Differential Geometry
Complex, contact, Riemannian, pseudo-Riemannian and Finsler geometry, relativity, gauge theory, global analysis.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Complex, contact, Riemannian, pseudo-Riemannian and Finsler geometry, relativity, gauge theory, global analysis.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
 2601.05228
2601.05228The standard definition of integration of differential forms is based on local coordinates and partitions of unity. This definition is mostly a formality and not used used in explicit computations or approximation schemes. We present a definition of the integral that uses triangulations instead. Our definition is a coordinate-free version of the standard definition of the Riemann integral on $\mathbb{R}^n$ and we argue that it is the natural definition in the contexts of Lie algebroids, stochastic integration and quantum field theory, where path integrals are defined using lattices. In particular, our definition naturally incorporates the different stochastic integrals, which involve integration over Hölder continuous paths. Furthermore, our definition is well-adapted to establishing integral identities from their combinatorial counterparts. Our construction is based on the observation that, in great generality, the things that are integrated are determined by cochains on the pair groupoid. Abstractly, our definition uses the van Est map to lift a differential form to the pair groupoid. Our construction suggests a generalization of the fundamental theorem of calculus which we prove: the singular cohomology and de Rham cohomology cap products of a cocycle with the fundamental class are equal.
 2601.05210
2601.05210We introduce and study a new general flow of $\mathrm{G}_2$-structures which we call the Ricci-harmonic flow of $\mathrm{G}_2$-structures. The flow is the coupling of the Ricci flow of underlying metrics and the isometric flow of $\mathrm{G}_2$-structures, but we also provide explicit lower order in the torsion terms. The lower order terms and the flow are obtained by analyzing the second order term in the Taylor series expansion of $\mathrm{G}_2$-structures in normal coordinates. As such, the Ricci-harmonic flow described in the paper can be interpreted as the "heat equation" for $\mathrm{G}_2$-structures. The lower order terms allow us to prove that the stationary points of the Ricci-harmonic flow are exactly torsion-free $\mathrm{G}_2$-structures on compact manifolds. We study various analytic and geometric properties of the flow. We show that the flow has short-time existence and uniqueness on compact manifolds starting with an arbitrary $\mathrm{G}_2$-structure and prove global Shi-type estimates. We also prove a modified local Shi-type estimates for the flow which assume bounds on the initial derivatives of the Riemann curvature tensor and the torsion but give uniform bounds on these quantities for all times. We prove a compactness theorem for the solutions of the flow and use it to prove that the Ricci-harmonic flow exists as long as the velocity of the flow remains bounded. We also study Ricci-harmonic solitons where we prove that there are no compact expanding solitons and the only steady solitons are torsion-free. We derive an analog of Hamilton's identity for gradient Ricci-harmonic solitons and prove some integral identities for the solitons. Finally, we prove a version of the Taylor series expansion for Spin(7)-structures and use it to derive the Ricci-harmonic flow of Spin(7)-structures.
 2601.05041
2601.05041We discuss the initial value problem for the Einstein equations in Hitchin's generalised geometry for the case of closed divergence (which correspond to the equations of motion in the bosonic part of the NS-NS sector in type II ten-dimensional supergravity) and establish the existence of a maximal globally hyperbolic development (MGHD). The dynamical fields, defined on a manifold of dimension $n+1$, are the space-time metric, a scalar field known as the dilaton function, and a two-form known as the $B$-field. We develop a generalisation of the Lorenz gauge which, applied to the $B$-field (and combined with a suitable gauge condition breaking diffeomorphism invariance), renders the system a wave equation with principal symbol given by the (dynamical) metric. Given initial data, we construct a development satisfying the gauge conditions. We show that all other developments are (in the appropriate sense) related to this development by a diffeomorphism, establishing geometric uniqueness. The existence of the MGHD follows then by a famous result by Choquet-Bruhat and Geroch. In showing existence and geometric uniqueness of developments, we follow an approach developed in detail by Ringström for the Einstein equations coupled to a scalar field. In a preliminary section, we present a formulation which is disentangled from the specific assumptions made on the matter, so that adaptation to other systems is straightforward.
 2601.04937
2601.04937We study compact complex $3$-dimensional non-Kähler Bismut Ricci flat pluriclosed Hermitian manifolds (BHE) via their dimensional reduction to a special Kähler geometry in complex dimension $2$, recently obtained by Barbaro, Streets and the first and third authors. We show that in the quasi-regular case, the reduced geometry satisfies a 6th order non-linear PDE which has infinite dimensional momentum map interpretation, similar to the much studied Kähler metrics of constant scalar curvature (cscK). We use this to associate to the reduced manifold or orbifold Mabuchi and Calabi functionals, as well as to obtain obstructions for the existence of solutions in terms of the authomorphism group, paralleling results by Futaki and Calabi-Lichnerowicz-Matsushima in the cscK case. This is used to characterize the Samelson locally homogeneous BHE geometries in complex dimension 3 as the only non-Kähler BHE $3$-folds with $2$-dimensional Bott-Chern $(1,1)$-cohomology group, for which the reduced space is a smooth Kähler surface. We also discuss explicit solutions of the PDE on orthotoric Kähler orbifold surfaces, extending examples found by Couzens-Gauntlett-Martelli-Sparks in the framework of supersymmetric ${\rm AdS}_3 \times Y_7$ type IIB supergravity. Our construction yields infinitely many non-Kähler BHE structures on $S^3\times S^3$ and $S^1\times S^2 \times S^3$, which are not locally isometric to a Samelson geometry. These appear to be the first such examples.
 2601.04495
2601.04495Let $F: T^{1,0}M\rightarrow[0,+\infty)$ be a strongly convex complex Finsler metric on a complex manifold $M$ and $\pmb{J}$ the canonical complex structure on the complex manifold $T^{1,0}M$. We give a geometric characterization of strongly convex Kähler-Berwald metrics. In particular, we prove that $\pmb{J}$ is horizontally parallel with respect to the Cartan connection iff $F$ is a Kähler-Berwald metric. We also prove that the Cartan connection and the Chern-Finsler connection associated to $F$ coincide iff $\pmb{J}$ is both horizontal and vertical parallel with respect to the Cartan connection. Based on these results, we give a rigidity theorem of strongly convex Kähler-Berwald metrics with constant holomorphic sectional curvatures.
 2601.04027
2601.04027We investigate the asymptotic behavior of high-codimensional area-minimizing locally rectifiable currents in hyperbolic space, addressing a problem posed by F.H. Lin and establishing ``boundary regularity at infinity" results for such currents near their asymptotic boundaries under the standard Euclidean metric. Intrinsic obstructions to high-order regularity arise for odd-dimensional minimal surfaces, revealing a constraint dependent on the geometry of the asymptotic boundary. Our work advances the asymptotic theory of high-codimensional minimal surfaces in hyperbolic space.
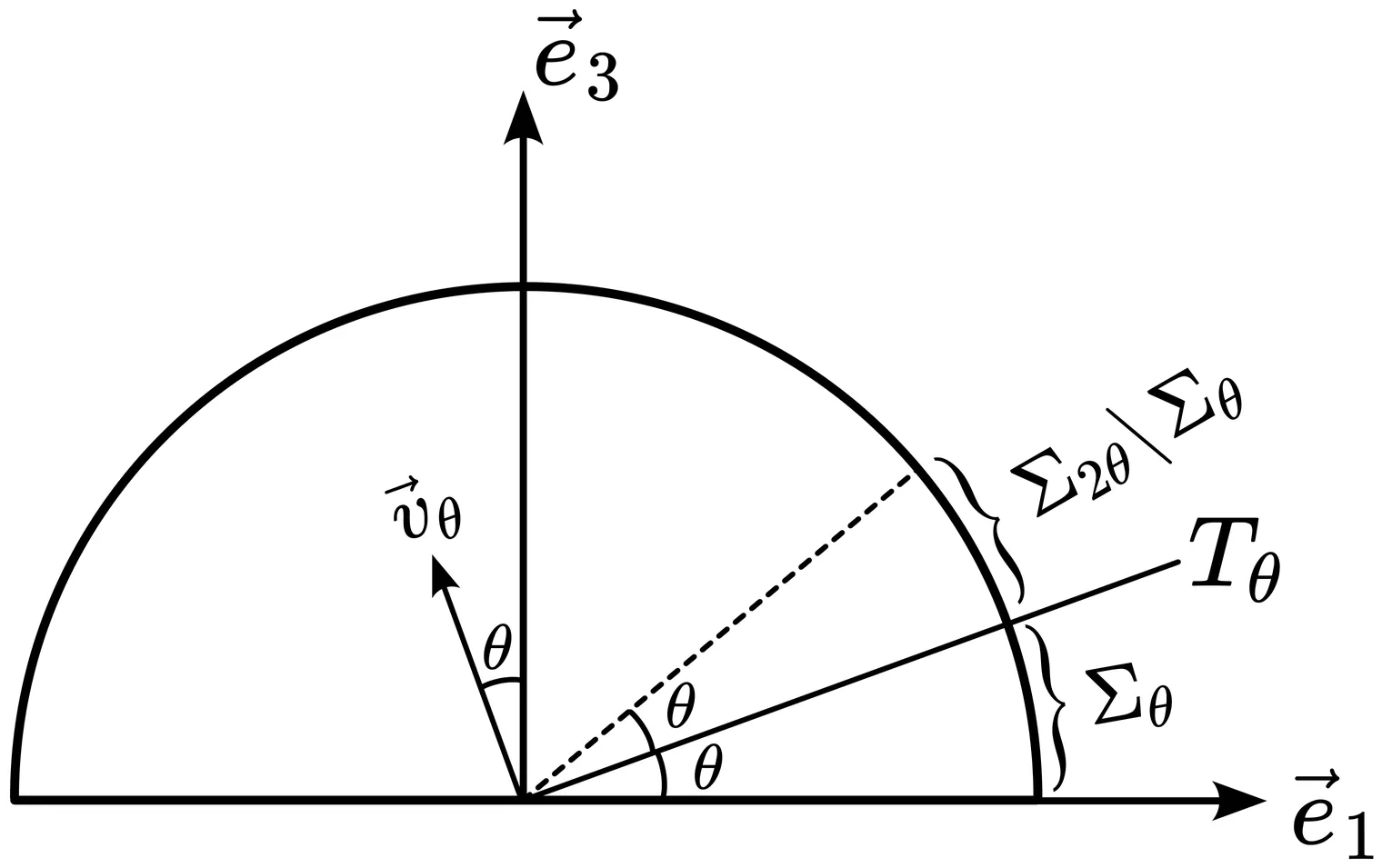
We verify a conjecture proposed by X. Chen and Y. Shi, which arises from their study of the Green function on spheres in Euclidean space. More precisely, let $M\subset \mathbb{R}^3$ be a closed $C^{2}$ embedded surface and suppose that there exists a point $p\in M$ so that its Green function $G$ is of the form $G(p,q)=-\frac{1}{2π} \ln d_{\mathbb{R}^3}(p,q)+c, \forall q\neq p$, then $M$ must be a round sphere.
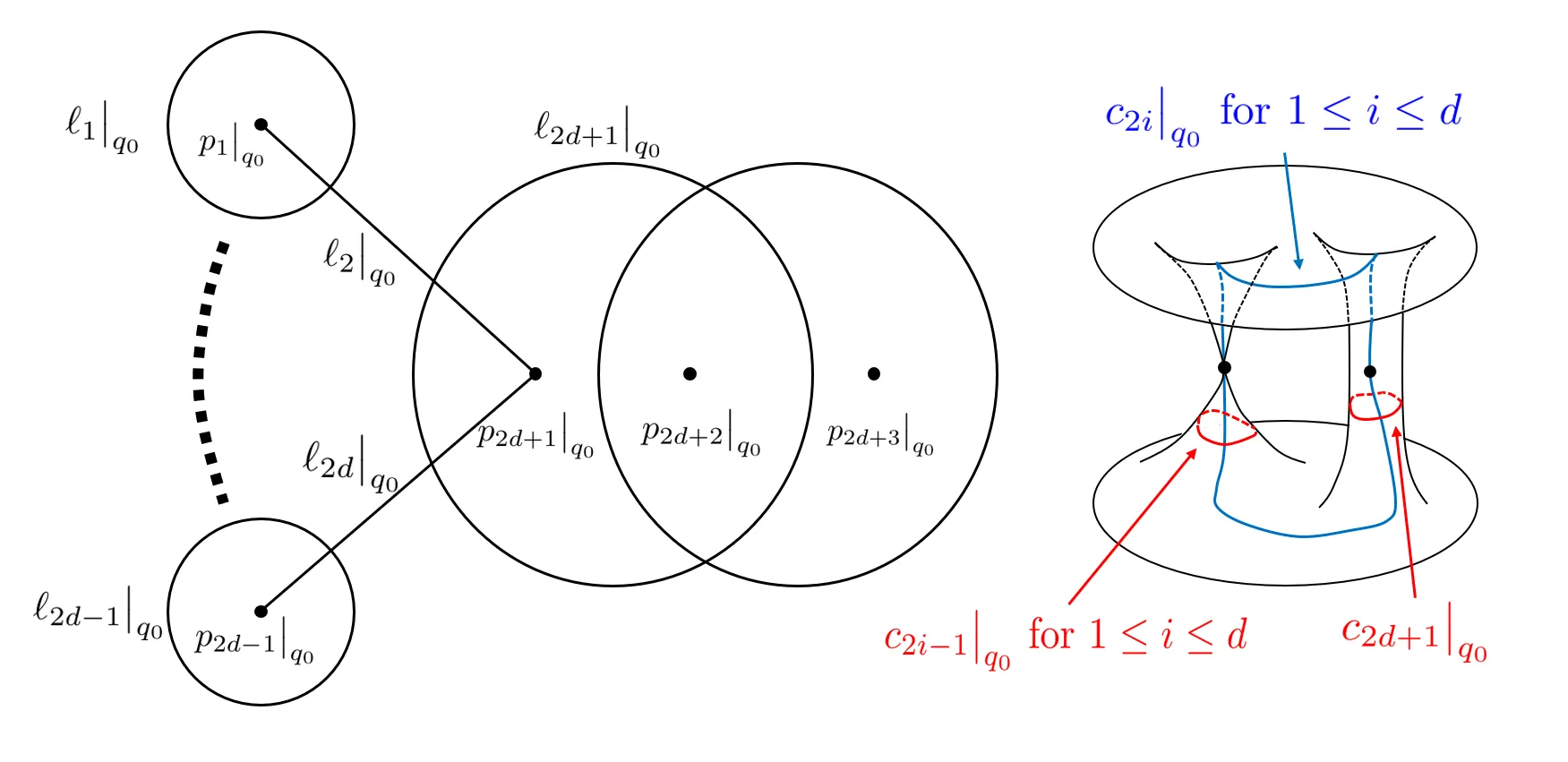
Freed (arXiv:hep-th/9712042) formulated special Kähler structures; in particular, the regular locus of the $\mathrm{SL}_2(\mathbb{C})$ Hitchin base $\mathcal{B}$ carries such a structure, while the associated metric $ω_{\mathrm{SK}}$ is singular along the discriminant locus $\mathcal{D}$. Baraglia-Huang (arXiv:1707.04975) computed its Taylor expansion near points of $\mathcal{B}\setminus\mathcal{D}$. Hitchin (arXiv:1712.09928) then defined subsystems attached to those components of $\mathcal{D}$ whose spectral curves have only nodal singularities; these components form smooth strata with induced special Kähler structures. We show that near such a stratum the canonical special Kähler metric has logarithmic asymptotics in transversal directions, whereas its tangential part converges to a metric on the stratum agreeing with the one from Hitchin's subsystems. Along any complex line through the origin of $\mathcal{B}$ and a point of the stratum, the metric restricts to a cone flat metric with cone angle $π$ at the origin only. Finally, the special Kähler potential extends continuously to these strata, and is $C^1$ on a portion of them.
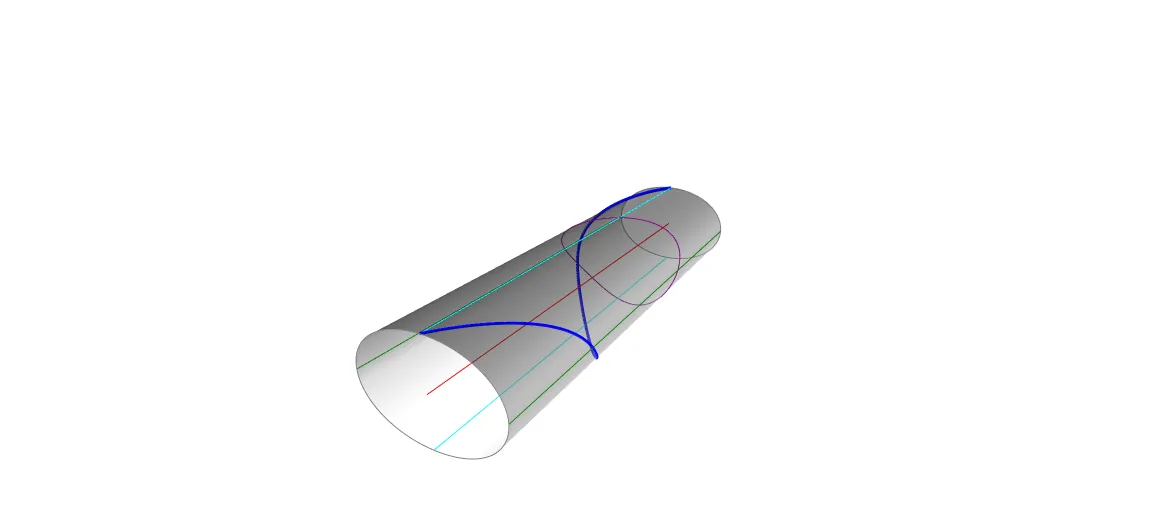
We provide a self-contained geometric description of the geodesic flow in the three-dimensional Lie group $\mathrm{Sol}$, one of Thurston's eight model geometries. The geometry of geodesics is governed by a single invariant $k\in[0,1]$, its modulus. Generic geodesics spiral around an axis, with well-defined amplitude $A(k)$, period $T(k)$, and horizontal drift $H(k)$. We characterize minimal geodesic segments and the cut locus, and obtain an asymptotic estimate showing that distances between points at the same altitude grow logarithmically. This work builds on previous work by Grayson and Coiculescu--Schwartz, but develops an alternative geometric and dynamical viewpoint.
 2601.03585
2601.03585Let $Γ\subset \mathsf{PSL}(2,\mathbb{R})$ be a lattice and $ρ:Γ\to \mathsf{Sp}(2n,\mathbb{R})$ be a maximal representation. We show that $ρ$ satisfies a measurable $(1,1,2)-$hypertransversality condition. With this we define a measurable Gromov product and the Bowen-Margulis-Sullivan measure associated to the unstable Jacobian introduced by Pozzetti, Sambarino and Wienhard. As a main application, we prove a strong entropy rigidity result for $ρ$.
 2601.03544
2601.03544Geometric Quantization is a term used to describe a wide collection of techniques dating back to the 1960s in the work of Kirillov, Kostant, and Souriau, which take symplectic manifolds and produce complex vector spaces. The name comes from the natural interpretation of symplectic manifolds as the phase spaces of classical mechanical systems and complex vector spaces as the natural domains of wave functions in quantum mechanics. In this thesis, I extend the classical framework of Geometric Quantization to handle a class of singular spaces called Symplectic Stratified Spaces, which date back to the work of Sjamaar and Lerman in the 1990s. As part of this work, I develop the theory of stratified pseudobundles to serve as singular replacements for important auxiliary information in Geometric Quantization: prequantum line bundles and polarizations. I then use this formalism to provide [Q,R]=0 results for singular quotients of toric manifolds and cotangent bundles. I also provide an example of singular Geometric Quantization that does not arise from singular reduction.
 2601.03462
2601.03462In this paper, we first derive biharmonic equation for conformal hypersurfaces in a generic Riemannian manifold generalizing that for biharmonic hypersurfaces in \cite{Ou1} and that for biharmonic conformal surfaces in \cite{Ou3, Ou2, Ou4}. We then show that if a totally umbilical hypersurface in a space form admits a biharmonic conformal immersion into the ambient space, then the conformal factor has to be an isoparametric function. We also prove that no part of a non-minimal totally umbilical hypersurface in a space form of nonpositive curvature admits a biharmonic conformally immersion into that space form whilst, for the positive curvature space form, we show that the totally umbilical hypersurface $S^4(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2})\hookrightarrow S^5$ does admit a biharmonic conformal immersion into $S^5$.
In this article, we study $c$-spherical Ricci metrics, that is, Riemannian metrics whose Gaussian curvature $K$ satisfies \begin{equation*} (K - c)ΔK - |\nabla K|^2 - 4K(K - c)^2 = 0, \end{equation*} for some $c>0$. We explicitly construct a two-parameter family of such metrics with rotational symmetry and show that infinitely many non-isometric examples can be realized on the same torus. Moreover, we investigate their realization as induced metrics on compact rotational surfaces in $\mathbb{S}^3$, establishing the existence of embedded compact spherical Ricci surfaces by controlling a period function associated with the isometric immersion.
 2601.03094
2601.03094We investigate several classes of submanifolds of almost quaternionic skew-Hermitian manifolds $(M^{4n}, Q, ω)$, including almost symplectic, almost complex, almost pseudo-Hermitian and almost quaternionic submanifolds. In the torsion-free case, we realize each type of submanifold considered in the theoretical part by constructing explicit examples of submanifolds of semisimple quaternionic skew-Hermitian symmetric spaces.
 2601.03092
2601.03092In this work, we discuss the stability of Donaldson's flow of surfaces in a hyperkähler 4-manifold. In \cite{WT2}, Wang and Tsai proved a uniqueness theorem and $C^1$ dynamic stability theorem of the mean curvature flow for minimal surface. We extend their results and obtain a similar dynamic stability theorem of the hyperkähler flow.
 2601.02901
2601.02901We study the 2-systole on compact Kähler surfaces of positive scalar curvature. For any such surface $(X,ω)$, we prove the sharp estimate \(\min_X S(ω)\cdot\syst_2(ω)\le12π\), with equality if and only if $X=\PP^2$ and $ω$ is the Fubini--Study metric. Using the classification of positive scalar curvature Kähler surfaces by their minimal models, we also determine the optimal constant in each case and describe the corresponding rigid models: $12π$ when the minimal model is $\PP^2$, $8π$ for Hirzebruch surfaces, and $4π$ for non-rational ruled surfaces. In the non-rational ruled case, we also give an independent analytic proof, adapting Stern's level set method to the holomorphic fibration in Kähler setting.

We prove an upper bound for the Morse index of min-max stationary integral varifolds realizing the $d$-dimensional $p$-width of a closed Riemannian manifold.
 2601.02853
2601.02853Using a modified curve shortening flow, we construct $λ$-Angenent curve, which was first constructed by the shooting method.
 2601.02742
2601.02742The Riemann curvature tensor fully encodes local geometry, but its Ricci contraction retains only limited information: only the Ricci tensor and the scalar curvature survive, while the Weyl curvature vanishes identically. We show that contracting instead the double dual of the Riemann tensor unlocks the full curvature structure, producing a canonical hierarchy of symmetric, divergence--free $(p,p)$ double forms. These tensors satisfy the first Bianchi identity and obey a hereditary contraction relation interpolating between the double dual tensor and the Einstein tensor. We prove that, in a generic geometric setting, each tensor in this hierarchy is the unique divergence--free $(p,p)$ double form depending linearly on the Riemann curvature tensor, thereby providing canonical higher--rank parents of the Einstein tensor. Their sectional curvatures coincide with the $p$--curvatures; notably, the $2$--curvature determines the full Riemann curvature tensor and forces the $\hat A$--genus of a compact spin manifold to vanish when nonnegative, a property not shared by Ricci or scalar curvature. Finally, we extend the construction to Gauss--Kronecker curvature tensors and Lovelock theory, showing in particular that the second Lovelock tensor $T_4$ admits a genuine four--index parent tensor.
 2601.02733
2601.02733We give a detailed description of the nearly Kähler $\frac{\mathrm{SL}(3,\mathbb R)}{\mathbb R\times \mathrm{SO}(2)}$, which is one of the pseudo-Riemannian counterparts of the flag manifold $F(\mathbb{C}^3)$. The main result is the classification of totally geodesic almost complex surfaces in this space.