Quantum Physics
Quantum information, quantum computation, quantum communication, quantum cryptography, quantum foundations, and quantum technologies.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Quantum information, quantum computation, quantum communication, quantum cryptography, quantum foundations, and quantum technologies.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
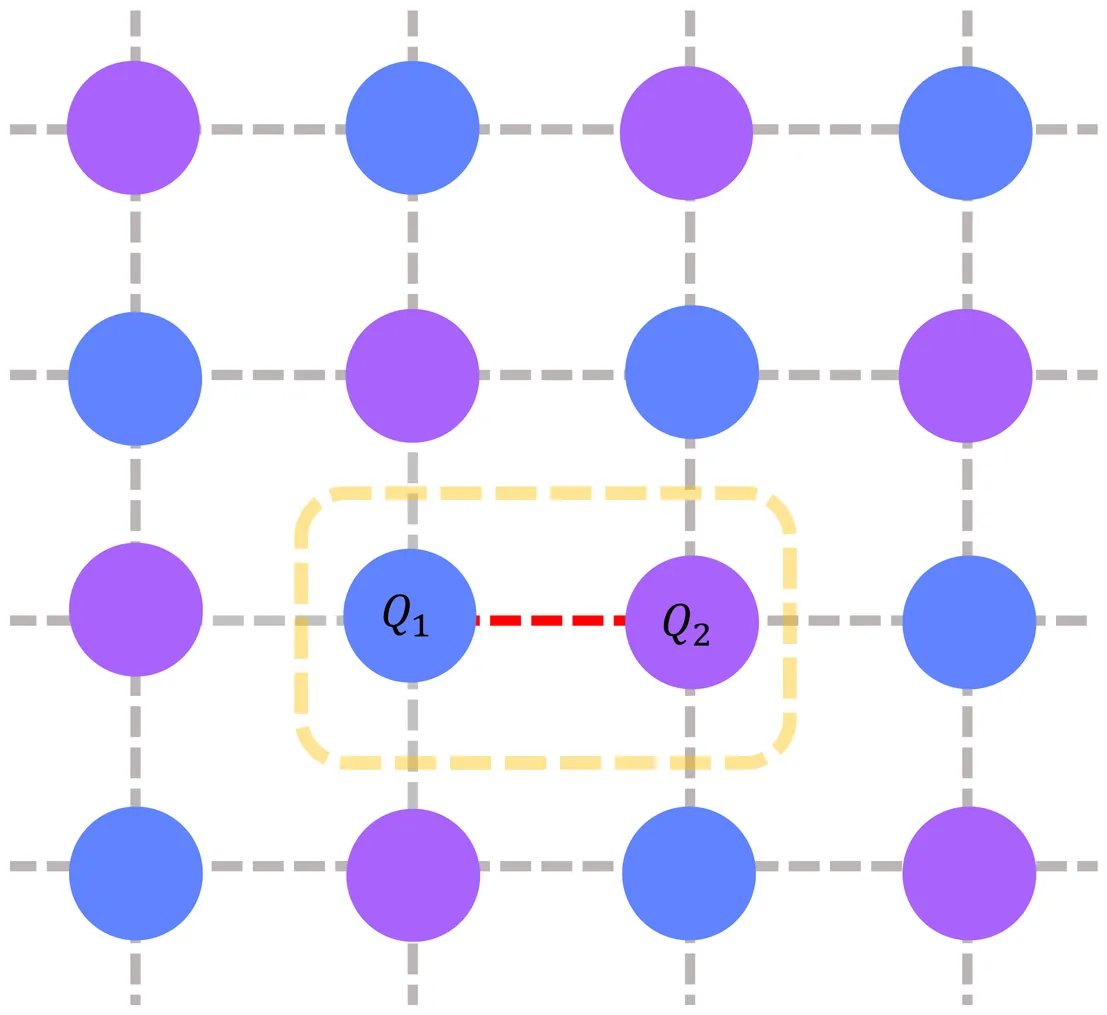
As superconducting quantum processors continue to scale, high-performance quantum control becomes increasingly critical. In densely integrated architectures, unwanted interactions between nearby qubits give rise to crosstalk errors that limit operational performance. In particular, direct exchange-type (XY) interactions are typically minimized by designing large frequency detunings between neighboring qubits at the hardware level. However, frequency crowding in large-scale systems ultimately restricts the achievable frequency separation. While such XY coupling facilitates entangling gate operations, its residual presence poses a key challenge during single-qubit controls. Here, we propose a scalable pulse-level control framework, incorporating frequency modulation (FM) and dynamical decoupling (DD), to suppress XY crosstalk errors. This framework operates independently of coupling strengths, reducing calibration overhead and naturally supporting multi-qubit connectivity. Numerical simulations show orders-of-magnitude reductions in infidelity for both idle and single-qubit gates in a two-qubit system. We further validate scalability in a five-qubit layout, where crosstalk between a central qubit and four neighbors is simultaneously suppressed. Our crosstalk suppression framework provides a practical route toward high-fidelity operation in dense superconducting architectures.
Simulating the time dynamics of an observable under Hamiltonian evolution is one of the most promising candidates for quantum advantage as we do not expect efficient classical algorithms for this problem except in restricted settings. Here, we introduce such a setting by showing that Majorana Propagation, a simple algorithm combining Trotter steps and truncations, efficiently finds a low-degree approximation of the time-evolved observable as soon as such an approximation exists. This provides the first provable guarantee about Majorana Propagation for Hamiltonian evolution. As an application of this result, we prove that Majorana Propagation can efficiently simulate the time dynamics of any sparse quartic Hamiltonian up to time $t_{\text{max}}(u)$ depending on the interaction strength $u$. For a time horizon $t \leq t_{\text{max}}(u)$, the runtime of the algorithm is $N^{O(\log(t/\varepsilon))}$ where $N$ is the number of Majorana modes and $\varepsilon$ is the error measured in the normalized Frobenius norm. Importantly, in the limit of small $u$, $t_{\text{max}}(u)$ goes to $+\infty$, formalizing the intuition that the algorithm is accurate at all times when the Hamiltonian is quadratic.
Molecular dynamics simulations are a central computational methodology in materials design for relating atomic composition to mechanical properties. However, simulating materials with atomic-level resolution on a macroscopic scale is infeasible on current classical hardware, even when using the simplest elastic network models (ENMs) that represent molecular vibrations as a network of coupled oscillators. To address this issue, we introduce Quantum Elastic Network Models (QENMs) and utilize the quantum algorithm of Babbush et al. (PRX, 2023), which offers an exponential advantage when simulating systems of coupled oscillators under some specific conditions and assumptions. Here, we demonstrate how our method enables the efficient simulation of planar materials. As an example, we apply our algorithm to the task of simulating a 2D graphene sheet. We analyze the exact complexity for initial-state preparation, Hamiltonian simulation, and measurement of this material, and provide two real-world applications: heat transfer and the out-of-plane rippling effect. We estimate that an atomistic simulation of a graphene sheet on the centimeter scale, classically requiring hundreds of petabytes of memory and prohibitive runtimes, could be encoded and simulated with as few as $\sim 160$ logical qubits.
 2601.05158
2601.05158Bell non-locality is a powerful framework to distinguish classical, quantum and post-quantum resources, which relies on non-communicating players. Under which restriction can we have the same separations, if we allow for communication? Non-signalling state assemblages, and the fact that they can always be simultaneously purified, turned out to be the key element to restrict the simplest bipartite communication scenario, the prepare-and-measure, to the standard bipartite Bell scenario. Yet, many distinctive features of quantum theory are genuinely multipartite and cannot be reduced to two-party behaviour. In this work we are interested in extending this simultaneous purification inspired result to all multipartite communication schemes. As a first step, we unify and extend the simultaneous purification result from states to instruments and super-instruments, which are composable structures, and open up the possibility to explore more complex communication scenarios. Our main contribution is to establish that arbitrary compositions of non-signalling assemblages cannot escape the standard spatial quantum Bell correlations set. As a consequence, any interactive quantum realization of correlations outside of this set must involve at least one signalling assemblage of quantum operations, even when the resulting correlations are non-signalling.
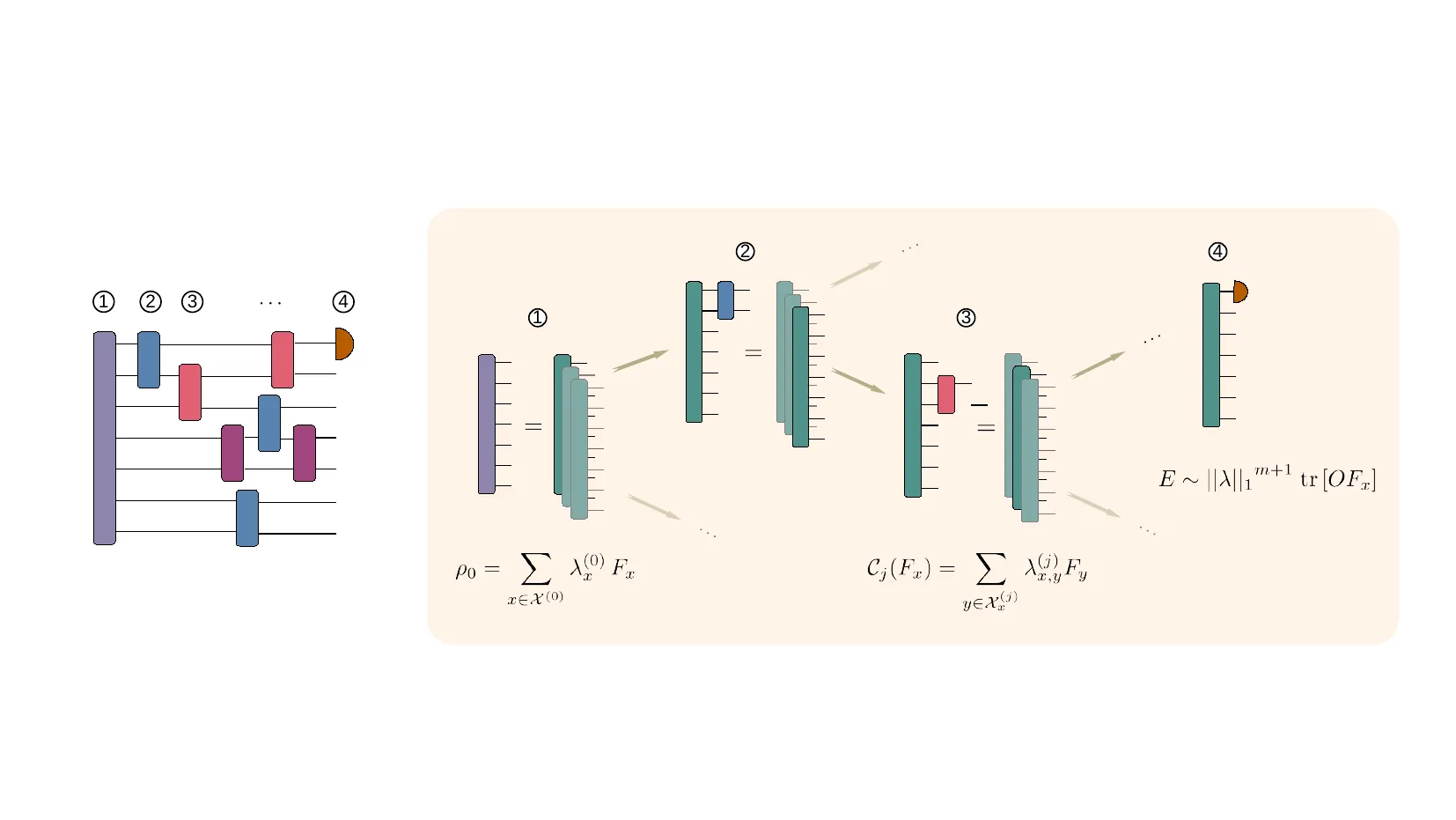
One of the core research questions in the theory of quantum computing is to find out to what precise extent the classical simulation of a noisy quantum circuits is possible and where potential quantum advantages can set in. In this work, we introduce a unified framework for the classical simulation of quantum circuits based on frame theory, encompassing and generalizing a broad class of existing simulation strategies. Within this framework, the computational cost of a simulation algorithm is determined by the one-norm of an associated quasi-probability distribution, providing a common quantitative measure across different simulation approaches. This enables a comprehensive perspective on common methods for the simulation of noisy circuits based on different quantum resources, such as entanglement or non-stabilizerness. It further provides a clear scheme for generating novel classical simulation algorithms. Indeed, by exploring different choices of frames within this formalism and resorting to tools of convex optimization, we are able not only to obtain new insights and improved bounds for existing methods -- such as stabilizer state simulation or Pauli back-propagation -- but also to discover a new approach with an improved performance based on a generalization of the Pauli frame. We, thereby, show that classical simulation techniques can directly benefit from a perspective -- that of frames -- that goes beyond the traditional classification of quantum resources.
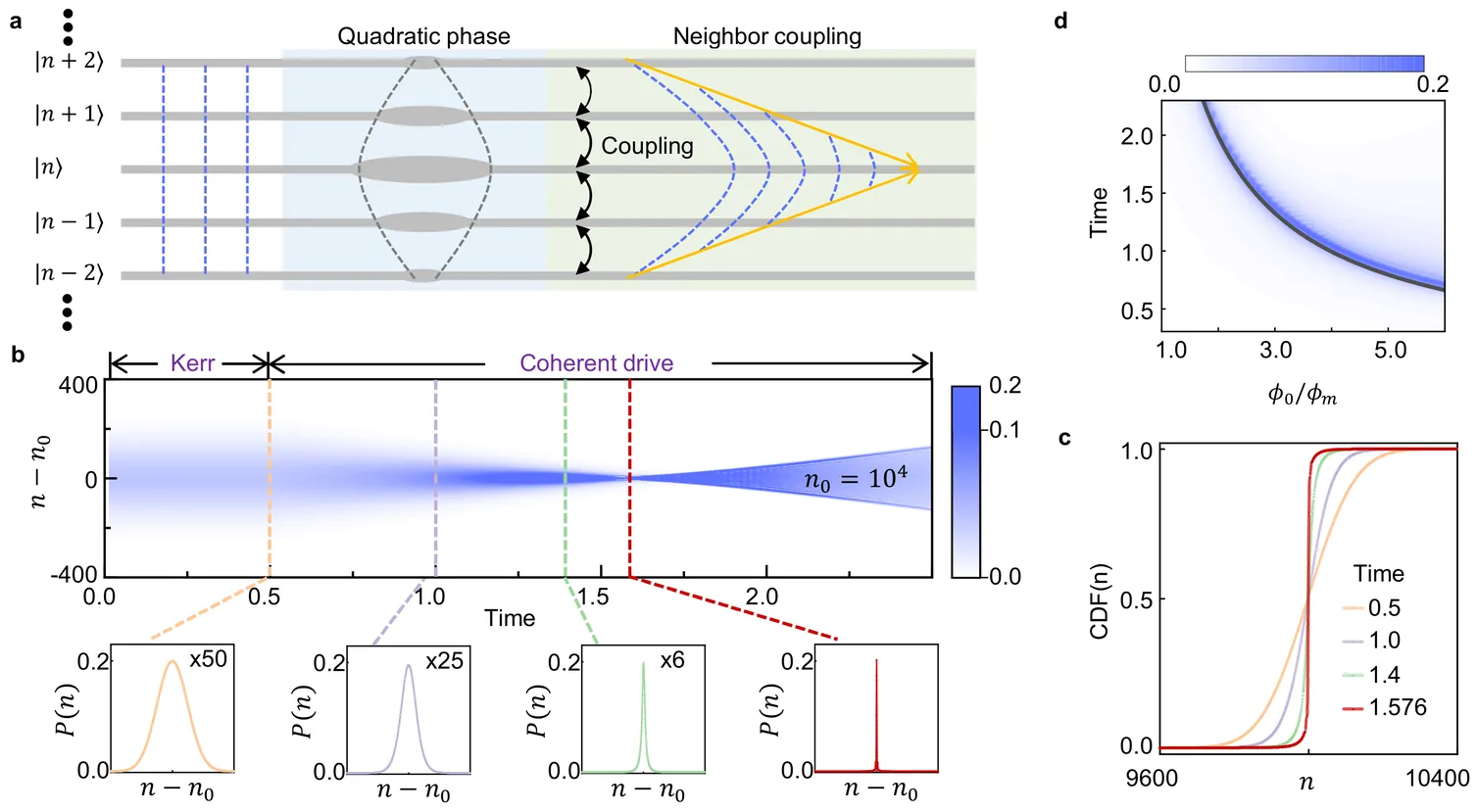
The scalable preparation of bosonic quantum states with macroscopic excitations poses a fundamental challenge in quantum technologies, limited by control complexity and photon-loss rates that severely constrain prior theoretical and experimental efforts to merely dozens of excitations per mode. Here, based on the duality of the quantum state evolution in Fock state space and the optical wave-function propagation in a waveguide array, we introduce a Kerr-engineered multi-lens protocol in a single bosonic mode to deterministically generate Fock states exceeding $10,000$ photons. By optimizing phase and displacement operations across lens groups, our approach compensates for non-paraxial aberrations, achieving fidelities above $73\%$ in numerical simulations for photon numbers up to $N=100,000$. Counterintuitively, the protocol's execution time scales as $N^{-1/2}$ with the target photon number $N$, exhibiting robustness against the photon loss. Our framework enables exploration of quantum-to-classical transitions of giant Fock states, paving the way for advanced quantum metrology with significant quantum gains, and error-corrected quantum information processing in high-dimensional Hilbert spaces.
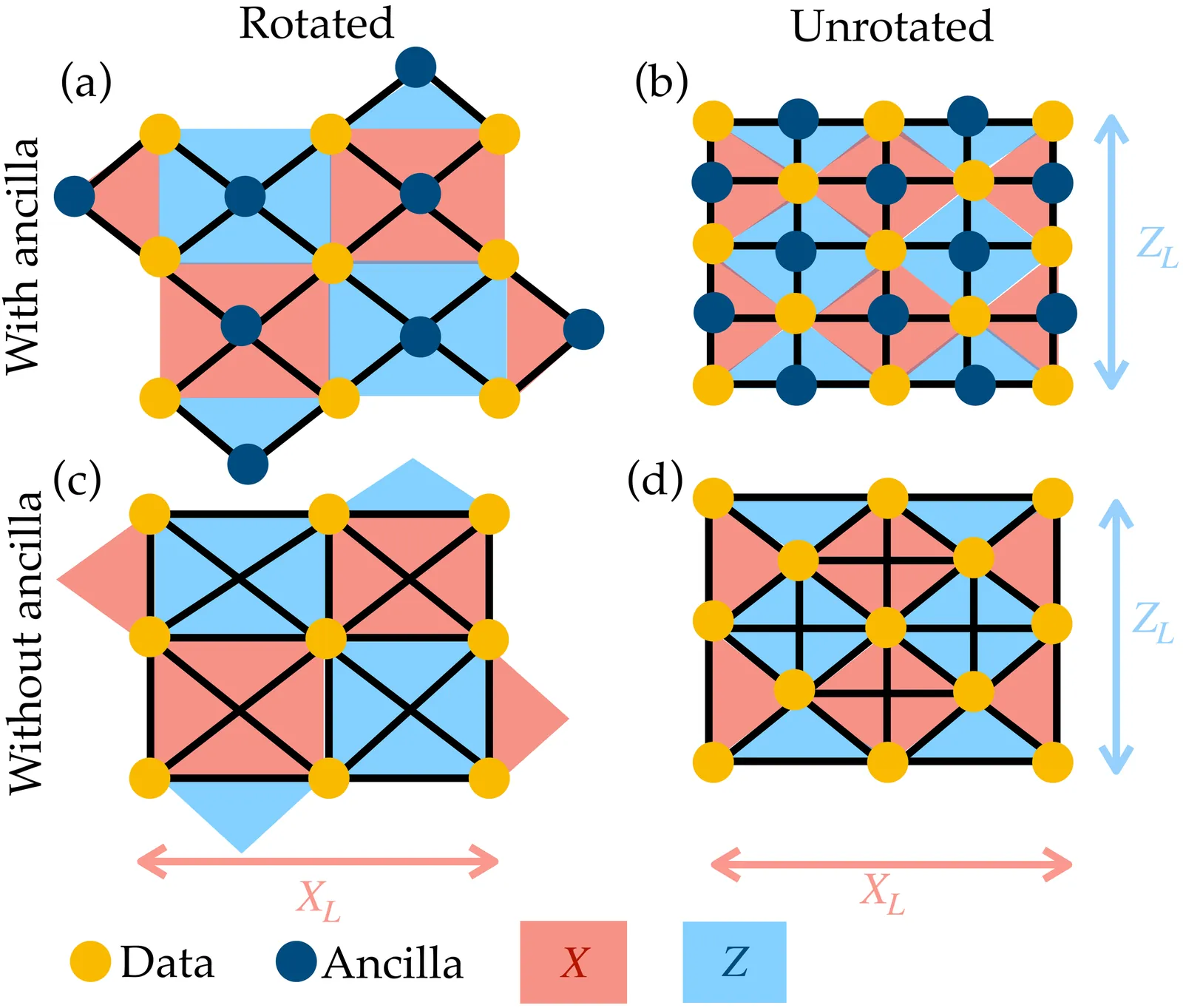
In fault-tolerant quantum computation, the preparation of logical states is a ubiquitous subroutine, yet significant challenges persist even for the simplest states required. In the present work, we present a unitary, scalable, distance-preserving encoding scheme for preparing Pauli eigenstates in surface codes. Unlike previous unitary approaches whose fault-distance remains constant with increasing code distance, our scheme ensures that the protection offered by the code is preserved during state preparation. Building on strategies discovered by reinforcement learning for the surface-17 code, we generalize the construction to arbitrary code distances and both rotated and unrotated surface codes. The proposed encoding relies only on geometrically local gates, and is therefore fully compatible with planar 2D qubit connectivity, and it achieves circuit depth scaling as $\mathcal{O}(d)$, consistent with fundamental entanglement-generation bounds. We design explicit stabilizer-expanding circuits with and without ancilla-mediated connectivity and analyze their error-propagation behavior. Numerical simulations under depolarizing noise show that our unitary encoding without ancillas outperforms standard stabilizer-measurement-based schemes, reducing logical error rates by up to an order of magnitude. These results make the scheme particularly relevant for platforms such as trapped ions and neutral atoms, where measurements are costly relative to gates and idling noise is considerably weaker than gate noise. Our work bridges the gap between measurement-based and unitary encodings of surface-code states and opens new directions for distance-preserving state preparation in fault-tolerant quantum computation.
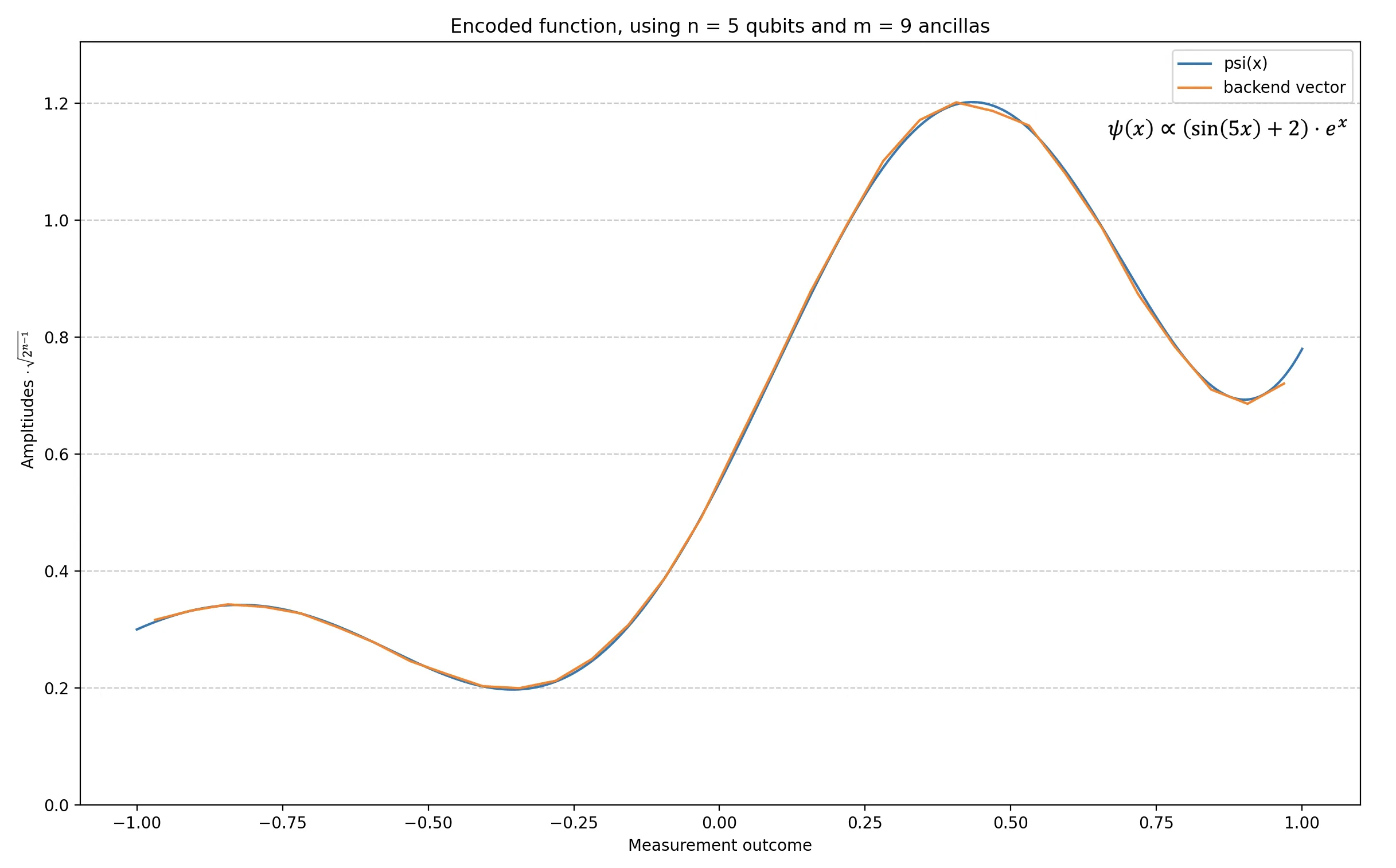
Numerically solving partial differential equations is a ubiquitous computational task with broad applications in many fields of science. Quantum computers can potentially provide high-degree polynomial speed-ups for solving PDEs, however many algorithms simply end with preparing the quantum state encoding the solution in its amplitudes. Trying to access explicit properties of the solution naively with quantum amplitude estimation can subsequently diminish the potential speed-up. In this work, we present a technique for extracting a smooth positive function encoded in the amplitudes of a quantum state, which achieves the Heisenberg limit scaling. We improve upon previous methods by allowing higher dimensional functions, by significantly reducing the quantum complexity with respect to the number of qubits encoding the function, and by removing the dependency on the minimum of the function using preconditioning. Our technique works by sampling the cumulative distribution of the given function, fitting it with Chebyshev polynomials, and subsequently extracting a representation of the whole encoded function. Finally, we trial our method by carrying out small scale numerical simulations.
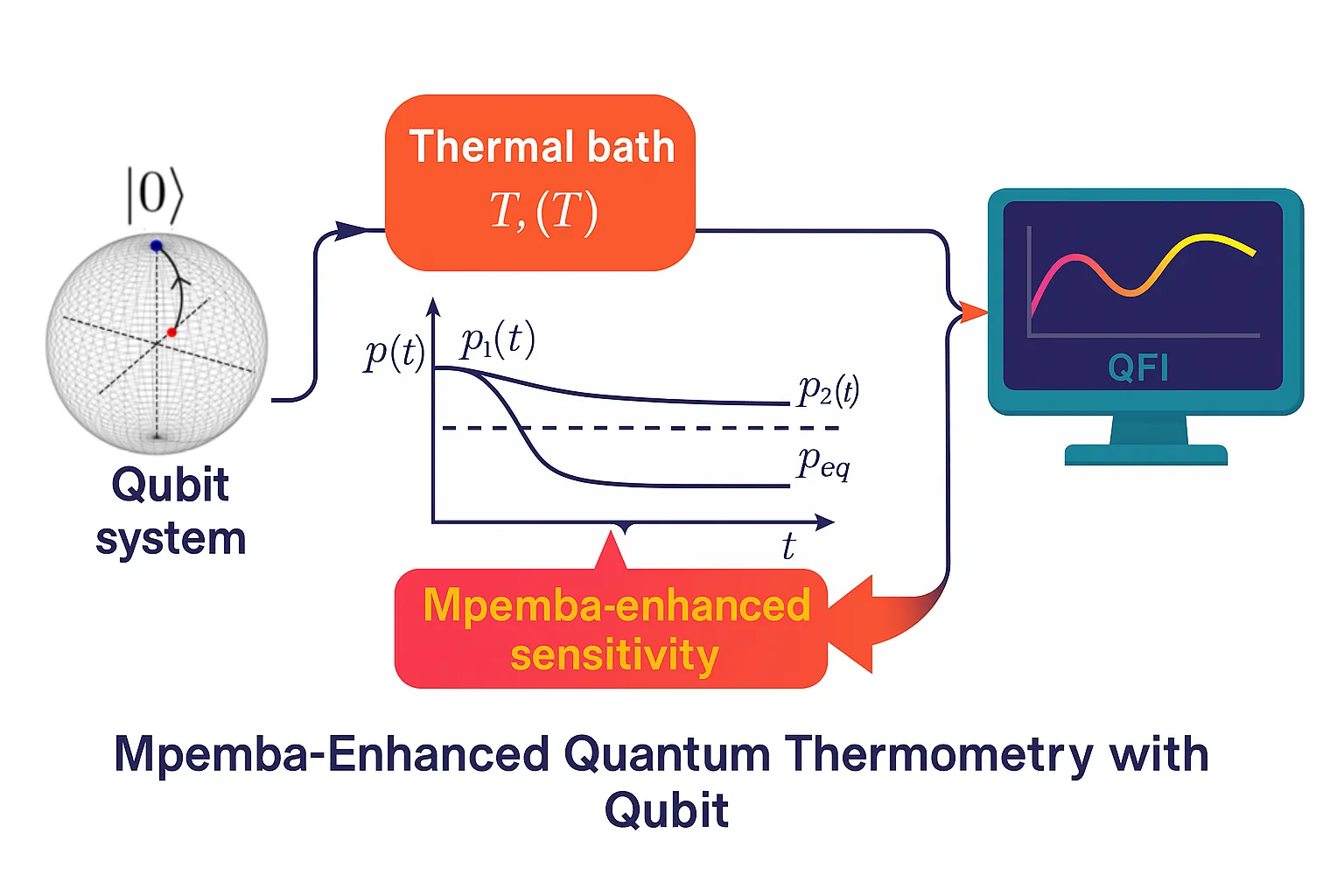
Quantum thermometry provides a key capability for nanoscale devices and quantum technologies, but most existing strategies rely on probes initialized near equilibrium. This equilibrium paradigm imposes intrinsic limitations: sensitivity is tied to long-time thermalization and often cannot be improved in fast, noisy, or nonstationary settings. In contrast, the \textit{Mpemba effect}, the counterintuitive phenomenon where hotter states relax faster than colder ones, has mostly been viewed as a thermodynamic anomaly. Here, we bridge this gap by proving that Mpemba-type inversions generically yield a finite-time enhancement of the quantum Fisher information (QFI) for temperature estimation, thereby converting an anomalous relaxation effect into a concrete metrological resource. Through explicit analyses of two-level and $Λ$-level probes coupled to bosonic baths, we show that nonequilibrium initializations can transiently outperform both equilibrium strategies and colder states, realizing a \emph{metrological Mpemba effect}. Our results establish anomalous relaxation as a general design principle for nonequilibrium quantum thermometry, enabling ultrafast and nanoscale sensing protocols that exploit, rather than avoid, transient dynamics.
Quantum generative modeling is a very active area of research in looking for practical advantage in data analysis. Quantum generative adversarial networks (QGANs) are leading candidates for quantum generative modeling and have been applied to diverse areas, from high-energy physics to image generation. The latent style-based QGAN, relying on a classical variational autoencoder to encode the input data into a latent space and then using a style-based QGAN for data generation has been proven to be efficient for image generation or drug design, hinting at the use of far less trainable parameters than their classical counterpart to achieve comparable performance, however this advantage has never been systematically studied. We present in this work the first comprehensive experimental analysis of this advantage of QGANS applied to SAT4 image generation, obtaining an exponential advantage in capacity scaling for a quantum generator in the hybrid latent style-based QGAN architecture. Careful tuning of the autoencoder is crucial to obtain stable, reliable results. Once this tuning is performed and defining training optimality as when the training is stable and the FID score is low and stable as well, the optimal capacity (or number of trainable parameters) of the classical discriminator scales exponentially with respect to the capacity of the quantum generator, and the same is true for the capacity of the classical generator. This hints toward a type of quantum advantage for quantum generative modeling.
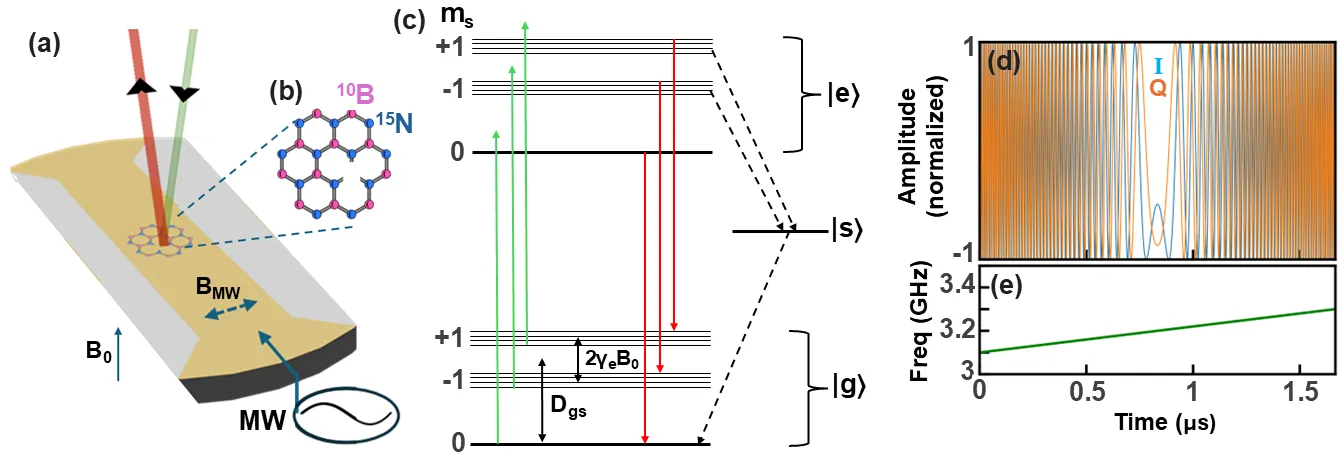
Negatively charged boron vacancies (V$_{\text{B}}^{-}$) in hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) comprise a promising quantum sensing platform, optically addressable at room temperature and transferrable onto samples. However, broad hyperfine-split spin transitions of the ensemble pose challenges for quantum sensing with conventional resonant excitation due to limited spectral coverage. While isotopically enriched hBN using $^{10}$B and $^{15}$N isotopes (h$^{10}$B$^{15}$N) exhibits sharper spectral features, significant inhomogeneous broadening persists. We demonstrate that, implemented via frequency modulation on an FPGA, a frequency-ramped microwave pulse achieves around 4-fold greater $|0\rangle\rightarrow|-1\rangle$ spin-state population transfer and thus contrast than resonant microwave excitation and thus 16-fold shorter measurement time for spin relaxation based quantum sensing. Quantum dynamics simulations reveal that an effective two-state Landau-Zener model captures the complex relationship between population inversion and pulse length with relaxations incorporated. Our approach is robust and valuable for quantum relaxometry with spin defects in hBN in noisy environments.
We propose a protocol for effectively implementing complex-balanced thermalization via Markovian processes on a quantum-circuit platform that couples the system with engineered reservoir qubits. The non-orthogonality of qubit eigenstates facilitates non-uniform heating through a modified Kubo-Martin-Schwinger relation, while simultaneously supports amplification-dissipation dynamics by violating microscopic time-reversibility. This offers a new approach to realizing out-of-equilibrium states at given temperatures. We show two applications of this platform: temporally-correlated dichromatic emission and Liouvillian exception point protected quantum synchronization at finite temperatures, both of which are challenging to achieve with conventional thermal reservoirs.
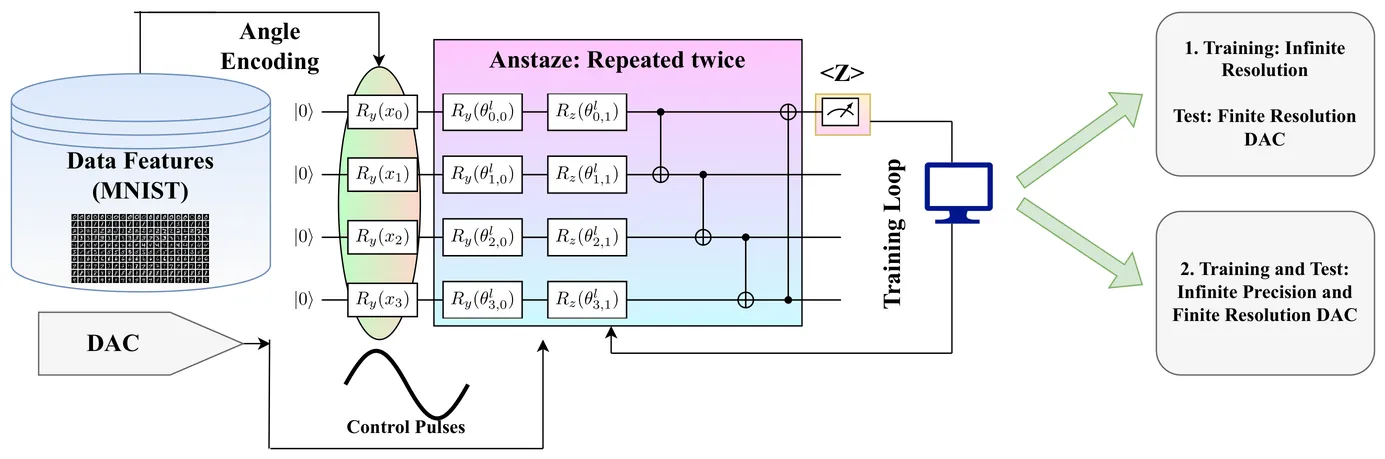
Scaling quantum computers requires tight integration of cryogenic control electronics with quantum processors, where Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs) face severe power and area constraints. We investigate quantum neural network (QNN) training and inference under finite DAC resolution constraints across various DAC resolutions. Pre-trained QNNs achieve accuracy nearly indistinguishable from infinite-precision baselines when deployed on quantum systems with 6-bit DAC control electronics, exhibiting an elbow curve with diminishing returns beyond 4 bits. However, training under quantization reveals gradient deadlock below 12-bit resolution as gradient magnitudes fall below quantization step sizes. We introduce temperature-controlled stochasticity that overcomes this through probabilistic parameter updates, enabling successful training at 4-10 bit resolutions that remarkably matches or exceeds infinite-precision baseline performance. Our findings demonstrate that low-resolution control electronics need not compromise QML performance, enabling significant power and area reduction in cryogenic control systems for practical deployment as quantum hardware scales.
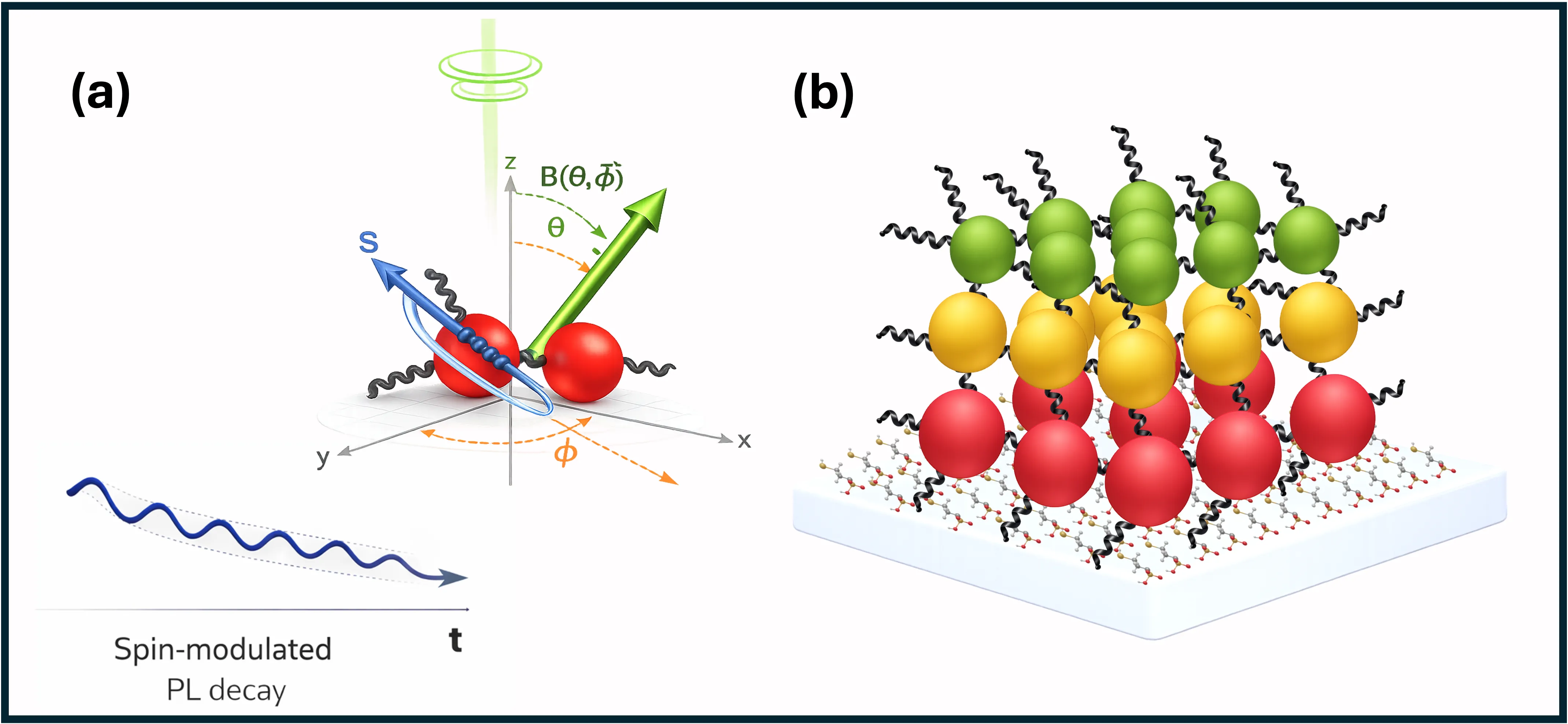
Chiral-induced spin selectivity (CISS) enables spin selectivity of charge carriers in chiral molecular systems without magnetic materials. While spin selectivity has been widely investigated, its quantum coherence has not yet been explored. Here, we investigate spin-dependent photoluminescence (PL) dynamics in multilayer quantum-dot (QD) assemblies coupled by chiral linkers. Using circularly polarized excitation in the presence of an external magnetic field, we observe a pronounced modulation of the PL lifetime that depends on the magnetic field magnitude and geometry. The lifetime difference between left- and right-circularly polarized excitations exhibits a field-angle dependence, consistent with spin precession driven by the transverse magnetic-field component relative to the chiral axis. A model incorporating coupled spin precession and decay processes reproduces the experimental trends. These results establish chiral QD assemblies as a room-temperature platform for probing quantum coherent manifestations of the CISS effect, with implications for spintronic and quantum technologies.
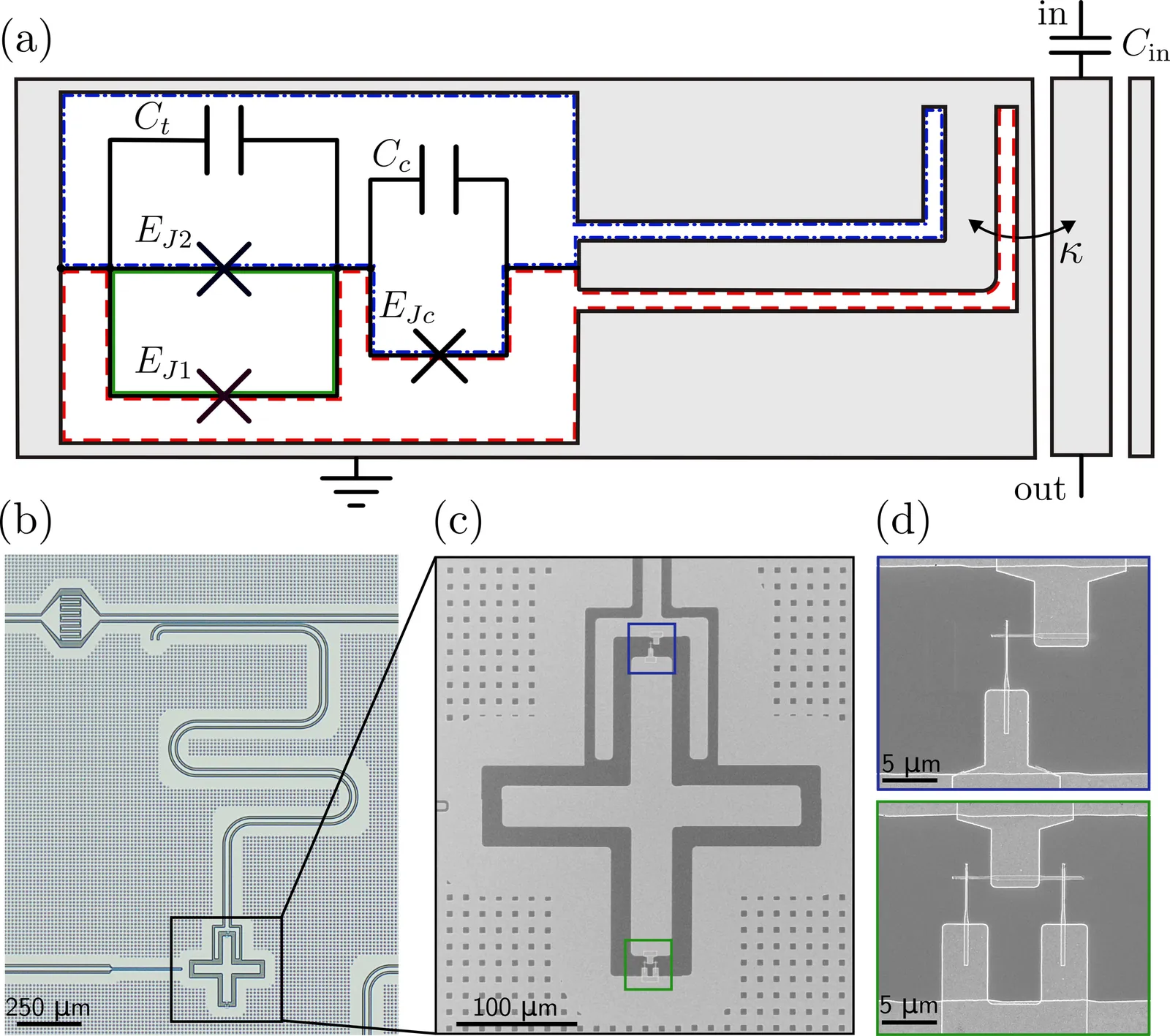
Dispersive readout of superconducting qubits relies on a transverse capacitive coupling that hybridizes the qubit with the readout resonator, subjecting the qubit to Purcell decay and measurement-induced state transitions (MIST). Despite the widespread use of Purcell filters to suppress qubit decay and near-quantum-limited amplifiers, dispersive readout often lags behind single- and two-qubit gates in both speed and fidelity. Here, we experimentally demonstrate junction readout, a simple readout architecture that realizes a strong qubit-resonator cross-Kerr interaction without relying on a transverse coupling. This interaction is achieved by coupling a transmon qubit to its readout resonator through both a capacitance and a Josephson junction. By varying the qubit frequency, we show that this hybrid coupling provides intrinsic Purcell protection and enhanced resilience to MIST, enabling readout at high photon numbers. While junction readout is compatible with conventional linear measurement, in this work we exploit the nonlinear coupling to intentionally engineer a large Kerr nonlinearity in the resonator, enabling bifurcation-based readout. Using this approach, we achieve a 99.4 % assignment fidelity with a 68 ns integration time and a 98.4 % QND fidelity without an external Purcell filter or a near-quantum-limited amplifier. These results establish the junction readout architecture with bifurcation-based readout as a scalable and practical alternative to dispersive readout, enabling fast, high-fidelity qubit measurement with reduced hardware overhead.
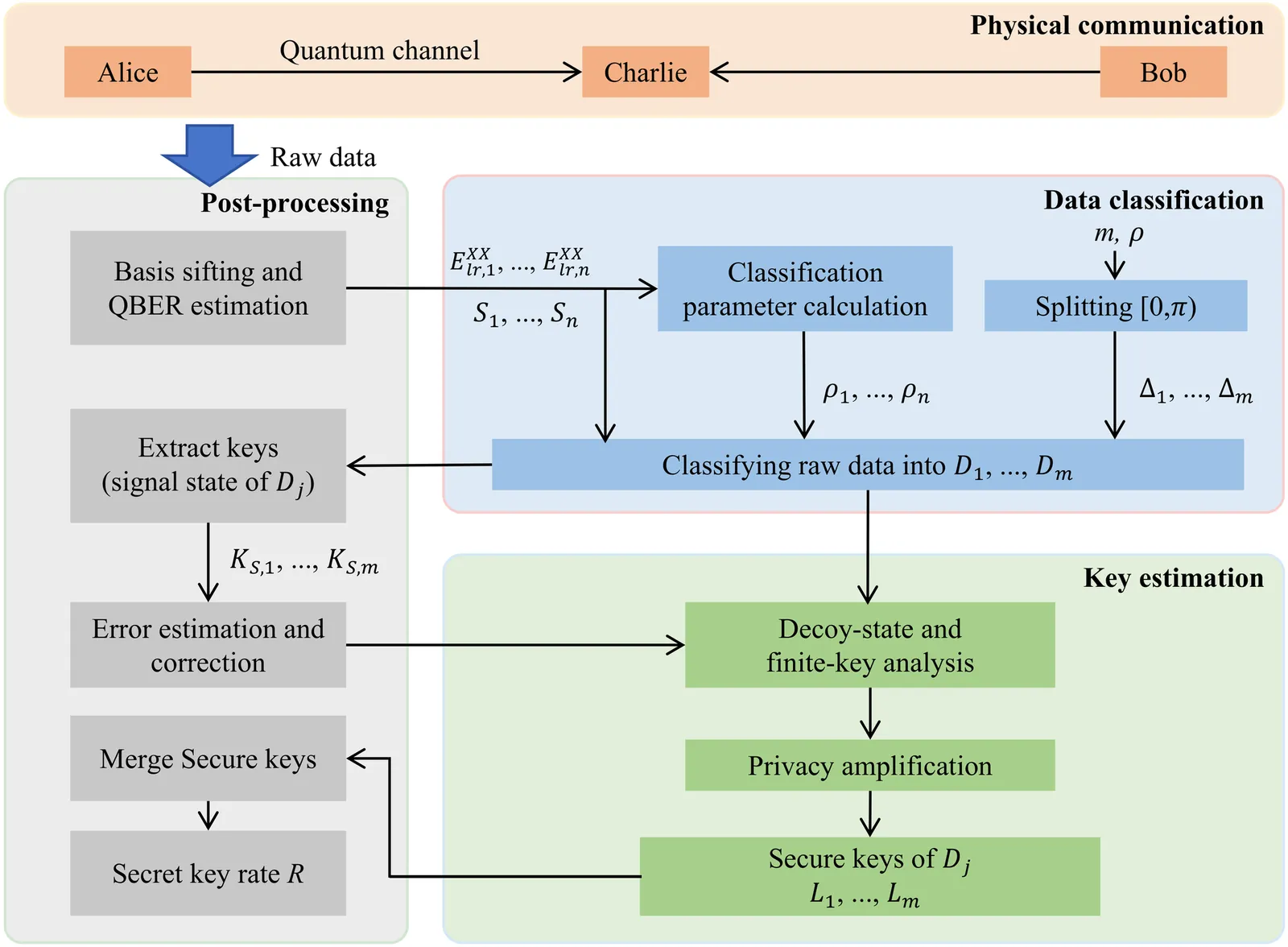
Reference-frame-independent measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (RFI-MDI-QKD) eliminates detector side-channel attacks and avoids reference-frame calibration. While its feasibility has been widely demonstrated, existing implementations typically assume fixed or slowly drifting reference-frame misalignment, conditions rarely satisfied outside the laboratory. In realistic environments, rapid and free-running reference-frame variations can severely degrade both the key rate and transmission distance of conventional RFI-MDI-QKD. Here we propose a free-running RFI-MDI-QKD protocol that maintains high-rate key generation under rapid reference-frame variations. By introducing a classification-distillation method that reclassifies total detection events, secure keys can be extracted without modifying the experimental setup. Our protocol achieves a key rate more than nine times higher than the best previous RFI-MDI-QKD scheme and tolerates channel losses exceeding 24 dB, where earlier approaches fail. These results enable practical quantum key distribution on mobile platforms, including satellite-to-ground links and airborne nodes.
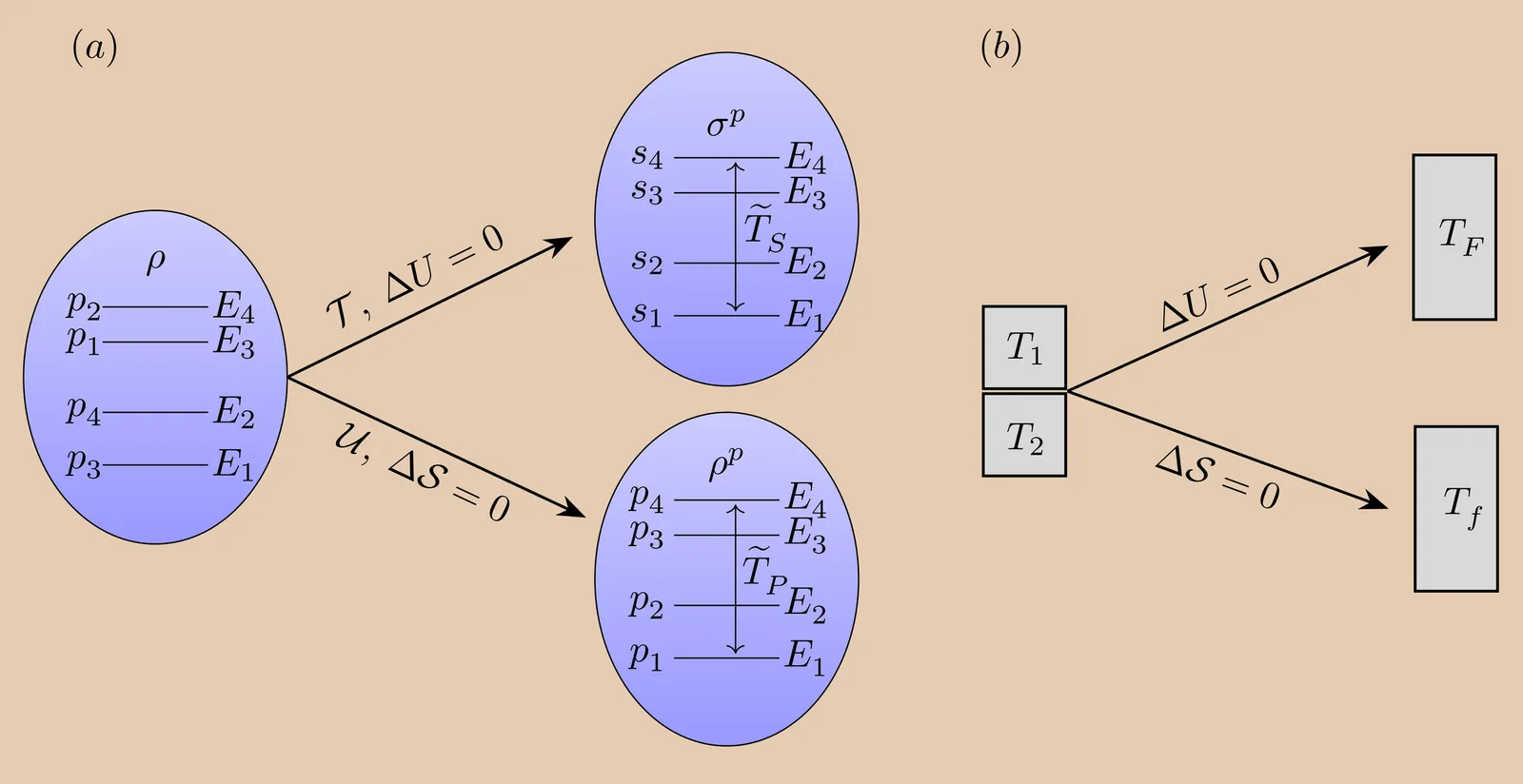
We analyze the role of virtual temperatures for passive quantum states through the lens of majorization theory. A mean temperature over the virtual temperatures of adjacent energy levels is defined to compare the passive states of the system resulting from isoenergetic and isoentropic transformations. The role of the minimum and the maximum (min-max) values of the virtual temperatures in determining the direction of heat flow between the system and the environment is argued based on majorization relations. We characterize the intermediate passive states in a quantum Otto engine using these virtual temperatures and derive an upper bound for the Otto efficiency that can be expressed in terms of the min-max virtual temperatures of the working medium. An explicit example of the coupled-spins system is worked out. Moreover, virtual temperatures serve to draw interesting parallels between the quantum thermodynamic processes and their classical counterparts. Thus, virtual temperature emerges as a key operational quantity linking passivity and majorization to the optimal performance of quantum thermal machines.
 2601.04880
2601.04880In this work we present an intuitive construction of the quantum logical axiomatic system provided by George Mackey. The goal of this work is a detailed discussion of the results from the paper 'Physical justification for using the tensor product to describe two quantum systems as one joint system' [1] published by Diederik Aerts and Ingrid Daubechies. This means that we want to show how certain composed physical systems from classical and quantum mechanics should be described logically. To reach this goal, we will, like in [1], discuss a special class of axiomatically defined composed physical systems. With the help of certain results from lattice and c-morphism theory (see [2] and [23]), we will present a detailed proof of the statement, that in the quantum mechanical case, a composed physical system must be described via a tensor product space.
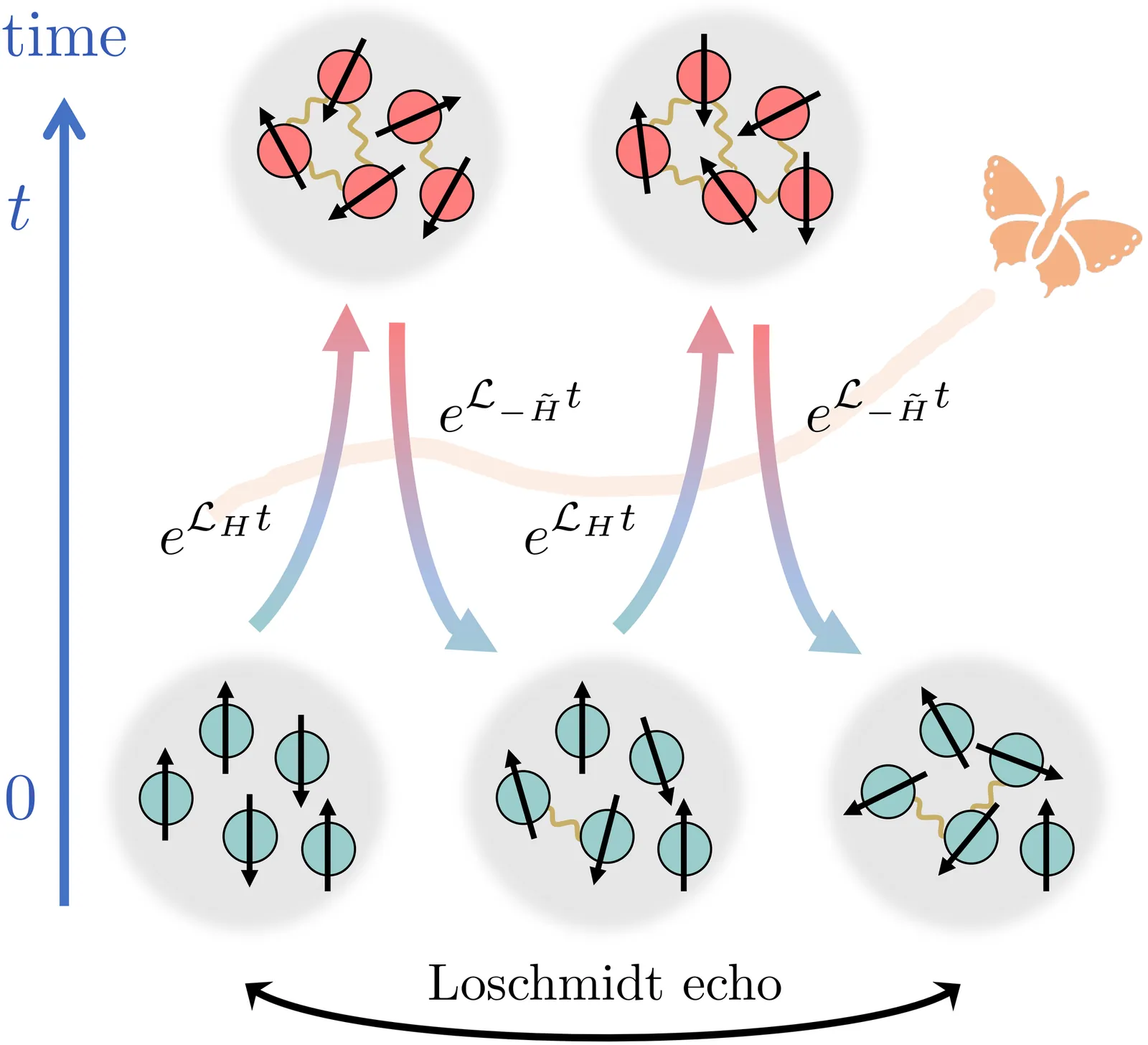
Despite the rapid development of quantum science and technology, errors are inevitable and play a crucial role in quantum simulation and quantum computation. In quantum chaotic systems, coherent errors arising from imperfect Hamiltonian control and incoherent errors induced by coupling to the environment are both exponentially amplified during time evolution due to information scrambling. A fundamental question is how these two classes of errors imprint distinct signatures on the emergent irreversibility of many-body dynamics. In this Letter, we address this question by investigating multi-round time-reversed dynamics in the presence of both coherent and incoherent errors. By applying scramblon theory, we obtain closed-form expressions for the Loschmidt echo over different rounds of time-reversed evolution. For incoherent errors, the error accumulates linearly with the number of rounds, whereas coherent errors exhibit a crossover from quadratic to linear accumulation. These predictions are explicitly verified using the solvable Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev model. Our results provide a theoretical foundation for characterizing and calibrating coherent and incoherent errors in reversed dynamics, with particular relevance to nuclear magnetic resonance systems.
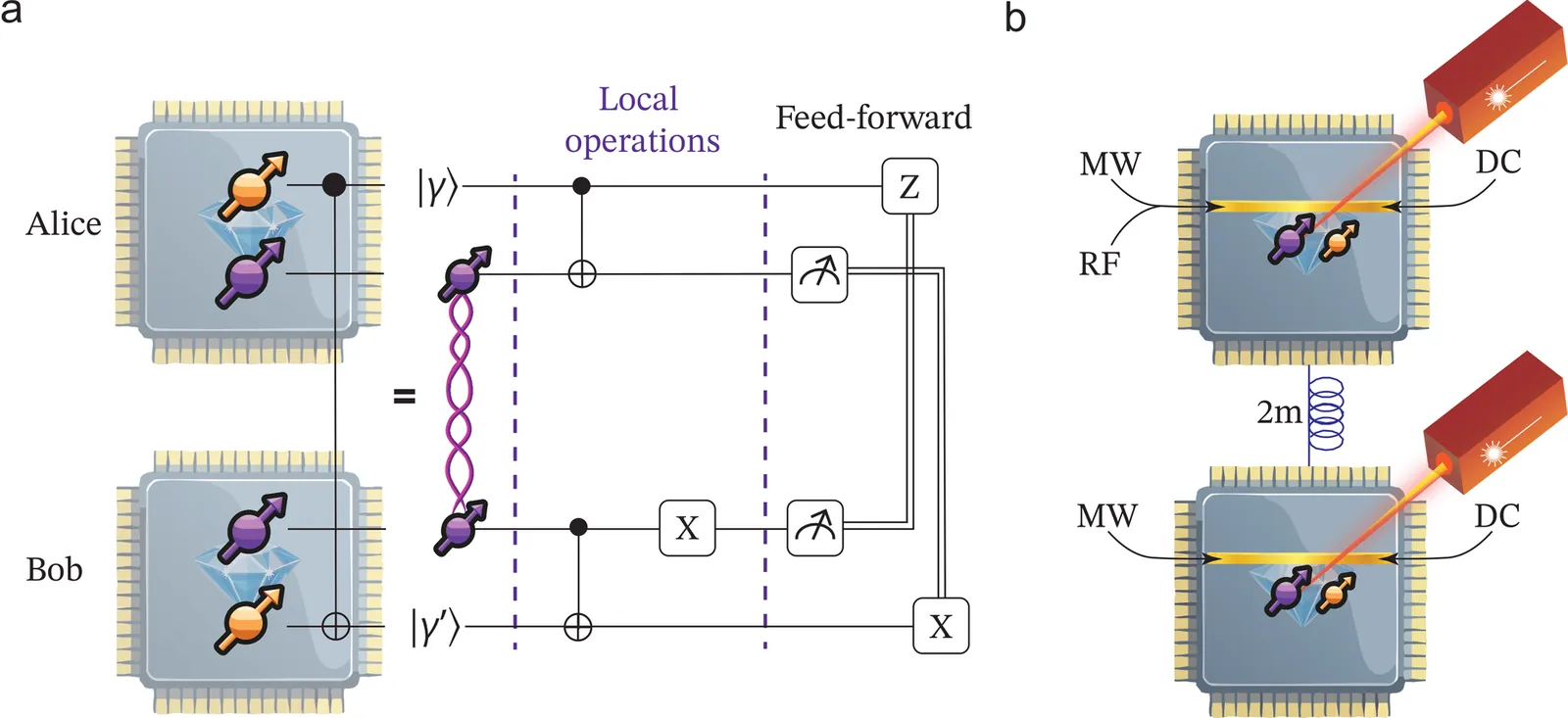
Quantum networks connecting quantum processing nodes via photonic links enable distributed and modular quantum computation. In this framework, quantum gates between remote qubits can be realized using quantum teleportation protocols. The essential requirements for such non-local gates are remote entanglement, local quantum logic within each processor, and classical communication between nodes to perform operations based on measurement outcomes. Here, we demonstrate an unconditional Controlled-NOT quantum gate between remote diamond-based qubit devices. The control and target qubits are Carbon-13 nuclear spins, while NV electron spins enable local logic, readout, and remote entanglement generation. We benchmark the system by creating a Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state, showing genuine 4-partite entanglement shared between nodes. Using deterministic logic, single-shot readout, and real-time feed-forward, we implement non-local gates without post-selection. These results demonstrate a key capability for solid-state quantum networks, enabling exploration of distributed quantum computing and testing of complex network protocols on fully integrated systems.