Medical Physics
Medical physics, radiation therapy physics, medical imaging.
Medical physics, radiation therapy physics, medical imaging.
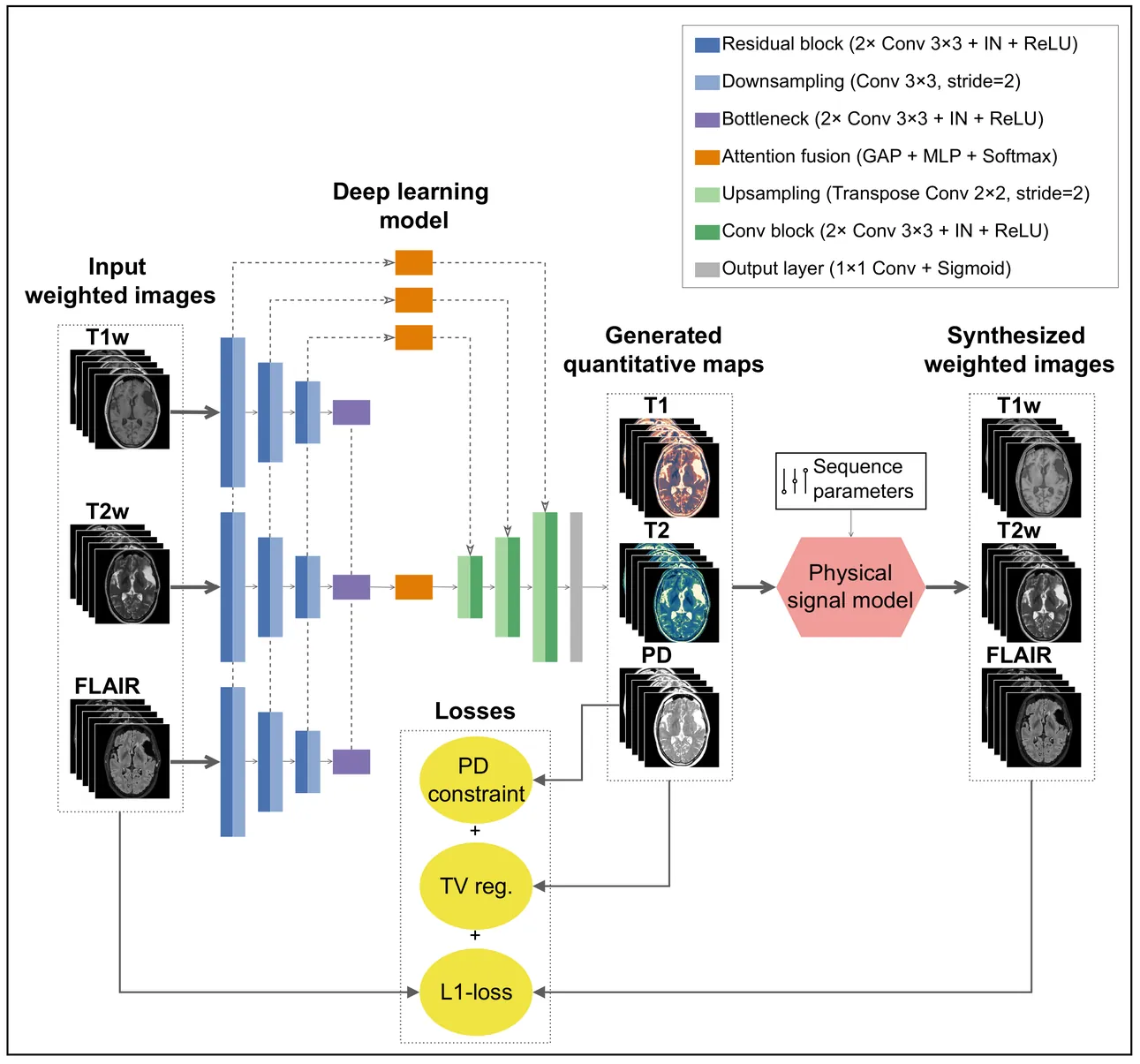
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of clinical neuroimaging, yet conventional MRIs provide qualitative information heavily dependent on scanner hardware and acquisition settings. While quantitative MRI (qMRI) offers intrinsic tissue parameters, the requirement for specialized acquisition protocols and reconstruction algorithms restricts its availability and impedes large-scale biomarker research. This study presents a self-supervised physics-guided deep learning framework to infer quantitative T1, T2, and proton-density (PD) maps directly from widely available clinical conventional T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and FLAIR MRIs. The framework was trained and evaluated on a large-scale, clinically heterogeneous dataset comprising 4,121 scan sessions acquired at our institution over six years on four different 3 T MRI scanner systems, capturing real-world clinical variability. The framework integrates Bloch-based signal models directly into the training objective. Across more than 600 test sessions, the generated maps exhibited white matter and gray matter values consistent with literature ranges. Additionally, the generated maps showed invariance to scanner hardware and acquisition protocol groups, with inter-group coefficients of variation $\leq$ 1.1%. Subject-specific analyses demonstrated excellent voxel-wise reproducibility across scanner systems and sequence parameters, with Pearson $r$ and concordance correlation coefficients exceeding 0.82 for T1 and T2. Mean relative voxel-wise differences were low across all quantitative parameters, especially for T2 ($<$ 6%). These results indicate that the proposed framework can robustly transform diverse clinical conventional MRI data into quantitative maps, potentially paving the way for large-scale quantitative biomarker research.
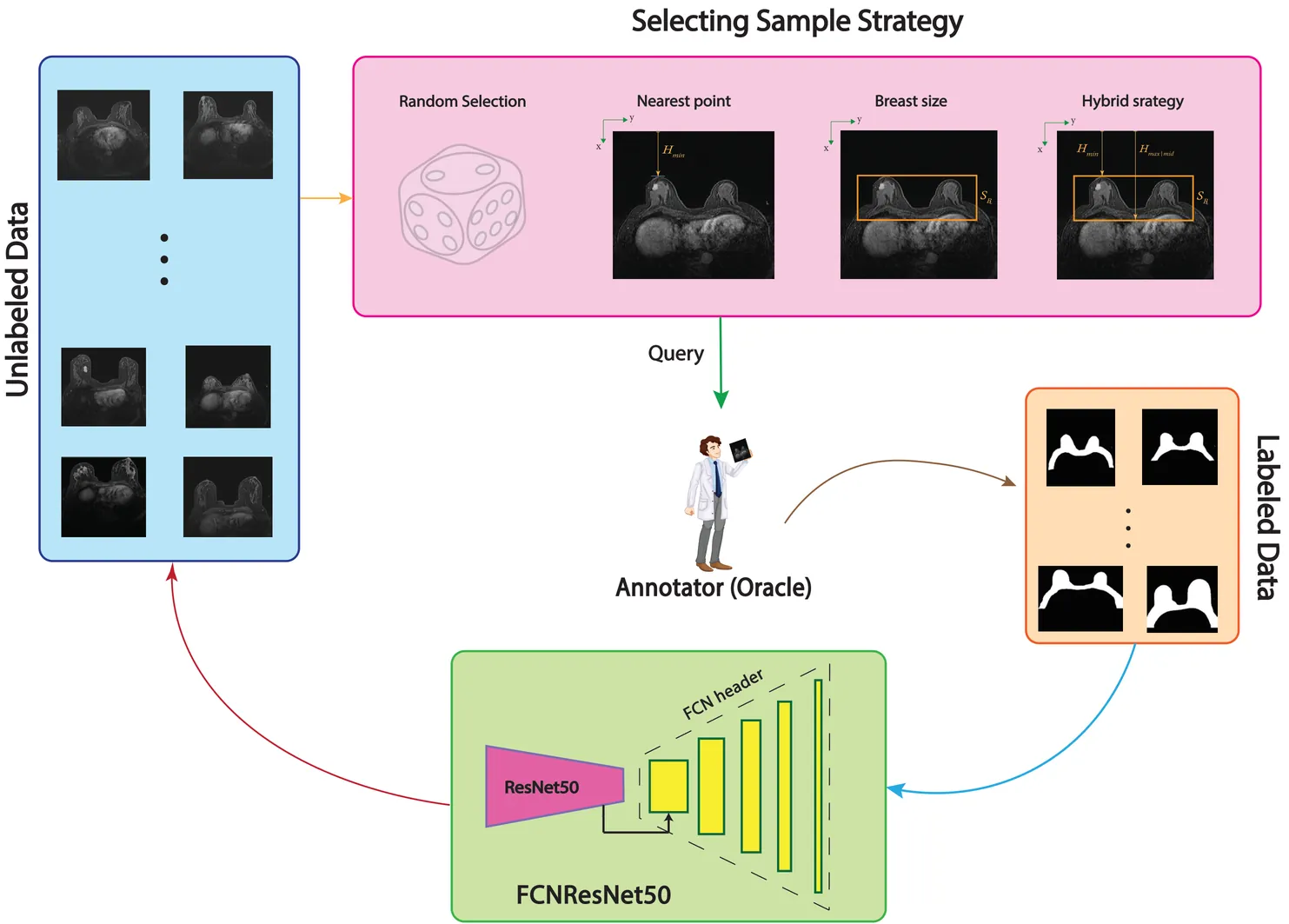
Purpose: Annotation of medical breast images is an essential step toward better diagnostic but a time consuming task. This research aims to focus on different selecting sample strategies within deep active learning on Breast Region Segmentation (BRS) to lessen computational cost of training and effective use of resources. Methods: The Stavanger breast MRI dataset containing 59 patients was used in this study, with FCN-ResNet50 adopted as a sustainable deep learning (DL) model. A novel sample selection approach based on Breast Anatomy Geometry (BAG) analysis was introduced to group data with similar informative features for DL. Patient positioning and Breast Size were considered the key selection criteria in this process. Four selection strategies including Random Selection, Nearest Point, Breast Size, and a hybrid of all three strategies were evaluated using an active learning framework. Four training data proportions of 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40% were used for model training, with the remaining data reserved for testing. Model performance was assessed using Dice score, Intersection over Union, precision, and recall, along with 5-fold cross-validation to enhance generalizability. Results: Increasing the training data proportion from 10% to 40% improved segmentation performance for nearly all strategies, except for Random Selection. The Nearest Point strategy consistently achieved the lowest carbon footprint at 30% and 40% data proportions. Overall, combining the Nearest Point strategy with 30% of the training data provided the best balance between segmentation performance, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Keywords: Deep Active Learning, Breast Region Segmentation, Human-center analysis
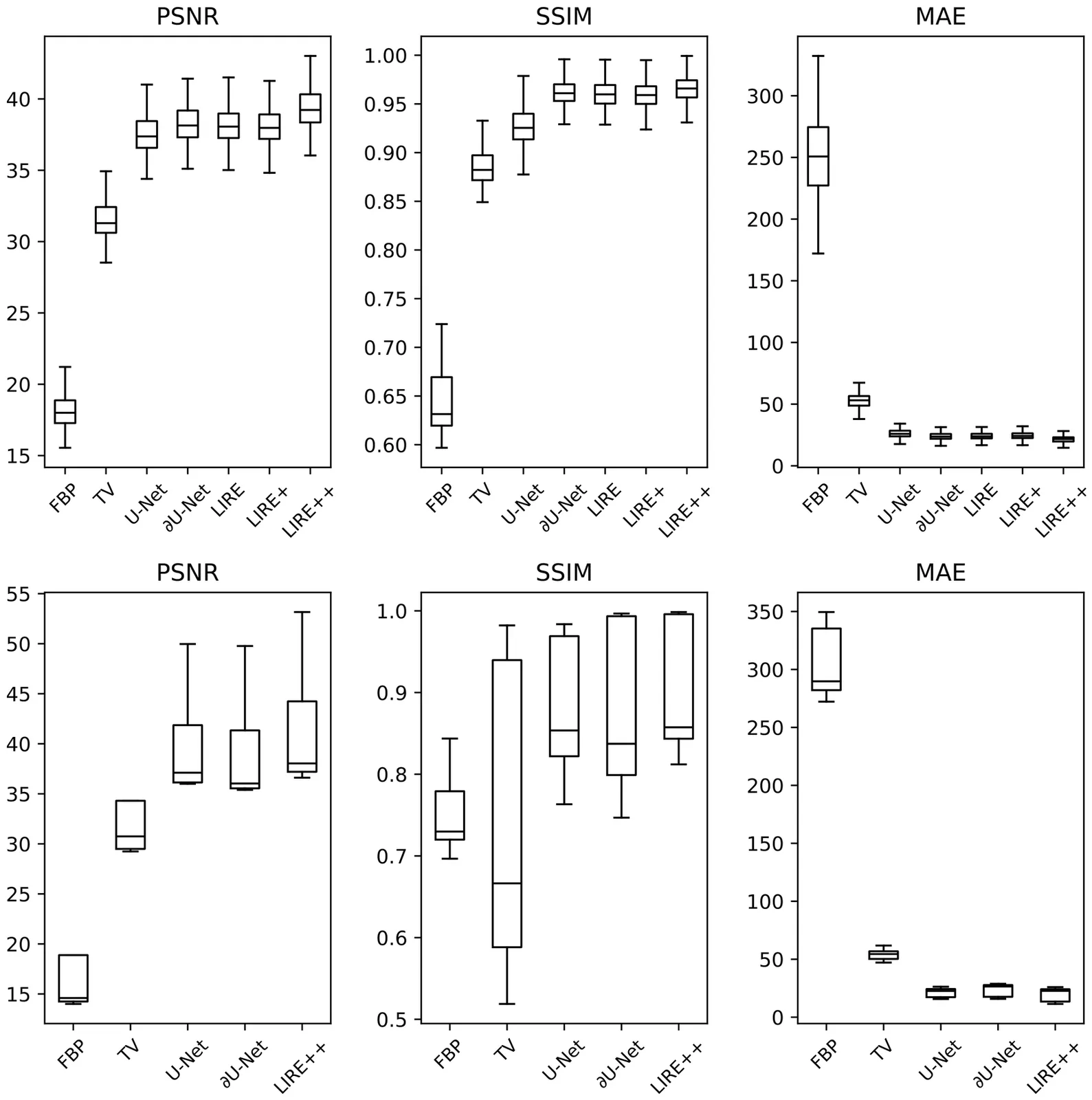
Cone Beam CT (CBCT) is an important imaging modality nowadays, however lower image quality of CBCT compared to more conventional Computed Tomography (CT) remains a limiting factor in CBCT applications. Deep learning reconstruction methods are a promising alternative to classical analytical and iterative reconstruction methods, but applying such methods to CBCT is often difficult due to the lack of ground truth data, memory limitations and the need for fast inference at clinically-relevant resolutions. In this work we propose LIRE++, an end-to-end rotationally-equivariant multiscale learned invertible primal-dual scheme for fast and memory-efficient CBCT reconstruction. Memory optimizations and multiscale reconstruction allow for fast training and inference, while rotational equivariance improves parameter efficiency. LIRE++ was trained on simulated projection data from a fast quasi-Monte Carlo CBCT projection simulator that we developed as well. Evaluated on synthetic data, LIRE++ gave an average improvement of 1 dB in Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio over alternative deep learning baselines. On real clinical data, LIRE++ improved the average Mean Absolute Error between the reconstruction and the corresponding planning CT by 10 Hounsfield Units with respect to current proprietary state-of-the-art hybrid deep-learning/iterative method.
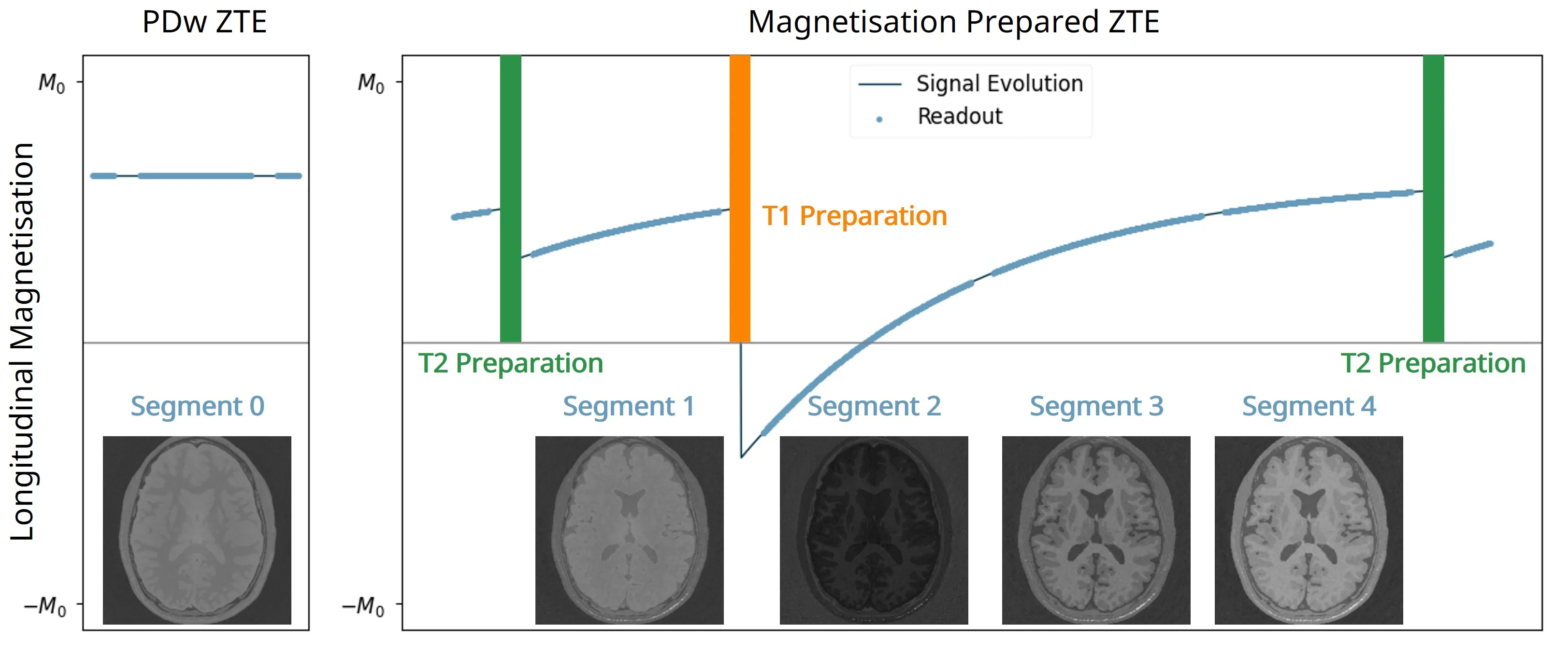
The 3D fast silent multi-parametric mapping sequence with zero echo time (MuPa-ZTE) is a novel quantitative MRI (qMRI) acquisition that enables nearly silent scanning by using a 3D phyllotaxis sampling scheme. MuPa-ZTE improves patient comfort and motion robustness, and generates quantitative maps of T1, T2, and proton density using the acquired weighted image series. In this work, we propose a diffusion model-based qMRI mapping method that leverages both a deep generative model and physics-based data consistency to further improve the mapping performance. Furthermore, our method enables additional acquisition acceleration, allowing high-quality qMRI mapping from a fourfold-accelerated MuPa-ZTE scan (approximately 1 minute). Specifically, we trained a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) to map MuPa-ZTE image series to qMRI maps, and we incorporated the MuPa-ZTE forward signal model as an explicit data consistency (DC) constraint during inference. We compared our mapping method against a baseline dictionary matching approach and a purely data-driven diffusion model. The diffusion models were trained entirely on synthetic data generated from digital brain phantoms, eliminating the need for large real-scan datasets. We evaluated on synthetic data, a NISM/ISMRM phantom, healthy volunteers, and a patient with brain metastases. The results demonstrated that our method produces 3D qMRI maps with high accuracy, reduced noise and better preservation of structural details. Notably, it generalised well to real scans despite training on synthetic data alone. The combination of the MuPa-ZTE acquisition and our physics-informed diffusion model is termed q3-MuPa, a quick, quiet, and quantitative multi-parametric mapping framework, and our findings highlight its strong clinical potential.
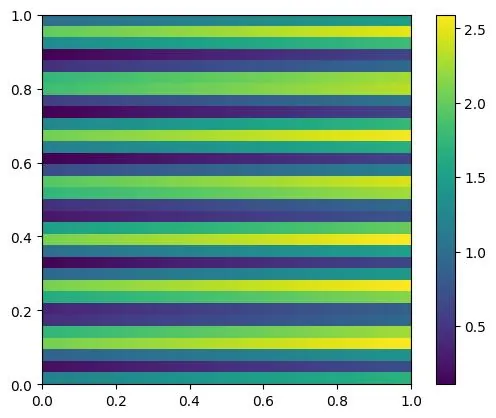
Subject-specific cardiovascular models rely on parameter estimation using measurements such as 4D Flow MRI data. However, acquiring high-resolution, high-fidelity functional flow data is costly and taxing for the patient. As a result, there is growing interest in using highly undersampled MRI data to reduce acquisition time and thus the cost, while maximizing the information gain from the data. Examples of such recent work include inverse problems to estimate boundary conditions of aortic blood flow from highly undersampled k-space data. The undersampled data is selected based on a predefined sampling mask which can significantly influences the performance and the quality of the solution of the inverse problem. While there are many established sampling patterns to collect undersampled data, it remains unclear how to select the best sampling pattern for a given set of inference parameters. In this paper we propose an Optimal Experimental Design (OED) framework for MRI measurements in k-space, aiming to find optimal masks for estimating specific parameters directly from k-space. As OED is typically applied to sensor placement problems in spatial locations, this is, to our knowledge, the first time the technique is used in this context. We demonstrate that the masks optimized by employing OED consistently outperform conventional sampling patterns in terms of parameter estimation accuracy and variance, facilitating a speed-up of 10x of the acquisition time while maintaining accuracy.
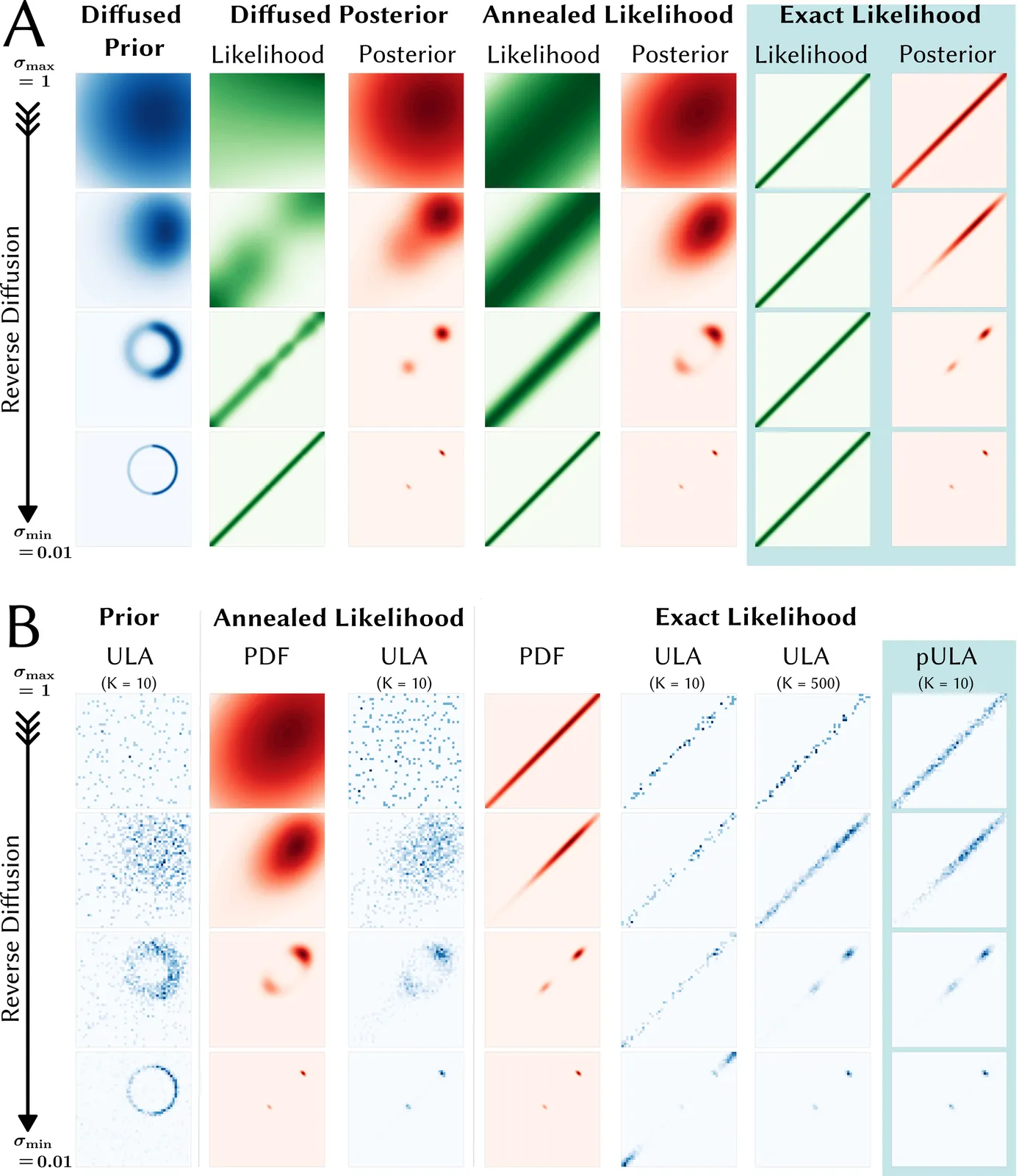
Purpose: The Unadjusted Langevin Algorithm (ULA) in combination with diffusion models can generate high quality MRI reconstructions with uncertainty estimation from highly undersampled k-space data. However, sampling methods such as diffusion posterior sampling or likelihood annealing suffer from long reconstruction times and the need for parameter tuning. The purpose of this work is to develop a robust sampling algorithm with fast convergence. Theory and Methods: In the reverse diffusion process used for sampling the posterior, the exact likelihood is multiplied with the diffused prior at all noise scales. To overcome the issue of slow convergence, preconditioning is used. The method is trained on fastMRI data and tested on retrospectively undersampled brain data of a healthy volunteer. Results: For posterior sampling in Cartesian and non-Cartesian accelerated MRI the new approach outperforms annealed sampling in terms of reconstruction speed and sample quality. Conclusion: The proposed exact likelihood with preconditioning enables rapid and reliable posterior sampling across various MRI reconstruction tasks without the need for parameter tuning.
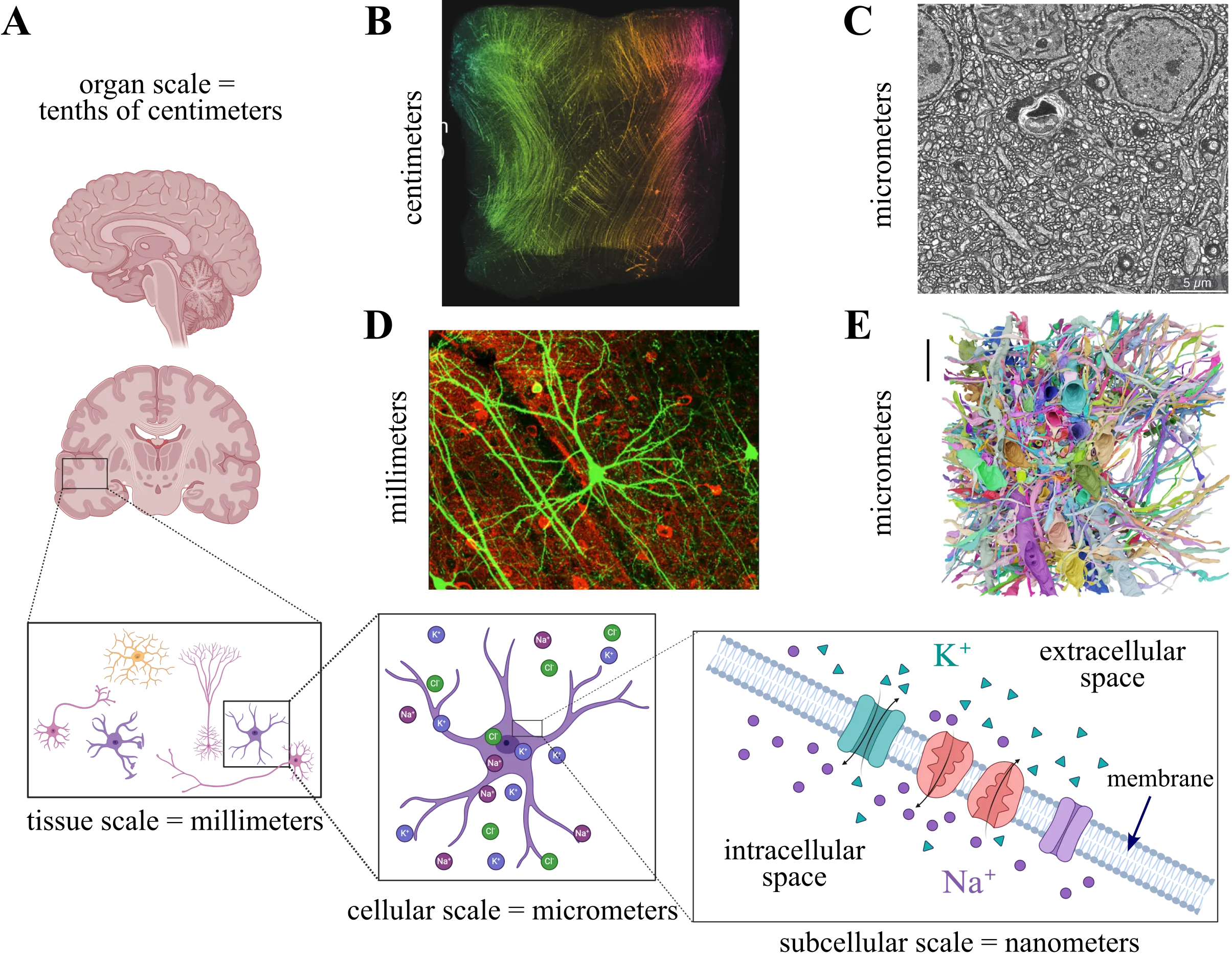
Excitable tissue is fundamental to brain function, yet its study is complicated by extreme morphological complexity and the physiological processes governing its dynamics. Consequently, detailed computational modeling of this tissue represents a formidable task, requiring both efficient numerical methods and robust implementations. Meanwhile, efficient and robust methods for image segmentation and meshing are needed to provide realistic geometries for which numerical solutions are tractable. Here, we present a computational framework that models electrodiffusion in excitable cerebral tissue, together with realistic geometries generated from electron microscopy data. To demonstrate a possible application of the framework, we simulate electrodiffusive dynamics in cerebral tissue during neuronal activity. Our results and findings highlight the numerical and computational challenges associated with modeling and simulation of electrodiffusion and other multiphysics in dense reconstructions of cerebral tissue.
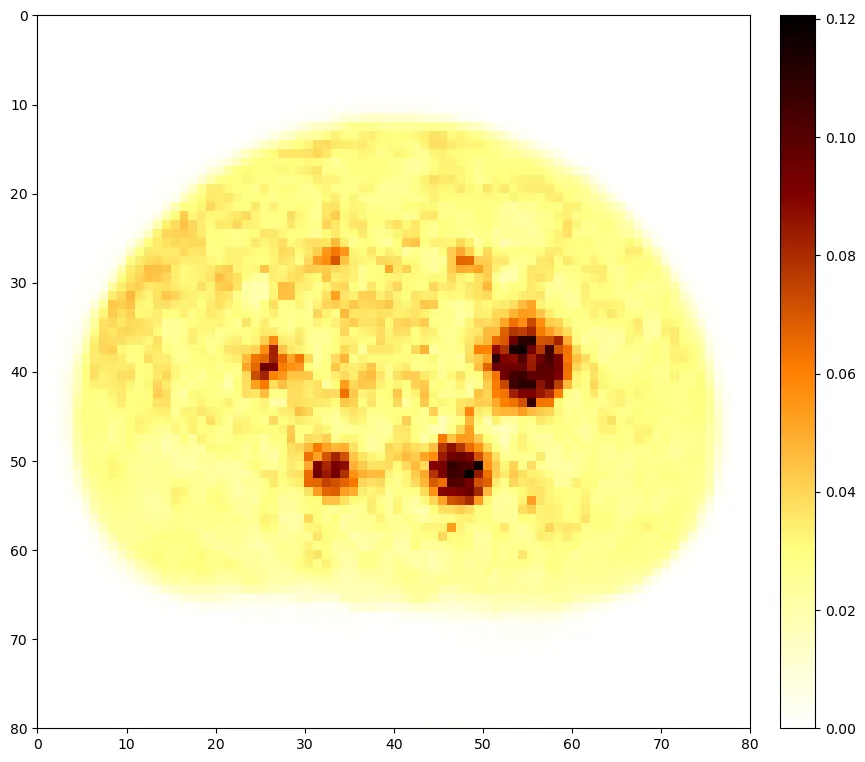
Introduction: We describe the foundation of PETRIC, an image reconstruction challenge to minimise the computational runtime of related algorithms for Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Purpose: Although several similar challenges are well-established in the field of medical imaging, there have been no prior challenges for PET image reconstruction. Methods: Participants are provided with open-source software for implementation of their reconstruction algorithm(s). We define the objective function and reconstruct "gold standard" reference images, and provide metrics for quantifying algorithmic performance. We also received and curated phantom datasets (acquired with different scanners, radionuclides, and phantom types), which we further split into training and evaluation datasets. The automated computational framework of the challenge is released as open-source software. Results: Four teams with nine algorithms in total participated in the challenge. Their contributions made use of various tools from optimisation theory including preconditioning, stochastic gradients, and artificial intelligence. While most of the submitted approaches appear very similar in nature, their specific implementation lead to a range of algorithmic performance. Conclusion: As the first challenge for PET image reconstruction, PETRIC's solid foundations allow researchers to reuse its framework for evaluating new and existing image reconstruction methods on new or existing datasets. Variant versions of the challenge have and will continue to be launched in the future.
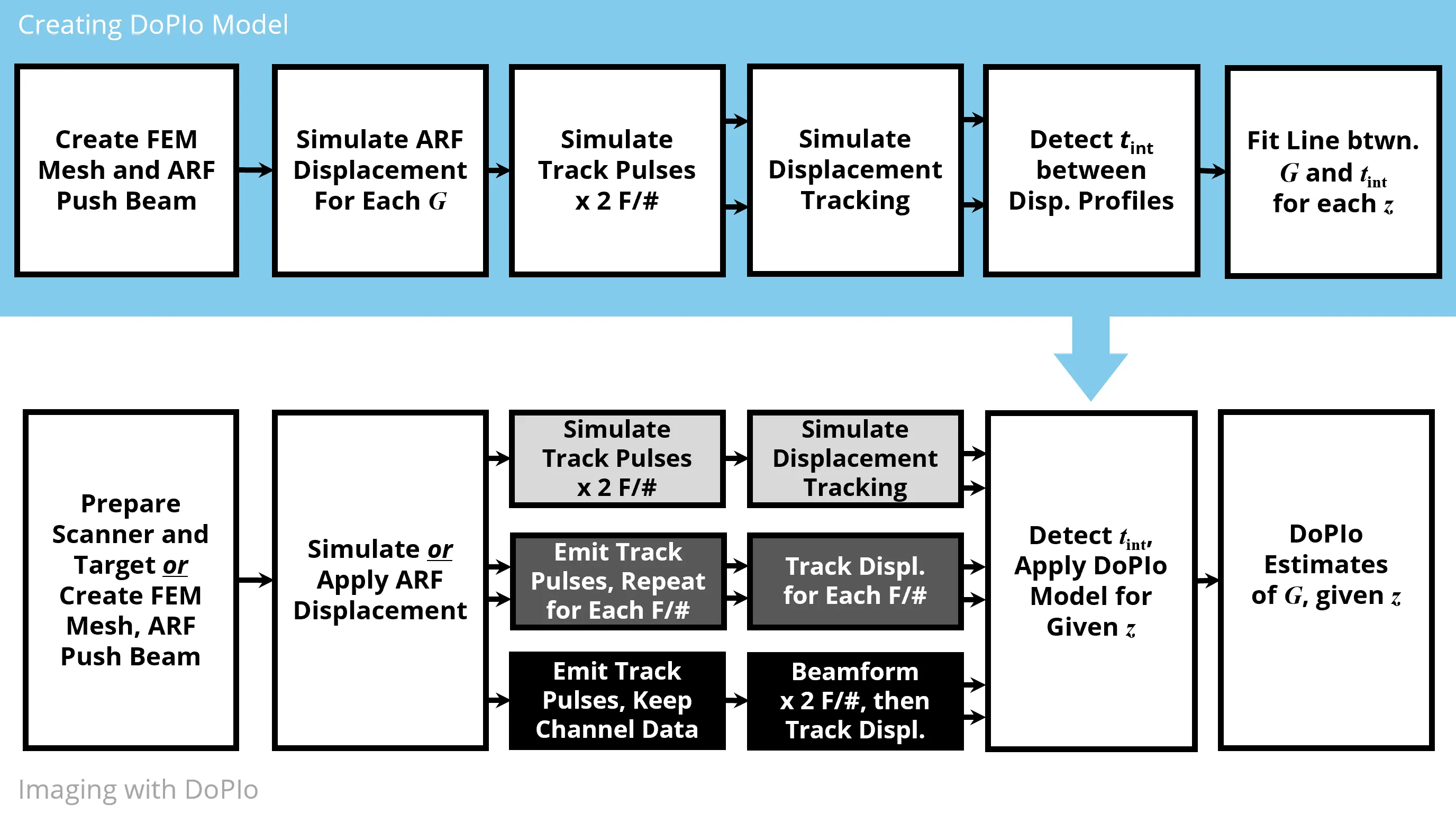
Current acoustic radiation force (ARF) based methods for quantifying tissue elasticity primarily rely on shear wave propagation. However, their spatial resolution is limited by the need for spatial averaging, and their accuracy is affected by shear wave guidance, out of plane reflections, and geometric dispersion, which reduce their applicability in mechanically complex tissues. This study introduces a novel technique called Double Profile Intersection (DoPIo) ultrasound, which enables pointwise estimation of shear elastic modulus within the region of ARF excitation by leveraging the scatterer shearing rate. This rate is inferred by tracking ARF induced displacement using two tracking beams with different lateral widths. The wider beam captures scatterers located outside the ARF excitation region that begin to displace as shearing propagates. The time at which the two resulting displacement profiles intersect is mapped to shear elastic modulus using an empirically derived model based on finite element simulations. In silico, DoPIo estimated shear elastic modulus with a median error of -0.02 kPa and a median absolute deviation of 1.98 kPa in elastic materials up to 35 kPa. Experimental validation in vitro and ex vivo demonstrated that DoPIo reliably distinguished softer regions from stiffer ones, and its modulus estimates remained consistent across varying ARF push amplitudes, provided sufficient displacement estimation signal to noise ratio. DoPIo offers a feasible approach for high resolution, on axis shear elasticity estimation and holds promise as a quantitative biomarker that is independent of ARF amplitude.
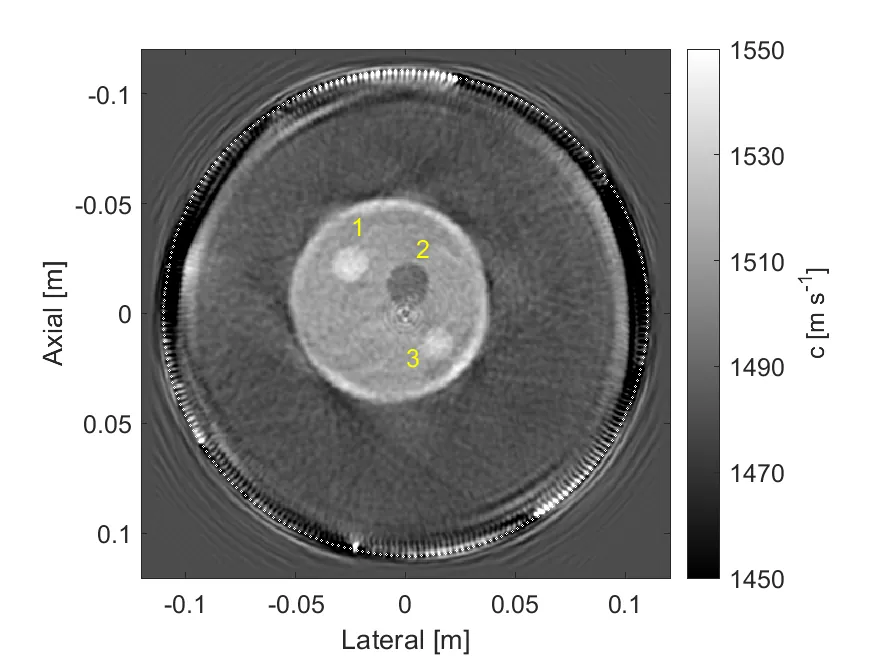
This study presents the first experimental validation of a Hessian-free ray-Born inversion technique for quantitative reconstruction of sound speed from transmission ultrasound data. The method combines single-scattering theory with high-frequency approximations, yielding an inversion framework well suited to the frequency ranges used in clinical ultrasound applications. Unlike previous singly-scattered inversion approaches that account for medium heterogeneities only in the scattering potential, the proposed ray-Born method employs Green's functions approximated along ray trajectories determined by high-frequency assumptions. The associated objective function is linearized and minimized sequentially across increasing frequency bands. At each frequency set, the linearized subproblem is solved using a weighting scheme applied to both the solution and data spaces, which diagonalizes the Hessian and enables its inversion in a single step. The method, previously reported and released as an open-source package, was applied to in-vitro and in-vivo datasets provided by the University of Rochester Medical Center. The reconstructed images were evaluated by comparison with those obtained using a full-wave inversion approach based on a frequency-domain Helmholtz solver. The results demonstrate the strong potential of the Hessian-free ray-Born inversion as a computationally efficient and accurate method suitable for clinical translation.
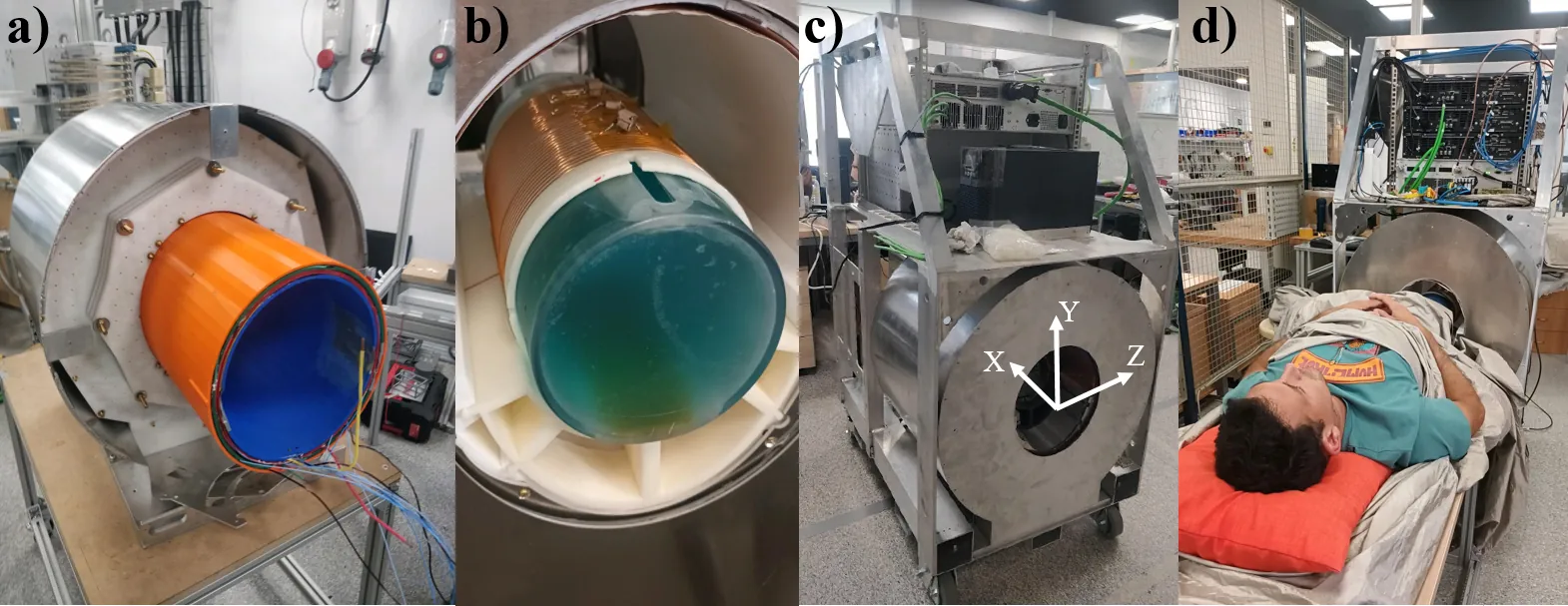
Purpose: To demonstrate the feasibility of performing in vivo imaging and quantitative relaxation mapping of soft and hard tissues using a low-cost, portable MRI scanner, and to establish the methodological foundations for zero echo time (ZTE) imaging in systems affected by strong field inhomogeneities. Methods: A complete framework for artifact-free ZTE imaging at low field was developed, including: (i) RF pulse pre/counteremphasis calibration to minimize ring-down and electronics switching time; (ii) an extension of a recent single-point double-shot (SPDS) protocol for simultaneous B0 and B1 mapping; and (iii) a model-based reconstruction incorporating these field maps into the encoding matrix. ZTE imaging and variable flip angle (VFA) T1 mapping were performed on phantoms and in vivo human knees and ankles, and benchmarked against standard RARE and STIR acquisitions. Results: The optimized PETRA sequence produced 3D images of knees and ankles within clinically compatible times (< 15 min), revealing hard tissues such as ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and bone that are invisible in spin-echo sequences. The extended SPDS method enabled accurate field mapping, while the VFA approach provided the first in vivo T1 measurements of hard tissues at B0 < 0.1 T. Conclusions: The proposed framework broadens the range of pulse sequences feasible in portable low-field MRI and demonstrates the potential of ZTE for quantitative and structural imaging of musculoskeletal tissues in affordable Halbach-based systems.
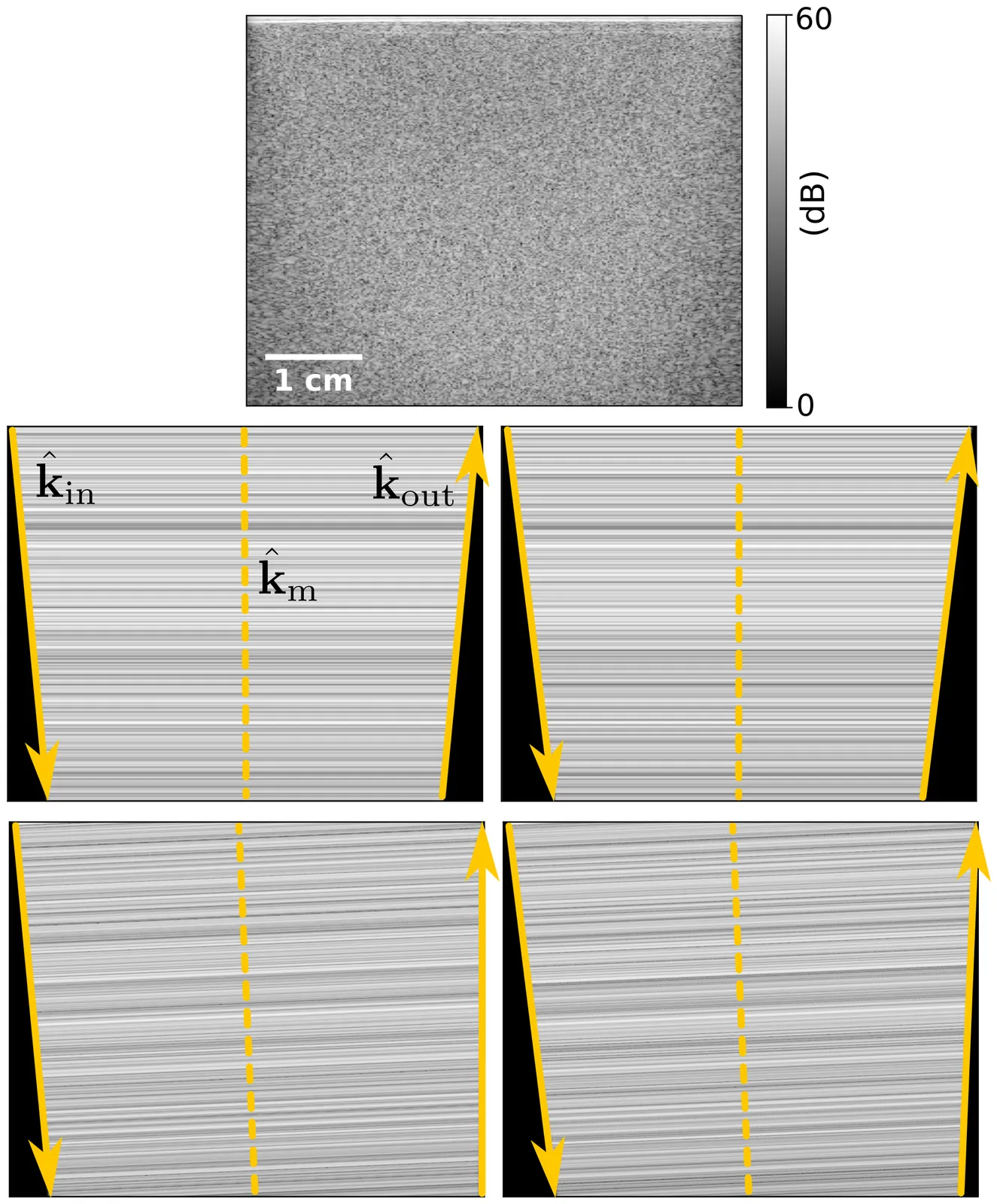
Phase aberrations, despite degrading ultrasound images, also encode valuable information about the spatial distribution of the speed of sound in tissue. In pulse-echo ultrasound, we can quantify them by exploiting speckle correlations. Among existing strategies, correlations between steered acquisitions that share a common mid-angle have proven particularly effective for inferring the speed of sound. Their phases can be linearly related to the phase aberrations undergone by both the incident and reflected wavefronts. This relationship has so far been demonstrated only through geometric arguments based on point reflectors. Here, we develop a rigorous theoretical formalism that extends this relationship to the speckle regime, completing the previously established linear model and clarifying its underlying assumptions. More importantly, we build on this formalism to analyze correlation-phase fluctuations arising from aberration-induced speckle decorrelation. The analysis reveals that phase variance is governed by the relative loss of coherence, which increases approximately linearly with the square of the correlation phases. Local correlation-phase estimates therefore become increasingly uncertain as their magnitude grows. Experimental measurements in a uniform tissue-mimicking phantom show excellent agreement with the predicted variance. Beyond providing a theoretical basis for advancing speed-of-sound imaging, this formalism establishes the accuracy limit of common-mid-angle correlation phases, offering a benchmark for evaluating more advanced aberration-estimation techniques.
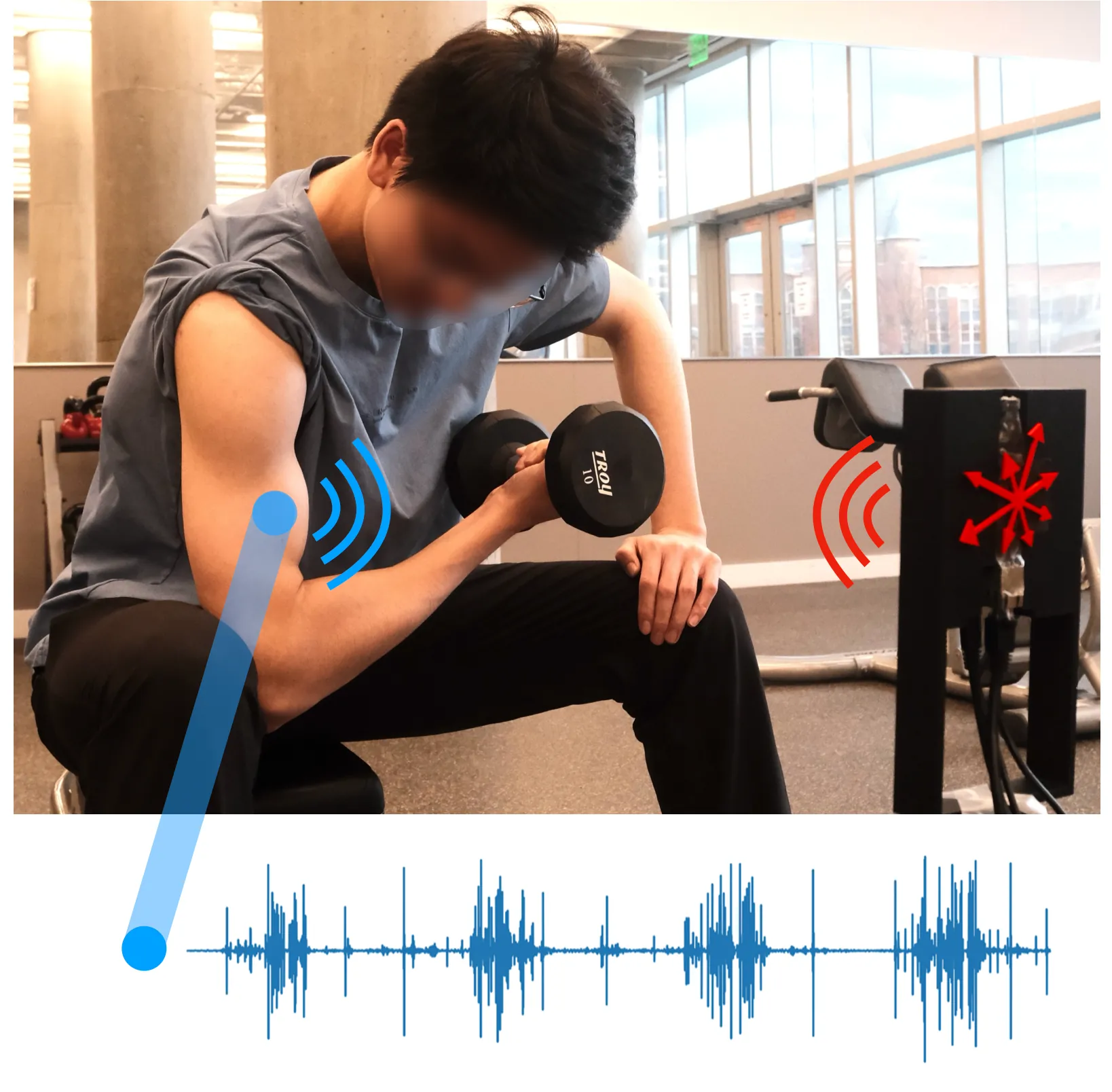

In this paper, our goal is to enable quantitative feedback on muscle fatigue during exercise to optimize exercise effectiveness while minimizing injury risk. We seek to capture fatigue by monitoring surface vibrations that muscle exertion induces. Muscle vibrations are unique as they arise from the asynchronous firing of motor units, producing surface micro-displacements that are broadband, nonlinear, and seemingly stochastic. Accurately sensing these noise-like signals requires new algorithmic strategies that can uncover their underlying structure. We present GigaFlex the first contactless system that measures muscle vibrations using mmWave radar to infer muscle force and detect fatigue. GigaFlex draws on algorithmic foundations from Chaos theory to model the deterministic patterns of muscle vibrations and extend them to the radar domain. Specifically, we design a radar processing architecture that systematically infuses principles from Chaos theory and nonlinear dynamics throughout the sensing pipeline, spanning localization, segmentation, and learning, to estimate muscle forces during static and dynamic weight-bearing exercises. Across a 23-participant study, GigaFlex estimates maximum voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) root mean square error (RMSE) of 5.9\%, and detects one to three Repetitions in Reserve (RIR), a key quantitative muscle fatigue metric, with an AUC of 0.83 to 0.86, performing comparably to a contact-based IMU baseline. Our system can enable timely feedback that can help prevent fatigue-induced injury, and opens new opportunities for physiological sensing of complex, non-periodic biosignals.
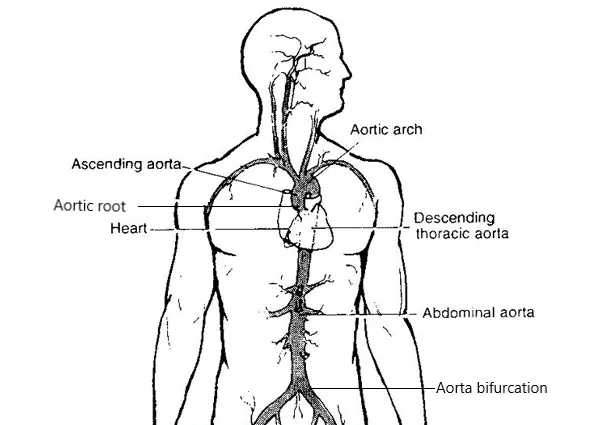
Segmentation of the aorta is crucial for various medical analyses, such as the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. This work presents mathematical models and methods yielding a semi-automatic segmentation of the aorta from non-enhanced CT data. Our framework consists of three steps. First, using the minimal path approach, we extract a path within the aorta from two user-supplied points. Then, using 3D Lagrangian curve evolution, we move the initial path to the approximate centerline of the aorta. The centered path is used in the last step to construct the initial condition for the generalized subjective surface method (GSUBSURF). Applying the GSUBSURF method with this initial condition yields an accurate segmentation of the aorta. The segmentation results and the manual segmentations overlap, with a worst-case mean Hausdorff distance of $2.175 \pm 0.605$ mm for a voxel spacing of $0.977$ mm. Using the aorta centerline and segmentation, we define precise regions of interest along the aorta to assess large-vessel vasculitis from patient FDG-PET/CT image data. The application shows promising results, as we demonstrated widespread inflammation throughout the aorta in a patient before treatment. After treatment, we observed a significant reduction in inflammation while accurately identifying the aorta regions where inflammation persisted. These findings also align with those of experienced medical doctors who have worked on the same cases.
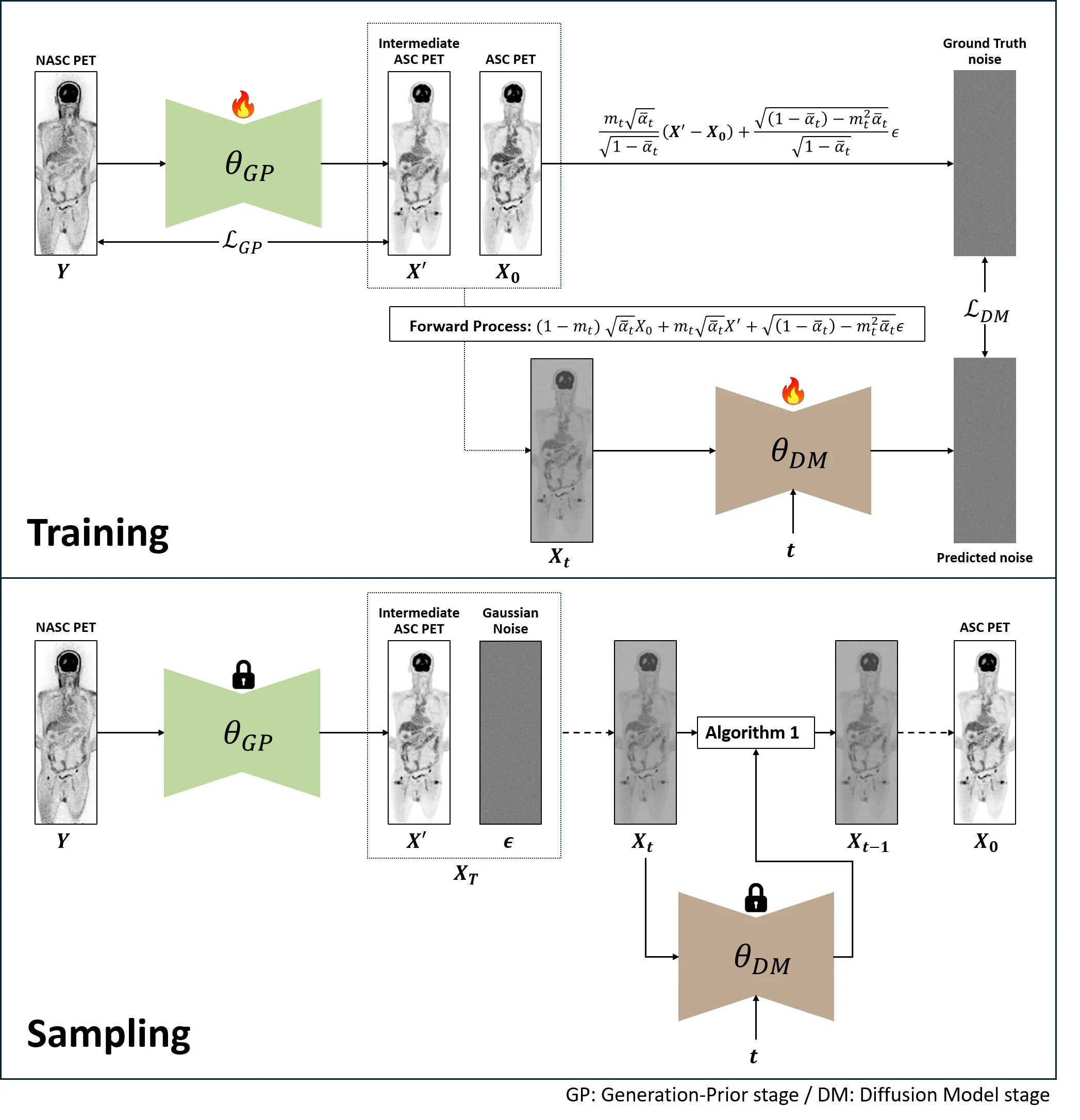
Accurate attenuation and scatter corrections are crucial in positron emission tomography (PET) imaging for accurate visual interpretation and quantitative analysis. Traditional methods relying on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have limitations in accuracy, radiation exposure, and applicability. Deep neural networks provide potential approaches to estimating attenuation and scatter-corrected (ASC) PET from non-attenuation and non-scatter-corrected (NASC) PET images based on VAE or CycleGAN. However, the limitations inherent to conventional GAN-based methods, such as unstable training and mode collapse, need further advancements. To address these limitations and achieve more accurate attenuation and scatter corrections, we propose a novel framework for generating high-quality ASC PET images from NASC PET images: Generation-Prior Diffusion Model (GPDM). Our GPDM framework is based on the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM), but instead of starting sampling from an entirely different image distribution, it begins from a distribution similar to the target images we aim to generate. This similar distribution is referred to as the Generation-Prior. By leveraging this Generation-Prior, the GPDM framework effectively reduces the number of sampling steps and generates more refined ASC PET images. Our experimental results demonstrate that GPDM outperforms existing methods in generating ASC PET images, achieving superior accuracy while significantly reducing sampling time. These findings highlight the potential of GPDM to address the limitations of conventional methods and establish a new standard for efficient and accurate attenuation and scatter correction in PET imaging.
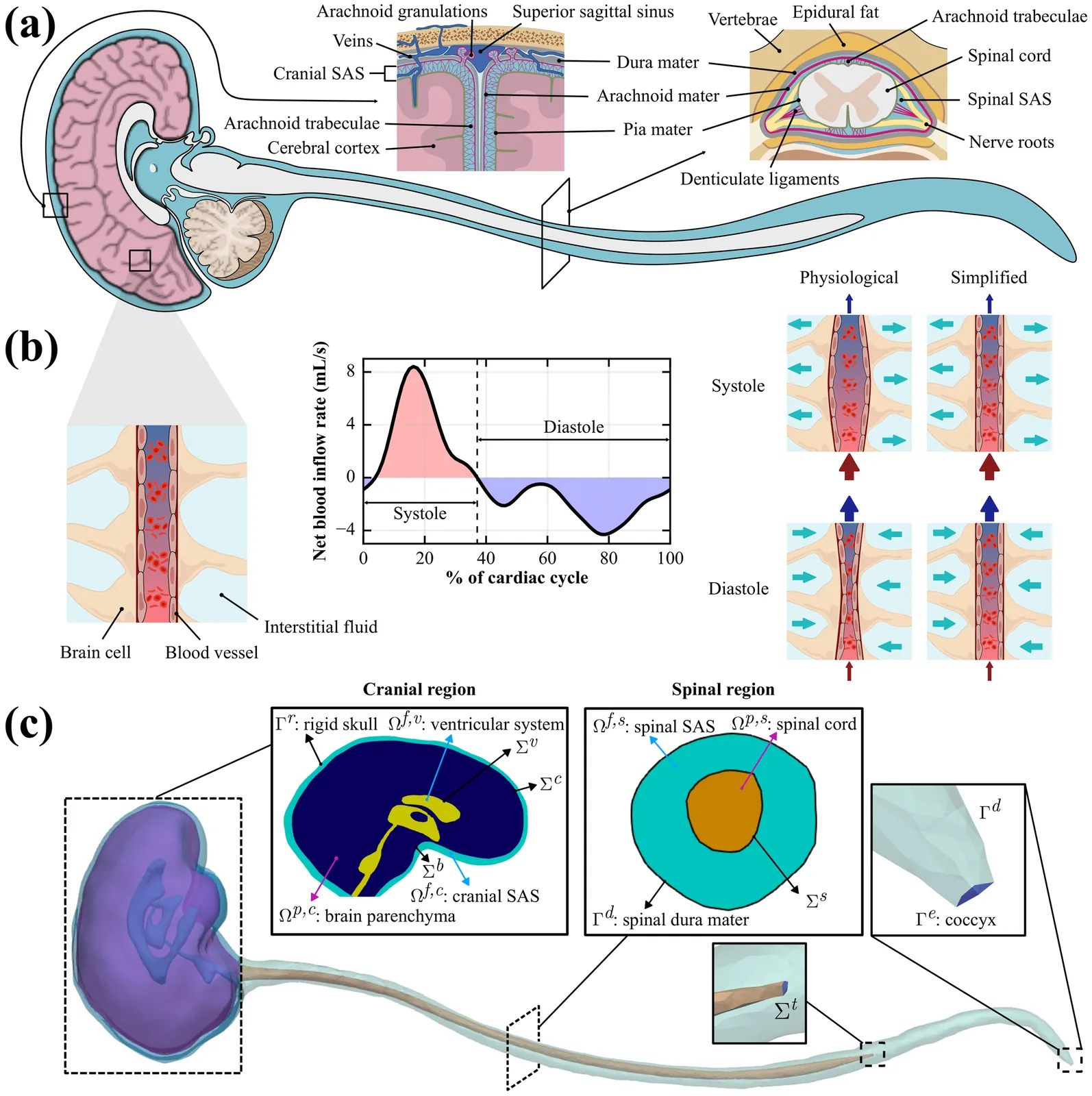
Intrathecal (IT) injection is an effective way to deliver drugs to the brain bypassing the blood-brain barrier. To evaluate and optimize IT drug delivery, it is necessary to understand the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) dynamics in the central nervous system (CNS). In combination with experimental measurements, computational modeling plays an important role in reconstructing CSF flow in the CNS. Existing models have provided valuable insights into the CSF dynamics; however, most neglect the effects of tissue mechanics, focus on partial geometries, or rely on measured CSF flow rates under specific conditions, leaving full-CNS CSF flow field predictions across different physiological states underexplored. Here, we propose a comprehensive multiphysics computational model of the CNS with three key features: (1) it is implemented on a fully closed geometry of CNS; (2) it includes the interaction between CSF and poroelastic tissue as well as the compliant spinal dura mater; (3) it has potential for predictive simulations because it only needs data on cardiac blood pulsation into the brain. Our simulations under physiological conditions demonstrate that our model accurately reconstructs the CSF pulsation and captures both the craniocaudal attenuation and phase shift of CSF flow along the spinal subarachnoid space (SAS). When applied to the simulation of IT drug delivery, our model successfully captures the intracranial pressure (ICP) elevation during injection and subsequent recovery after injections. The proposed multiphysics model provides a unified and extensible framework that allows parametric studies of CSF flow dynamics and optimization of IT injections, serving as a strong foundation for integration of additional physiological mechanisms.
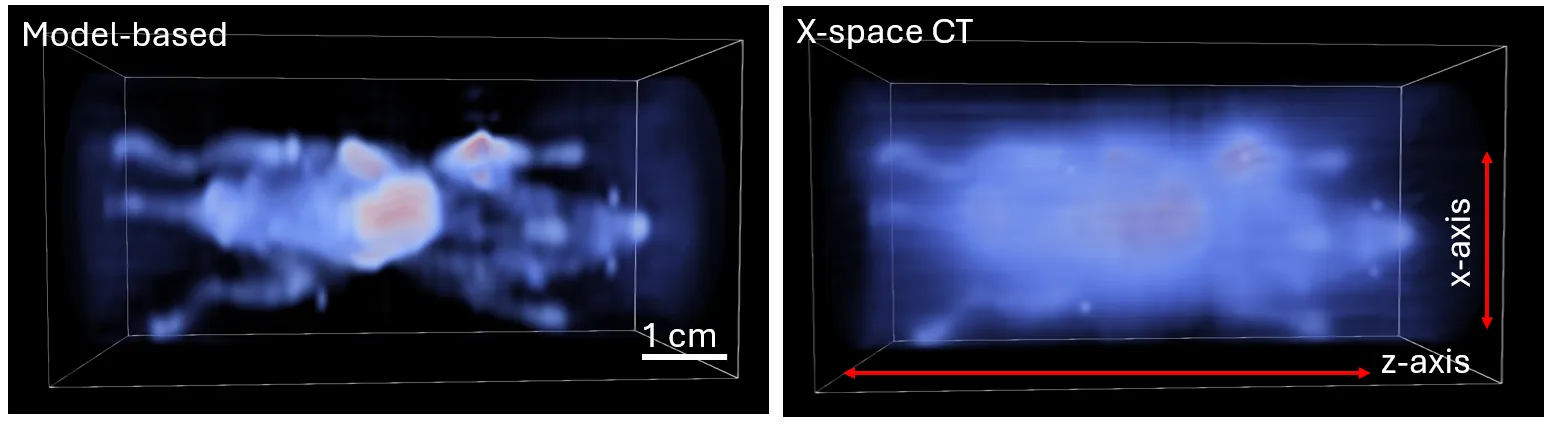
Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) is a tracer-based imaging modality that detects superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in vivo, with applications in cancer cell tracking, lymph node mapping, and cell therapy monitoring. We introduce a new 3D image reconstruction framework for MPI data acquired using multi-angle field-free line (FFL) scans, demonstrating improvements in spatial resolution, quantitative accuracy, and high dynamic range performance over conventional sequential reconstruction pipelines. The framework is built by combining a physics-based FFL signal model with tomographic projection operators to form an efficient 3D forward operator, enabling the full dataset to be reconstructed jointly rather than as a series of independent 2D projections. A harmonic-domain compression step is incorporated naturally within this operator formulation, reducing memory overhead by over two orders of magnitude while preserving the structure and fidelity of the model, enabling volumetric reconstructions on standard desktop GPU hardware in only minutes. Phantom and in vivo results demonstrate substantially reduced background haze and improved visualization of low-intensity regions adjacent to bright structures, with an estimated $\sim$11$\times$ improvement in iron detection sensitivity relative to the conventional X-space CT approach. These advances enhance MPI image quality and quantitative reliability, supporting broader use of MPI in preclinical and future clinical imaging.
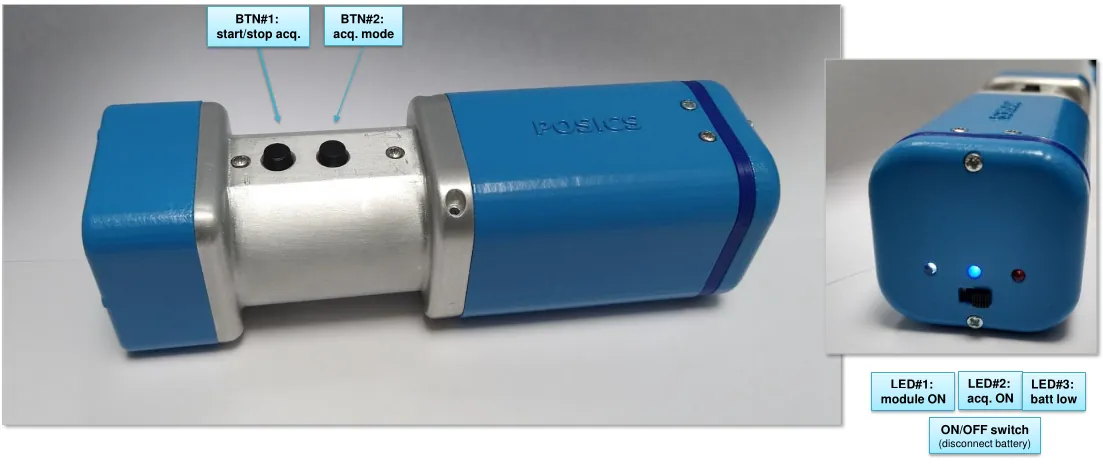
The POSiCS camera is a handheld, small field-of-view gamma camera developed for multipurpose use in radio-guided surgery (RGS), with sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) as its benchmark application. This compact and lightweight detector (weighing approximately 350 g) can map tissues labeled with Tc-99m nanocolloids and guide surgeons to the location of target lesions. By enabling intraoperative visualization in close proximity to the surgical field, its primary objective is to minimize surgical interventional invasiveness and operative time, thereby enhancing localization accuracy and reducing the incidence of post-operative complications. The design and components of the POSiCS camera emphasize ergonomic handling and compactness, providing, at the same time, rapid image formation and a spatial resolution of a few millimeters. These features are compatible with routine operating-room workflow, including wireless communication with the computer and a real-time display to support surgeon decision-making. The spatial resolution measured at a source-detector distance of 0 cm was 1.9 +/- 0.1 mm for the high-sensitivity mode and 1.4 +/- 0.1 mm for the high-resolution mode. The system sensitivity at 2 cm was evaluated as 481 +/- 14 cps/MBq (high sensitivity) and 134 +/- 8 cps/MBq (high resolution). For both working modes, we report an energy resolution of approximately 20 percent, even though the high-resolution collimator exhibits an increased scattered component due to the larger amount of tungsten.
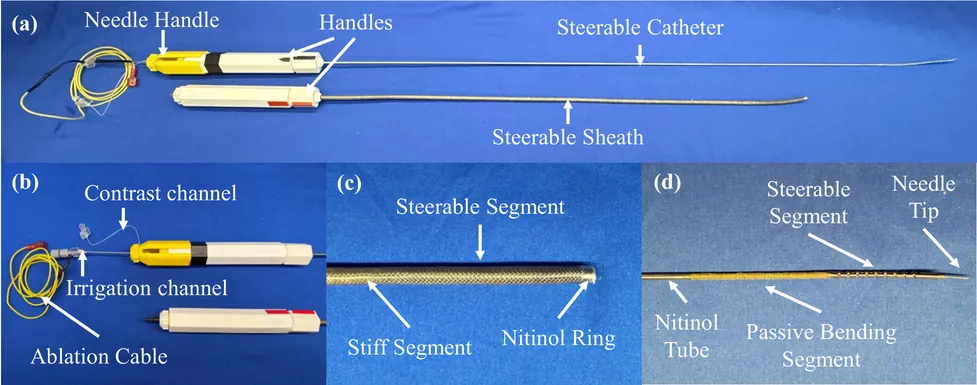
Radiofrequency ablation is widely used to prevent ventricular tachycardia (VT) by creating lesions to inhibit arrhythmias; however, the current surface ablation catheters are limited in creating lesions that are deeper within the left ventricle (LV) wall. Intramyocardial needle ablation (INA) addresses this limitation by penetrating the myocardium and delivering energy from within. Yet, existing INA catheters lack adequate dexterity to navigate the highly asymmetric, trabeculated LV chamber and steer around papillary structures, limiting precise targeting. This work presents a novel dexterous INA (d-INA) toolset designed to enable effective manipulation and creation of deep ablation lesions. The system consists of an outer sheath and an inner catheter, both bidirectionally steerable, along with an integrated ablation needle assembly. Benchtop tests demonstrated that the sheath and catheter reached maximum bending curvatures of 0.088~mm$^{-1}$ and 0.114~mm$^{-1}$, respectively, and achieved stable C-, S-, and non-planar S-shaped configurations. Ex-vivo studies validated the system's stiffness modulation and lesion-creation capabilities. In-vivo experiments in two swine demonstrated the device's ability to reach previously challenging regions such as the LV summit, and achieved a 219\% increase in ablation depth compared with a standard ablation catheter. These results establish the proposed d-INA as a promising platform for achieving deep ablation with enhanced dexterity, advancing VT treatment.
Objective: To validate a newly proposed stochastic differential equation (SDE)-based model for proton beam energy deposition by comparing its predictions with those from Geant4 in simplified phantom scenarios. Approach: Building on previous work in Crossley et al. (2025), where energy deposition from a proton beam was modelled using an SDE framework, we implemented the model with standard approximations to interaction cross sections and mean excitation energies, which makes simulations easily adaptable to new materials and configurations. The model was benchmarked against Geant4 in homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms. Main results: The SDE-based dose distributions agreed well with Geant4, showing range differences within 0.4 mm and 3D gamma pass rates exceeding 98% under 3%/2 mm criteria with a 1% dose threshold. The model achieved a computational speed-up of approximately fivefold relative to Geant4, consistent across different Geant4 physics lists. Significance: These results demonstrate that the SDE approach can reproduce accuracy comparable to high-fidelity Monte Carlo for proton therapy at a fraction of the computational cost, highlighting its potential for accelerating dose calculations and treatment planning.