Group Theory
Finite groups, topological groups, representation theory, cohomology, classification and structure.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
Finite groups, topological groups, representation theory, cohomology, classification and structure.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
 2601.03206
2601.03206I give a short proof of a recent result due to Kiefer and Ryzhikov showing that a finite irreducible semigroup of $n\times n$ matrices has cardinality at most $3^{n^2}$.
 2601.02844
2601.02844The sequence reconstruction problem asks for the recovery of a sequence from multiple noisy copies, where each copy may contain up to $r$ errors. In the case of permutations on \(n\) letters under the Hamming metric, this problem is closely related to the parameter $N(n,r)$, the maximum intersection size of two Hamming balls of radius $r$. While previous work has resolved \(N(n,r)\) for small radii (\(r \leq 4\)) and established asymptotic bounds for larger \(r\), we present new exact formulas for \(r \in \{5,6,7\}\) using group action techniques. In addition, we develop a formula for \(N(n,r)\) based on the irreducible characters of the symmetric group \(S_n\), along with an algorithm that enables computation of \(N(n,r)\) for larger parameters, including cases such as \(N(43,8)\) and \(N(24,14)\).
 2601.01133
2601.01133Given a finite group $G$, the difference graph of $G$, denoted by $\mathcal{D}(G)$, is the difference of the enhanced power graph of $G$ and the power graph of $G$, with all isolated vertices removed. This paper mainly studies the dominating sets of the difference graph of a finite group. In particular, we prove that the diameter of the difference graph of a nilpotent group has an upper bound of $4$. Furthermore, we generalize and refine the result by Biswas et al. by classifying all nilpotent groups whose difference graph has diameter $k$, for each $k\le 4$.
 2512.24357
2512.24357Let $A$ be a finite-dimensional associative $k$-algebra with identity. The primary aim of this paper is to study the rationality properties of the group of all $k$-algebra automorphisms of $A$, as an affine algebraic group over an arbitrary field $k$. We investigate mainly the $R$-equivalence property of the identity component of $\mathrm{Aut}_{k}(A)$ over a perfect field $k$.
 2512.22410
2512.22410Let $G$ be a finite group. For a prime $p$ and an integer $e \geq 0$, we denote by $Γ_{p,e}(G)$ the set of all pairs $(H, \varphi)$, where $H$ is a $p$-subgroup of $G$ of order greater than $p^e$ and $\varphi$ is a complex irreducible character of $H$. In this paper, we investigate the connected components of the poset $Γ_{p,e}(G)$. For the case $e = 0$, we prove that $Γ_{p,0}(G)$ is disconnected if and only if either $G$ has a strongly $p$-embedded subgroup, or every Sylow $p$-subgroup of $G$ contains a unique subgroup of order $p$. Furthermore, for $e = 1$ and $G$ a $p$-group, we show that the number of connected components of $Γ_{p,1}(G)$ equals the order of the intersection of all subgroups of $G$ of order $p^2$.
 2512.21611
2512.21611We characterize connected tetravalent graphs $Γ$ which admit groups $M<H$ of automorphisms such that $Γ$ is $M$-half-arc-transitive and $H$-arc-transitive. Examples for each case are constructed, including a counter-example to a question asked by A. R. Rivera and P. Šparl in 2019 as well as the first example of tetravalent normal-edge-transitive non-normal Cayley graph on a nonabelian simple group.
 2512.20524
2512.20524For $α\in \mathbb{R}$, let $$G_α:= \left< \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} , \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ α& 1 \end{bmatrix} \right> < \mathrm{SL}_2 (\mathbb{R}).$$ K. Kim and the first author established the orbit test, which provides a sufficient condition for $G_α$ not to be a rank-$2$ free group. In this article, we present two main applications of the orbit test. First, using the corresponding modulo homomorphism, we show that the converse of the orbit test does not hold. In particular, we construct explicit counterexamples, all of which are rational. As another application, we construct sequences of non-free rational numbers converging to $3$. These sequences are given by $$ 3 + \frac{3}{2 (9 n - 1)} \quad \text{and} \quad 3 + \frac{9 n + 5}{3 (2 n + 1) (9 n + 4)},$$ and their construction relies on the orbit test together with a modified Pell's equation.
 2512.19638
2512.19638We give a general lower bound on the rank of matrices of the form $ρ(h) - I$ with $ρ: G \rightarrow GL({\mathbb F}^n)$ an irreducible representation of a finite group $G$. The main tool in the proof is a (strengthening) of a reduction due to Efremenko from low rank matrices spanned by a few images of $ρ$ to Locally Decodable Codes (LDCs), which are a special kind of error correcting codes. We then apply the known results on 2-query LDCs to derive our rank bound.
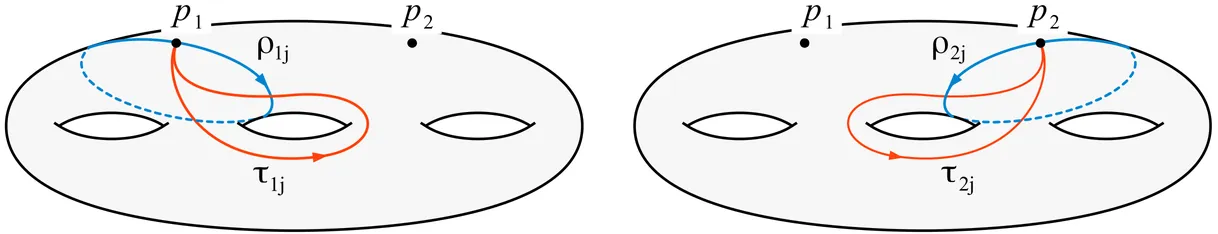
Let $Σ_b$ be a compact Riemann surface of genus $b \geq 2$ and let $\mathsf{P}_2(Σ_b)=π_1(Σ_b \times Σ_b - Δ)$ be the corresponding pure braid group on two strands. A finite quotient $\varphi \colon \mathsf{P}_2(Σ_b) \to G$ is called "admissible" if $\varphi$ does not factor through $π_1(Σ_b \times Σ_b)$. In this work we classify all admissible quotients of $\mathsf{P}_2(Σ_b)$ such that $|G| \leq 127$.
In this paper, we construct a higher dimensional generalization of affine buildings and introduce a new structure, which we call Babel buildings. These buildings are non-connected, non-convex metric spaces of non-positive curvature. Despite their non-standard properties, Babel buildings provide an effective framework for studying the structure of groups acting on them. We analyze the metric and nesting structures of Babel buildings and derive key results regarding the group actions consistent with this new framework.
 2512.18302
2512.18302Let $G$ be a finite group generated by $k$ elements. The well-known product replacement algorithm provides an effective method for sampling generating sets of $G$. We study a refinement of this algorithm that is designed to output individual elements of $G$. We show that after $O(k^2\log|G|)$ steps, the distribution of the output is close to uniform on $G$, which improves upon the best results known to date. The proof proceeds via spectral gap estimates and uses computer assisted calculations.
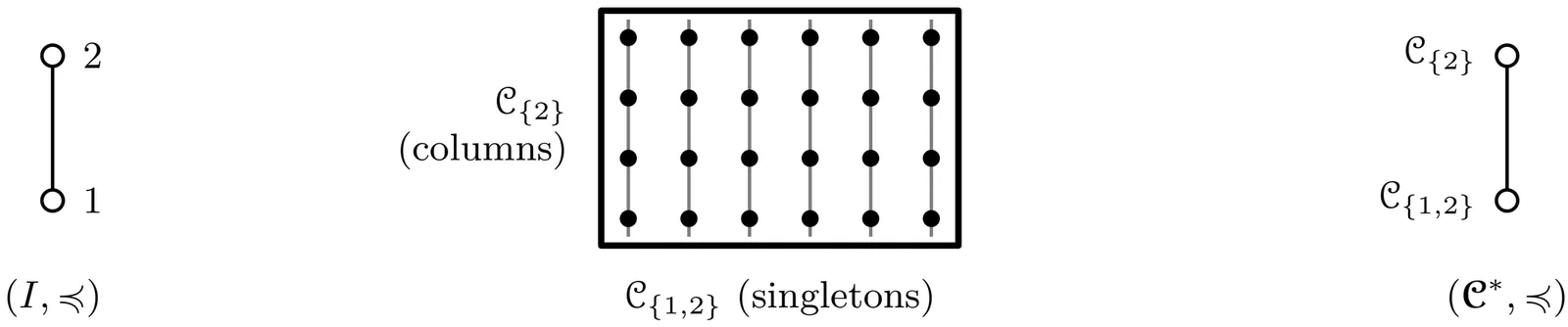
We study block designs which admit an automorphism group that is transitive on blocks and points, and leaves invariant every partition in a given finite poset of partitions of the point set. The full stabiliser $G$ of all the partitions in the poset is a generalised wreath product. We use the theory of generalised wreath products to give necessary and sufficient conditions, in terms of the `array' of a point-subset $B$, for the set of $G$-images of $B$ to form the block-set of a $G$-block-transitive $2$-design. This generalises previous results for the special cases where the poset is a chain or an anti-chain. We also give explicit infinite families of examples of $2$-designs for each poset involving three proper partitions, and for the famous $N$-poset with four partitions. (Posets with two proper partitions have been treated previously.) This suggests the problem of finding explicit examples for other posets.
 2512.16079
2512.16079Two fundamental ways to represent a group are as permutations and as matrices. In this paper, we study linear representations of groups that intertwine with a permutation representation. Recently, D'Alconzo and Di Scala investigated how small the matrices in such a linear representation can be. The minimal dimension of such a representation is the \emph{linear dimension of the group action} and this has applications in cryptography and cryptosystems. We develop the idea of linear dimension from an algebraic point of view by using the theory of permutation modules. We give structural results about representations of minimal dimension and investigate the implications of faithfulness, transitivity and primitivity on the linear dimension. Furthermore, we compute the linear dimension of several classes of finite primitive permutation groups. We also study wreath products, allowing us to determine the linear dimension of imprimitive group actions. Finally, we give the linear dimension of almost simple finite $2$-transitive groups, some of which may be used for further applications in cryptography. Our results also open up many new questions about linear representations of group actions.
 2512.15364
2512.15364We show that random walks on semisimple algebraic groups do not concentrate on proper algebraic subvarieties with uniform exponential rate of anti-concentration. This is achieved by proving a uniform spectral gap for quasi-regular representations of countable linear groups. The method makes key use of Diophantine heights and the Height Gap theorem. We also deduce a non-abelian version of the Littlewood--Offord inequalities and prove logarithmic bounds for escape from subvarieties. In a sequel to this paper, we will show how to transform this uniform gap into uniform expansion for Cayley graphs of finite simple groups of bounded rank $G(p)$ over almost all primes $p$.
 2512.14324
2512.14324For every Cuntz--Krieger groupoid, we show that there is a topologically free boundary action of the outer automorphism group of its topological full group on the Hilbert cube. In particular, these outer automorphism groups, including the outer automorphism groups of all Higman--Thompson groups, are C*-simple.
 2512.05569
2512.05569Let $G$ be a toral relatively hyperbolic group, and let $\varphi\in\mathrm{Aut}(G)$. We prove that, under iteration of $\varphi$, the conjugacy length $||\varphi^n(g)||$ of every element $g\in G$ grows like $n^dλ^n$ for some $d\in\mathbb{N}$ and some algebraic integer $λ\geq 1$. For a given $\varphi$, only finitely many values of $d$ and $λ$ occur as $g$ varies in $G$. The same statements hold for the growth of the word length $|\varphi^n(g)|$. For $G$ hyperbolic, we generalize polynomial subgroups: we show that, for a given growth type $n^dλ^n$ other than $1$, there is a malnormal family of quasiconvex subgroups $K_1,\dots,K_p$ such that a conjugacy class $[g]$ grows at most like $n^dλ^n$ if and only if $g$ is conjugate into one of the subgroups $K_i$.
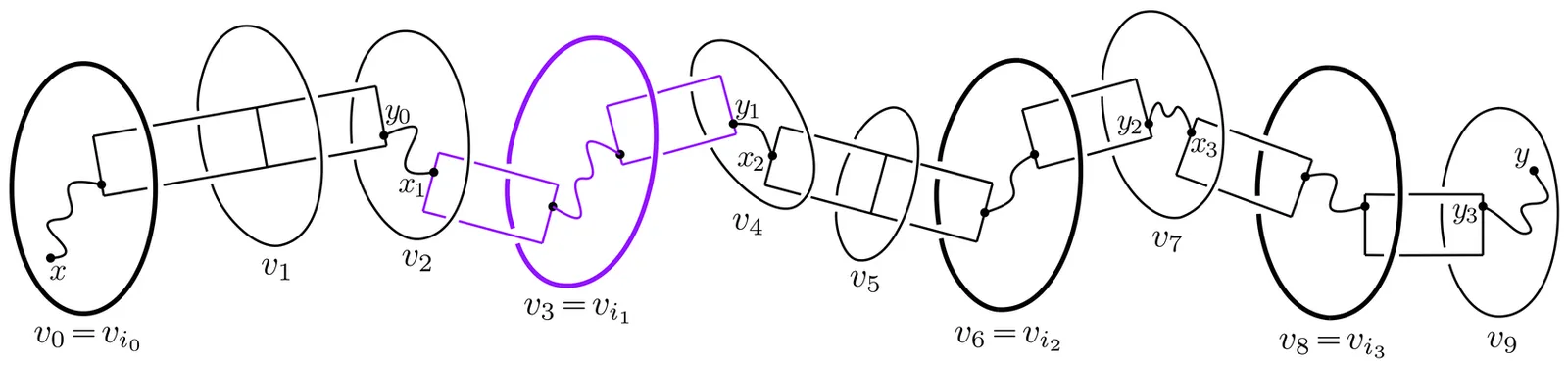
We show that every finitely generated free-by-cyclic group $G$ admits a largest acylindrical action on a hyperbolic space $X$ obtained by coning off maximal product subgroups of $G$. We characterise Morse geodesics of $G$ as those that project to quasigeodesics in $X$, thus showing that all finitely generated free-by-cyclic groups are Morse local-to-global. We also characterise the stable and strongly quasiconvex subgroups of $G$. Finally, we compute the Morse boundary for \{finitely generated free\}-by-cyclic groups with unipotent and polynomially growing monodromy.
 2512.04531
2512.04531We construct a continuum sized family $\{G_x\}_{x\in\{0,1\}^{\mathbb N}}$ of pairwise non-measure equivalent countable groups which have property (T) (hence are finitely generated), have zero $\ell^2$-Betti numbers of all orders, and are torsion-free.
 2512.03885
2512.03885The so-called $T$-sequences $\mathbf u$ in a group $G$, and the related finest Hausdorff group topology $T_\mathbf u$ on $G$ that makes $\mathbf u$ a null sequence, were introduced by Protasov and Zelenyuk 35 years ago and since then they became a fundamental tool in the field of topological groups. More recently, in the abelian case, the subfamily of $T$-sequences called $TB$-sequences was introduced, as well as the finest precompact group topology $T_\mathbf{pu}$ that makes $\mathbf u$ a null sequence. Here we study the counterpart of all these notions with respect to ideal convergence in place of the classical notion of convergence of a sequence. Also, we study their relation to the already established field of $I$-characterized subgroups of compact abelian groups.
 2512.02553
2512.02553In this paper, we establish the decomposition of morphisms from lattice of subgroup sets to generalized solvable extension formations. To achieve this, we develop a unified framework involving maximal subgroup functors, generating formation morphism and contraction-extension functors. In particular, solvability-induced sets of maximal subgroups are determined and generating formation morphism gives rise to generalized solvable extension formations.