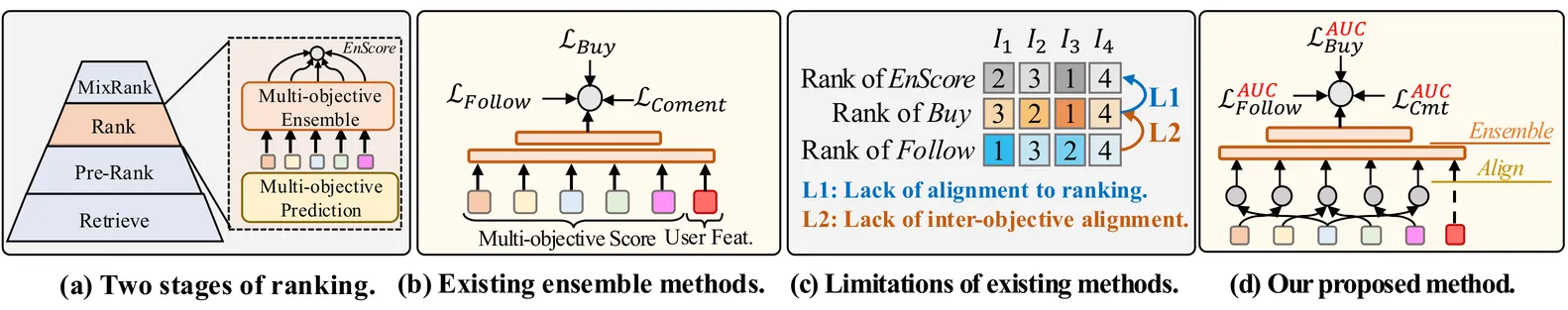
Recommendation for live-streaming e-commerce is gaining increasing attention due to the explosive growth of the live streaming economy. Different from traditional e-commerce, live-streaming e-commerce shifts the focus from products to streamers, which requires ranking mechanism to balance both purchases and user-streamer interactions for long-term ecology. To trade off multiple objectives, a popular solution is to build an ensemble model to integrate multi-objective scores into a unified score. The ensemble model is usually supervised by multiple independent binary classification losses of all objectives. However, this paradigm suffers from two inherent limitations. First, the optimization direction of the binary classification task is misaligned with the ranking task (evaluated by AUC). Second, this paradigm overlooks the alignment between objectives, e.g., comment and buy behaviors are partially dependent which can be revealed in labels correlations. The model can achieve better trade-offs if it learns the aligned parts of ranking abilities among different objectives. To mitigate these limitations, we propose a novel multi-objective ensemble framework HarmonRank to fulfill both alignment to the ranking task and alignment among objectives. For alignment to ranking, we formulate ranking metric AUC as a rank-sum problem and utilize differentiable ranking techniques for ranking-oriented optimization. For inter-objective alignment, we change the original one-step ensemble paradigm to a two-step relation-aware ensemble scheme. Extensive offline experiments results on two industrial datasets and online experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method has been fully deployed in Kuaishou's live-streaming e-commerce recommendation platform with 400 million DAUs, contributing over 2% purchase gain.
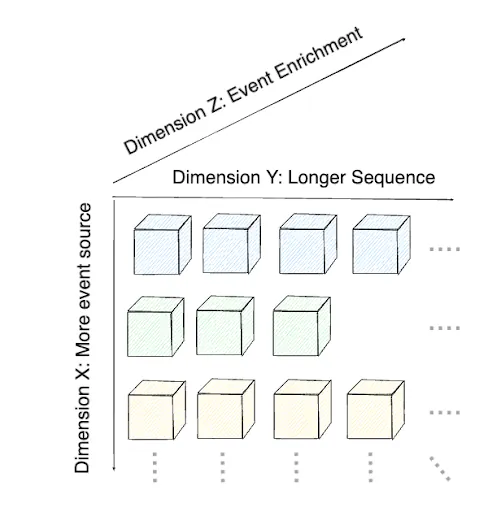
Diverse and enriched data sources are essential for commercial ads-recommendation models to accurately assess user interest both before and after engagement with content. While extended user-engagement histories can improve the prediction of user interests, it is equally important to embed activity sequences from multiple sources to ensure freshness of user and ad-representations, following scaling law principles. In this paper, we present a novel three-dimensional framework for enhancing user-ad representations without increasing model inference or serving complexity. The first dimension examines the impact of incorporating diverse event sources, the second considers the benefits of longer user histories, and the third focuses on enriching data with additional event attributes and multi-modal embeddings. We assess the return on investment (ROI) of our source enrichment framework by comparing organic user engagement sources, such as content viewing, with ad-impression sources. The proposed method can boost the area under curve (AUC) and the slope of scaling curves for ad-impression sources by 1.56 to 2 times compared to organic usage sources even for short online-sequence lengths of 100 to 10K. Additionally, click-through rate (CTR) prediction improves by 0.56% AUC over the baseline production ad-recommendation system when using enriched ad-impression event sources, leading to improved sequence scaling resolutions for longer and offline user-ad representations.

Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated success in various applications of user recommendation and personalization across e-commerce and entertainment. On many entertainment platforms such as Netflix, users typically interact with a wide range of titles, each represented by an artwork. Since users have diverse preferences, an artwork that appeals to one type of user may not resonate with another with different preferences. Given this user heterogeneity, our work explores the novel problem of personalized artwork recommendations according to diverse user preferences. Similar to the multi-dimensional nature of users' tastes, titles contain different themes and tones that may appeal to different viewers. For example, the same title might feature both heartfelt family drama and intense action scenes. Users who prefer romantic content may like the artwork emphasizing emotional warmth between the characters, while those who prefer action thrillers may find high-intensity action scenes more intriguing. Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach, we conduct post-training of pre-trained LLMs to make personalized artwork recommendations, selecting the most preferred visual representation of a title for each user and thereby improving user satisfaction and engagement. Our experimental results with Llama 3.1 8B models (trained on a dataset of 110K data points and evaluated on 5K held-out user-title pairs) show that the post-trained LLMs achieve 3-5\% improvements over the Netflix production model, suggesting a promising direction for granular personalized recommendations using LLMs.
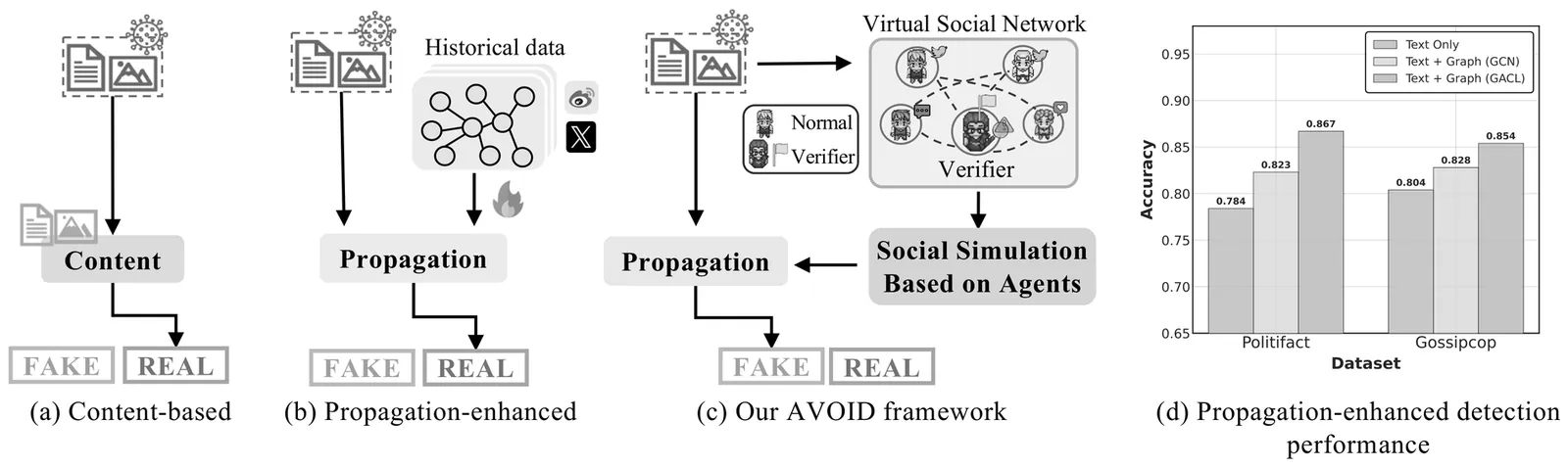
Early detection of fake news is critical for mitigating its rapid dissemination on social media, which can severely undermine public trust and social stability. Recent advancements show that incorporating propagation dynamics can significantly enhance detection performance compared to previous content-only approaches. However, this remains challenging at early stages due to the absence of observable propagation signals. To address this limitation, we propose AVOID, an \underline{a}gent-driven \underline{v}irtual pr\underline{o}pagat\underline{i}on for early fake news \underline{d}etection. AVOID reformulates early detection as a new paradigm of evidence generation, where propagation signals are actively simulated rather than passively observed. Leveraging LLM-powered agents with differentiated roles and data-driven personas, AVOID realistically constructs early-stage diffusion behaviors without requiring real propagation data. The resulting virtual trajectories provide complementary social evidence that enriches content-based detection, while a denoising-guided fusion strategy aligns simulated propagation with content semantics. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that AVOID consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, highlighting the effectiveness and practical value of virtual propagation augmentation for early fake news detection. The code and data are available at https://github.com/Ironychen/AVOID.

Information retrieval (IR) in dynamic data streams is emerging as a challenging task, as shifts in data distribution degrade the performance of AI-powered IR systems. To mitigate this issue, memory-based continual learning has been widely adopted for IR. However, existing methods rely on a fixed set of queries with ground-truth relevant documents, which limits generalization to unseen queries and documents, making them impractical for real-world applications. To enable more effective learning with unseen topics of a new corpus without ground-truth labels, we propose CREAM, a self-supervised framework for memory-based continual retrieval. CREAM captures the evolving semantics of streaming queries and documents into dynamically structured soft memory and leverages it to adapt to both seen and unseen topics in an unsupervised setting. We realize this through three key techniques: fine-grained similarity estimation, regularized cluster prototyping, and stratified coreset sampling. Experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that CREAM exhibits superior adaptability and retrieval accuracy, outperforming the strongest method in a label-free setting by 27.79\% in Success@5 and 44.5\% in Recall@10 on average, and achieving performance comparable to or even exceeding that of supervised methods.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly applied in recommendation scenarios due to their strong natural language understanding and generation capabilities. However, they are trained on vast corpora whose contents are not publicly disclosed, raising concerns about data leakage. Recent work has shown that the MovieLens-1M dataset is memorized by both the LLaMA and OpenAI model families, but the extraction of such memorized data has so far relied exclusively on manual prompt engineering. In this paper, we pose three main questions: Is it possible to enhance manual prompting? Can LLM memorization be detected through methods beyond manual prompting? And can the detection of data leakage be automated? To address these questions, we evaluate three approaches: (i) jailbreak prompt engineering; (ii) unsupervised latent knowledge discovery, probing internal activations via Contrast-Consistent Search (CCS) and Cluster-Norm; and (iii) Automatic Prompt Engineering (APE), which frames prompt discovery as a meta-learning process that iteratively refines candidate instructions. Experiments on MovieLens-1M using LLaMA models show that jailbreak prompting does not improve the retrieval of memorized items and remains inconsistent; CCS reliably distinguishes genuine from fabricated movie titles but fails on numerical user and rating data; and APE retrieves item-level information with moderate success yet struggles to recover numerical interactions. These findings suggest that automatically optimizing prompts is the most promising strategy for extracting memorized samples.
 2601.01997
2601.01997ChatGPT has emerged as a versatile tool, demonstrating capabilities across diverse domains. Given these successes, the Recommender Systems (RSs) community has begun investigating its applications within recommendation scenarios primarily focusing on accuracy. While the integration of ChatGPT into RSs has garnered significant attention, a comprehensive analysis of its performance across various dimensions remains largely unexplored. Specifically, the capabilities of providing diverse and novel recommendations or exploring potential biases such as popularity bias have not been thoroughly examined. As the use of these models continues to expand, understanding these aspects is crucial for enhancing user satisfaction and achieving long-term personalization. This study investigates the recommendations provided by ChatGPT-3.5 and ChatGPT-4 by assessing ChatGPT's capabilities in terms of diversity, novelty, and popularity bias. We evaluate these models on three distinct datasets and assess their performance in Top-N recommendation and cold-start scenarios. The findings reveal that ChatGPT-4 matches or surpasses traditional recommenders, demonstrating the ability to balance novelty and diversity in recommendations. Furthermore, in the cold-start scenario, ChatGPT models exhibit superior performance in both accuracy and novelty, suggesting they can be particularly beneficial for new users. This research highlights the strengths and limitations of ChatGPT's recommendations, offering new perspectives on the capacity of these models to provide recommendations beyond accuracy-focused metrics.
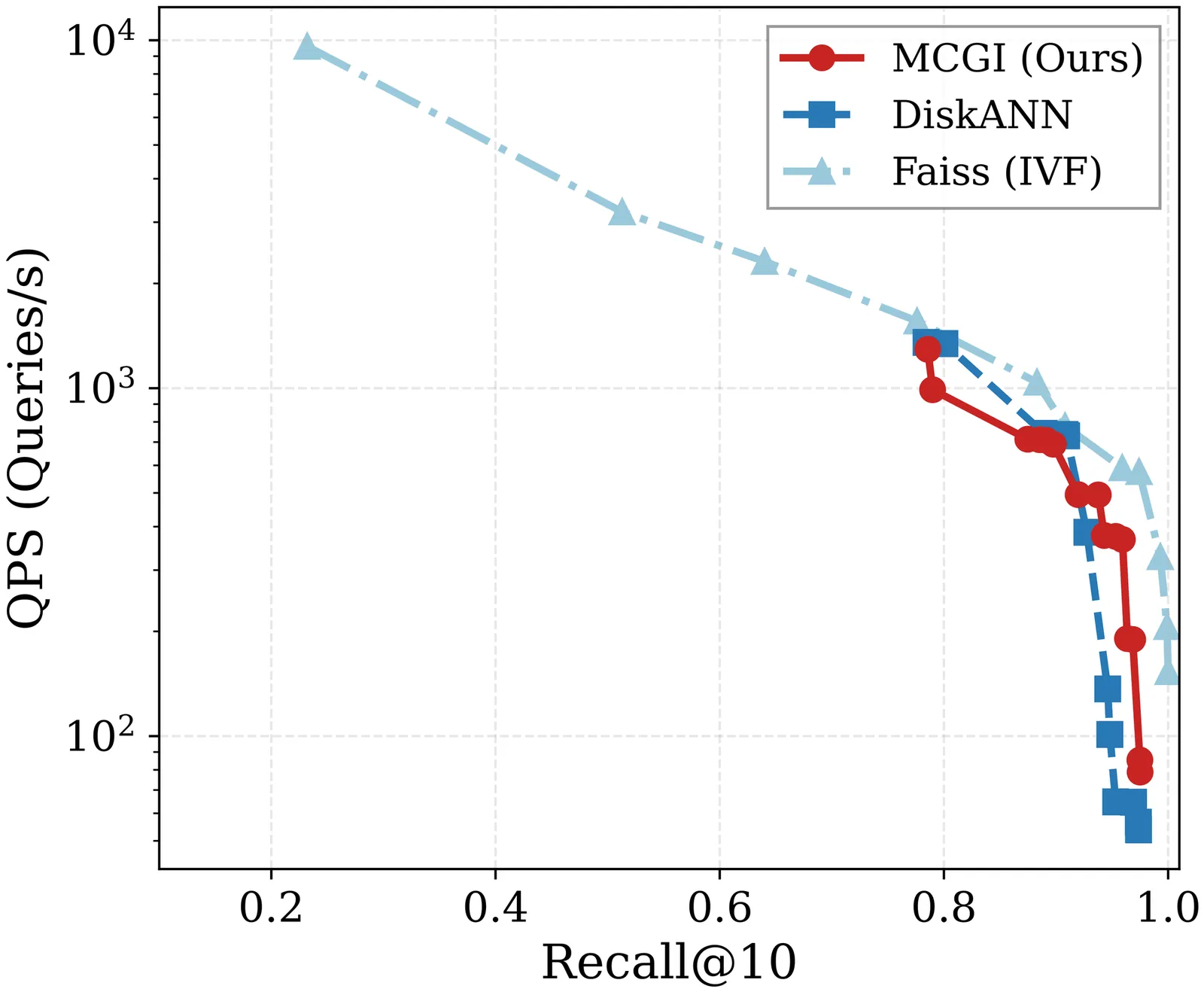
Graph-based Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search often suffers from performance degradation in high-dimensional spaces due to the ``Euclidean-Geodesic mismatch,'' where greedy routing diverges from the underlying data manifold. To address this, we propose Manifold-Consistent Graph Indexing (MCGI), a geometry-aware and disk-resident indexing method that leverages Local Intrinsic Dimensionality (LID) to dynamically adapt search strategies to the data's intrinsic geometry. Unlike standard algorithms that treat dimensions uniformly, MCGI modulates its beam search budget based on in situ geometric analysis, eliminating dependency on static hyperparameters. Theoretical analysis confirms that MCGI enables improved approximation guarantees by preserving manifold-consistent topological connectivity. Empirically, MCGI achieves 5.8$\times$ higher throughput at 95\% recall on high-dimensional GIST1M compared to state-of-the-art DiskANN. On the billion-scale SIFT1B dataset, MCGI further validates its scalability by reducing high-recall query latency by 3$\times$, while maintaining performance parity on standard lower-dimensional datasets.