Number Theory
Algebraic and analytic number theory, arithmetic geometry
Algebraic and analytic number theory, arithmetic geometry
 2601.05189
2601.05189In this article we study the value distribution theory for the first derivative of the logarithmic derivative of Dirichlet $L$-functions, generalizing certain results of Ihara, Matsumoto et. al. related to ``$M$-functions" for $σ= $ Re$(s) > 1$. We then discuss how things evolve for higher derivatives.
 2601.05133
2601.05133We consider selected aspects of (non-Archimedean) quantum mathematics and non-Archimedean (quantum) computation.
 2601.05121
2601.05121Let $k$ be a natural number with $k\ge 2$, and let $\varepsilon>0$. We consider the number $V_k^*(P)$ of integral solutions of the system of simultaneous Diophantine equations \[ x_1^{2j-1}+\ldots +x_{k+1}^{2j-1}=y_1^{2j-1}+\ldots +y_{k+1}^{2j-1}\quad (1\le j\le k), \] with $1\le x_i,y_i\le P$ $(1\le i\le k+1)$. Writing $L_k^*(P)$ for the number of diagonal solutions with $\{x_1,\ldots ,x_{k+1}\}=\{y_1,\ldots ,y_{k+1}\}$, so that $L_k^*(P)\sim (k+1)!P^{k+1}$, we prove that \[ V_k^*(P)-L_k^*(P)\ll P^{\sqrt{8k+9}-1+\varepsilon}. \] This establishes a strong paucity result improving on earlier work of Brüdern and Robert.
 2601.05024
2601.05024In this paper, we employ contour integration and residue calculus to derive explicit parity formulas for (cyclotomic) multiple zeta values (MZVs). A key innovation lies in applying double shuffle regularization to the contour integrals, which leads to two distinct regularized parity formulas-one via shuffle and one via stuffle regularization. Notably, this demonstrates for the first time that the contour integral method can be extended to the regularized setting (including the case $k_r=1$), thereby overcoming a limitation of previous approaches. Our results not only provide explicit parity relations at arbitrary depths but also lay the groundwork for extending this technique to other variants of multiple zeta values.
 2601.04972
2601.04972Hrushovski observed that the new gap principle of Gao-Ge-Kühne is essentially equivalent to the Bogomolov conjecture over arbitrary globally valued fields of characteristic $0$. Building on this observation, we prove a new gap principle for semiabelian varieties by reducing the Bogomolov conjecture for semiabelian varieties to the Bogomolov conjecture for abelian varieties over arbitrary GVFs. This reduction remains valid in positive characteristic; however, the corresponding Bogomolov conjecture for abelian varieties is not yet known in that setting. We prove an unconditional new gap principle in positive characteristic for semiabelian varieties whose abelian quotient is an elliptic curve.
 2601.04743
2601.04743We prove an infinite family of linear identities for the number $A_5(n)$ of partition pairs of $n$ with $5$-cores by using certain theta function identities involving the Ramanujan's parameter $k(q)$ due to Cooper, and Lee and Park. Consequently, we deduce an infinite family of congruences for $A_5(n)$ using these linear identities.
In this study, we introduce the theory of what we call Hecke vector-forms. A Hecke vector-form can be viewed as a vector function representation of some quasiautomorphic form that transforms like an automorphic form on an arbitrarily chosen Hecke triangle group. In other words, because quasiautomorphic forms have complicated transformation behavior when compared with automorphic forms, the construction of a Hecke vector-form is to retrieve a transformation behavior analogous to the simpler, automorphic case. In this way, a Hecke vector-form can be viewed as the vector function analogue of an automorphic form. Since our work is for any quasi-automorphic form over an arbitrary Hecke triangle group, we briefly review the construction of such groups. Furthermore, we review the derivation of the hauptmodul, the automorphic forms, and the normalized quasiautomorphic form of weight 2 for any Hecke triangle group. We then proceed to the theory of Hecke vector-forms and establish the desired transformation behavior with respect to the generators of the associated group. A proof of this fact is strictly elementary, relying on fine properties of binomial coefficients. Lastly, we relate the vector-forms to Hecke automorphic linear differential equations, which are analogues of the frequently researched modular linear differential equations. Our results include Hecke vector-forms of the classical quasimodular forms as the simplest case.
 2601.04503
2601.04503We study the distribution of $2$-torsion in class groups and narrow class groups of cubic fields and cubic orders subject to prescribed shape conditions. The \emph{shape} of a cubic order in a number field is a natural geometric invariant taking values in the modular surface $\mathbb{H}/\operatorname{GL}_2(\mathbb{Z})$. Fix a subset $W$ of the modular surface with positive hyperbolic measure and boundary of measure zero. Refining the methods of Bhargava and Varma, we prove that among cubic fields with shape in $W$, the average size of the $2$-torsion subgroup of the class group is $5/4$ for totally real fields and $3/2$ for complex fields, while the average size of the $2$-torsion subgroup of the narrow class group for totally real cubic fields is $2$. We also obtain analogous results for cubic orders satisfying prescribed local conditions at all primes.
 2601.04437
2601.04437Let $K$ be a number field of degree $d$ so that $K/\mathbb Q$ is a Galois extension. The {\it normal basis theorem} states that $K$ has a $\mathbb Q$-basis consisting of algebraic conjugates, in fact $K$ contains infinitely many such bases. We prove an effective version of this theorem, obtaining a normal basis for $K/\mathbb Q$ of bounded Weil height with an explicit bound in terms of the degree and discriminant of $K$. In the case when $d$ is prime, we obtain a particularly good bound using a different method.
 2601.04189
2601.04189We establish standard zero-free regions with no exceptional Landau-Siegel zeros for Rankin-Selberg $L$-functions and triple product $L$-functions in several new families for which modularity is not yet known.
 2601.04014
2601.04014Recently, Andrews and Bachraoui considered a generating function $F_{k,m}(q)$ associated with certain two-color partitions, and conjectured that this function has non-negative coefficients for $m=1$. They showed this property for $1 \leq k \leq 4$. In this note, we prove that $F_{k,1}(q)$ has non-negative coefficients for $5 \leq k \leq 10$. Moreover, we show that, as $k\to\infty$, $F_{k,1}(q)$ is related to Ramanujan's third order mock theta function $ω(q)$ and to quotients of certain $q$-binomial coefficients.
 2601.03998
2601.03998In this paper we study restricted overpartitions and concave compositions. Using q-series transformations, we show that their generating functions are related to modular forms, mock theta functions, false theta functions, and mock Maass theta functions. Moreover, we obtain their asymptotic main terms. We also study related rank statistics.
 2601.03984
2601.03984We consider cubic number fields ordered by their discriminants, and show that there exist arbitrarily long sequences that contain only fields with class numbers greater than a given bound.
 2601.03949
2601.03949In this work, we study a numeral system with a natural base $s \geq 2$ and a redundant alphabet $A_r=\{0,1, \dots, r\}$, where $s \leq r \leq 2s-2$. We investigate the topological, metric, and fractal properties of the set of numbers in the interval $\left[0,\frac{r}{s-1}\right]$ that admit a unique representation $x=\sum\limits_{n=1}^{\infty}\frac{α_n} {s^n}\equivΔ^{r_s}_{α_1α_2...α_n...}$, $α_n\in A_r$. The criterion for the uniqueness of the number representation is established. It is proved that the Hausdorff--Besicovitch dimension of the set of numbers with a unique representation is equal to $\frac{\ln(2s-r-1)}{\ln s}$. An analysis of the quantity of representations of numbers having purely periodic representations with a simple period (a single-digit period) is carried out. It is proved that the set of numbers that admit a continuum of distinct representations has full Lebesgue measure. Conditions for a number to belong to this set are given in terms of one of its representations.
 2601.04284
2601.04284Presentaremos una nueva demostración del teorema de Shafarevich sobre finitud de curvas elípticas con buena reducción fuera de un conjunto finito de primos dado. Esto da un nuevo punto de entrada a teoremas fundamentales de finitud diofantina tales como el teorema de Siegel sobre la ecuación $S$-unidad. Nuestro argumento está libre de aproximación diofantina o teoría de trascendencia, y se acerca más a las ideas de Faltings en su demostración de la conjetura de Mordell. -- We present a new proof of Shafarevich's theorem on finiteness of elliptic curves with good reduction outside a given finite set of primes. This gives a new entry point to fundamental diophantine finiteness theorems such as Siegel's theorem on the $S$-unit equation. Our proof is free from diophantine approximation or transcendence theory, and it is closer to the ideas of Faltings in his proof of Mordell's conjecture .
We prove an equivalence between filtrations of primitive bialgebras and filtrations of factorizable perverse sheaves, generalizing the results obtained by Kapranov-Schechtman. Under this equivalence, we find that the word length filtration of quantum shuffle algebras as defined in Ellenberg-Tran-Westerland corresponds to the codimension filtration of factorizable perverse sheaves. Furthermore, we find that the geometric weight filtration of factorizable perverse sheaves corresponds to a filtration on quantum shuffle algebras which has not been previously defined in the literature, and we call this the algebraic weight filtration. To apply this to Hurwitz spaces, we prove a comparison theorem between the weight filtrations for Hurwitz spaces over $\mathbb F_p$ and $\mathbb C$, generalizing the comparison theorem of Ellenberg-Venkatesh-Westerland. This allows us to determine the cohomological weights for Hurwitz spaces explicitly using the algebraic weight filtration of the corresponding quantum shuffle algebra. As a consequence, we find that most weights of Hurwitz spaces are smaller than expected from cohomological degree, and we prove explicit nontrivial upper bounds for weights in some cases, such as when $G=S_3$ and $c$ is the conjugacy class of transpositions.
 2601.03797
2601.03797In this article, we study the structure of the difference set $E - E$ for subsets $E \subseteq \mathbb{Z}^2$ of positive upper Banach density. In [Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 146 (2018), 3449-3453, Problem 2] Fish asked whether, for every such set $E$, there exists a nonzero integer $k$ such that \[ k \cdot \mathbb{Z} \subseteq \{\, xy : (x,y) \in E - E \,\}. \] Although this question remains open, we establish a relatively weaker form of this conjecture. Specifically, we prove that there exist infinitely many integers $k \in \mathbb{Z}$ and a sequence $\langle x_n \rangle_{n \in \mathbb{N}}$ in $\mathbb{Z}$ such that \[ k \cdot FS(\langle x_n \rangle_{n \in \mathbb{N}}) \subseteq \{\, xy : (x,y) \in E - E \,\}, \] where $FS(\langle x_n \rangle)$ denotes the finite sums set generated by the sequence.
 2601.03653
2601.03653We establish a connection between Drinfeld modules and rank metric codes, focusing on the case of semifield codes. Our framework constructs rank metric codes from linear subspaces of endomorphisms of a Drinfeld module, using tools such as characteristic polynomials on Tate modules and the Chebotarev density theorem. We show that Sheekey's construction [She20] fits naturally into this setting, yielding a short conceptual proof of one of his main results. We then give a new construction of infinite families of semifield codes arising from Drinfeld modules defined over finite fields.
 2601.03560
2601.03560This paper investigates the Waring problem of harmonic polynomials. By characterizing the annihilating ideal of a homogeneous harmonic polynomial, i.e., a real binary form that is in the kernel of the Laplacian, we show that its Waring rank equals its degree. Moreover, we show that any linear form can appear in a minimal Waring decomposition of a homogeneous harmonic polynomial, implying that the forbidden locus is empty. We also provide an explicit algorithm for computing the minimal Waring decompositions.
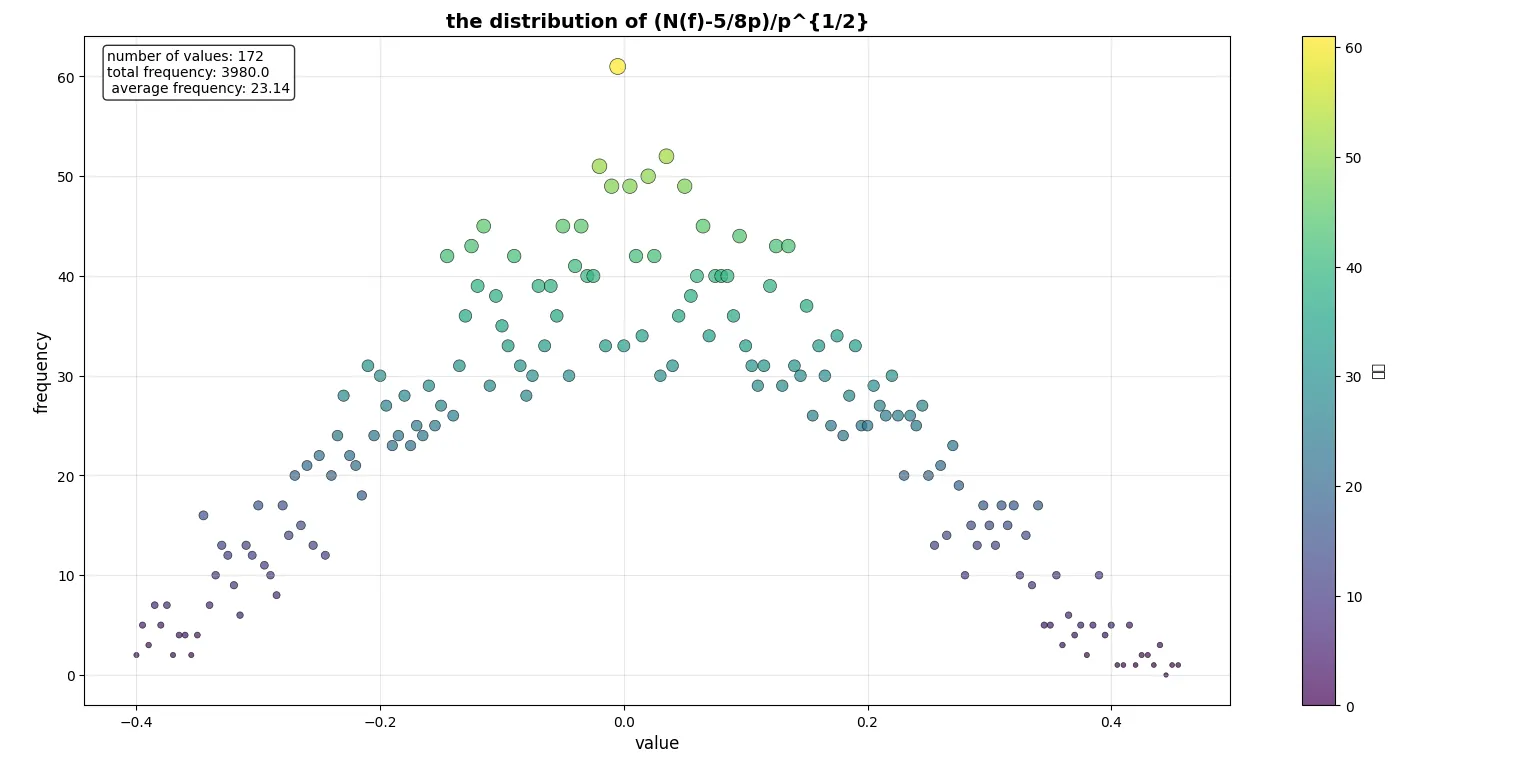
Let $\mathbb{F}_{q}$ be a finite field of characteristic $p$, and let $f \in \mathbb{F}_{q}[x]$ be a polynomial of degree $d > 0$. Denote the image set of this polynomial as $V_{f}=\{f(α)\midα\in\mathbb{F}_{q}\}$ and denote the cardinality of this set as $N_{f}$. A much sharper bound for $N_{f}$ is established in this paper. In particular, for any $p\neq 2, 3$, and for nearly every generic quartic polynomial $f \in \mathbb{F}_{q}[x]$, we obtain $$\lvert N_f - \frac{5}{8} q \rvert \leq \frac{1}{2}\sqrt{q} + \frac{3}{4},$$ which holds as a simple corollary of the main result.