General Relativity and Quantum Cosmology
General relativity, quantum gravity, cosmological models, gravitational waves, black holes, classical and quantum gravity.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
General relativity, quantum gravity, cosmological models, gravitational waves, black holes, classical and quantum gravity.
Looking for a broader view? This category is part of:
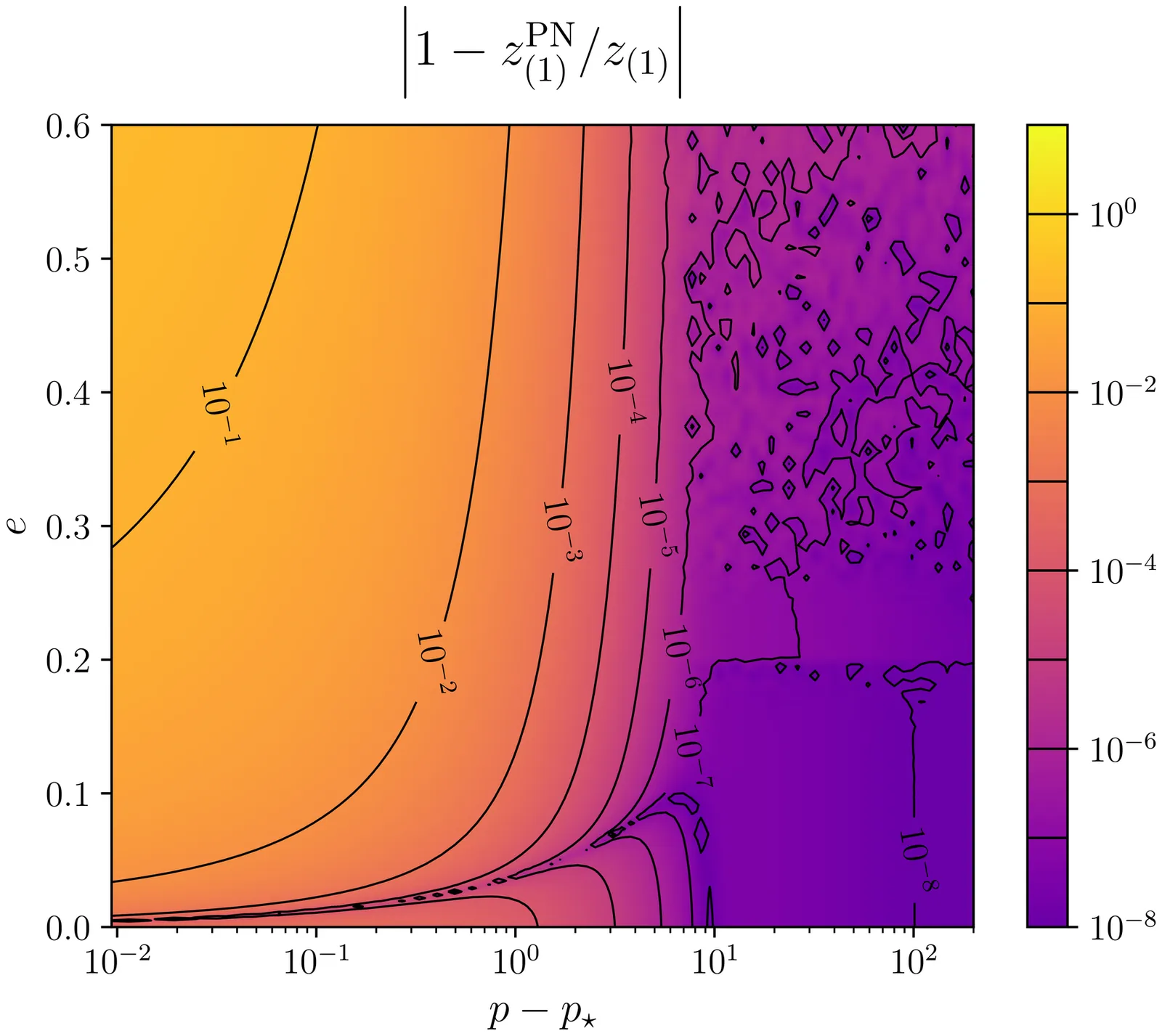
Synergies between self-force theory and other approaches to the gravitational two-body problem have traditionally relied on calculations of gauge-invariant observables as functions of orbital frequencies. However, in self-force theory one can also define a complete set of constants of motion: energy, azimuthal angular momentum, and radial and polar actions. Here we outline how directly utilizing these constants allows for more straightforward comparisons and hybridizations across the parameter space, as well as more streamlined waveform generation through flux-balance laws. Restricting to the case of nonspinning binaries and first order in self-force, we compute the constants of motion and the corrections to fundamental frequencies numerically as well as analytically (to 9PN in a post-Newtonian expansion), establishing consistency with the highest-order (4PN) results available from post-Newtonian theory. We also apply the results to identify the perturbed locations of special curves in the parameter space: circular orbits and the separatrix between bound and plunging orbits.
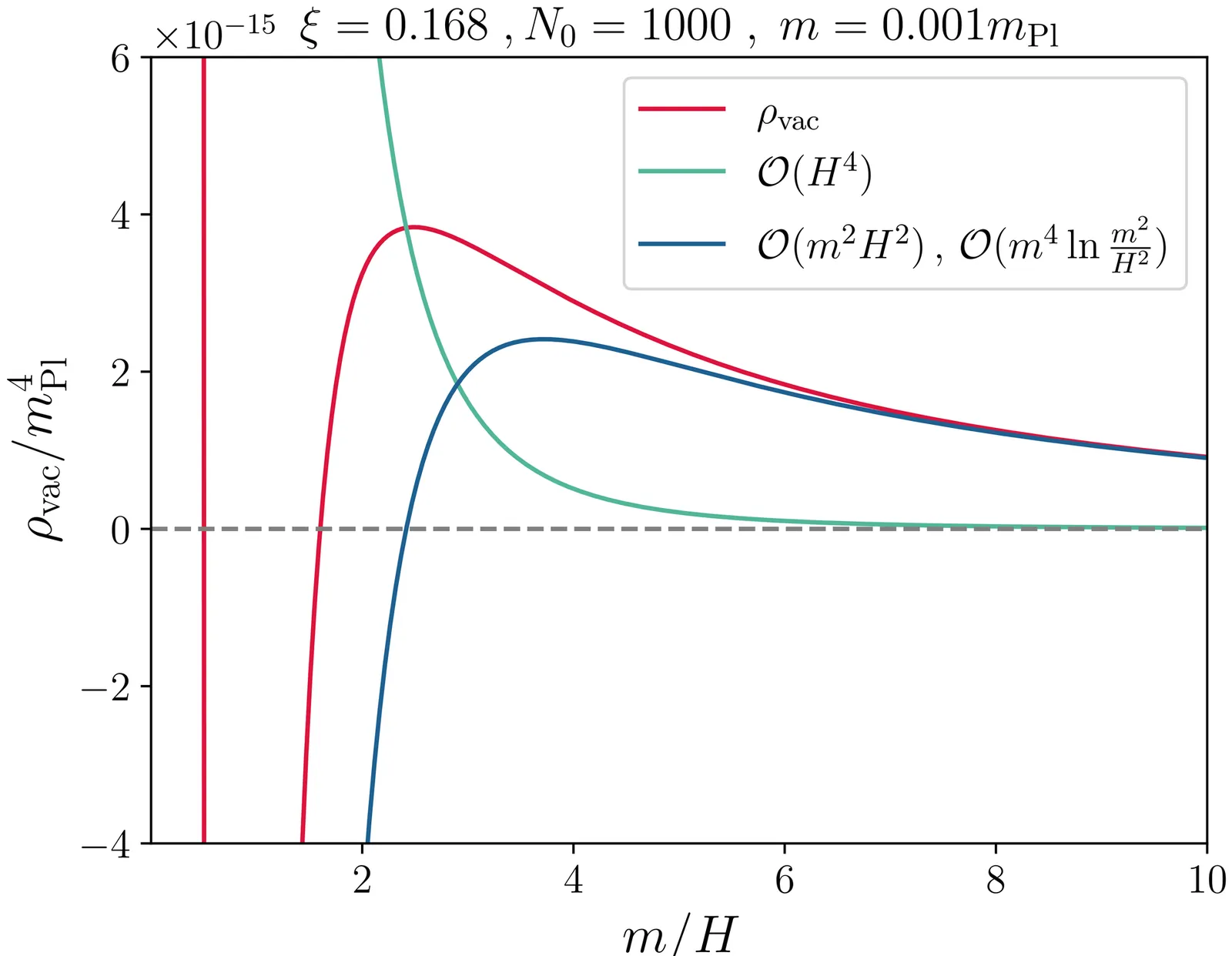
Inflation is a necessary cosmic mechanism to cure basic inconsistencies of the standard model of cosmology. These problems are usually `fixed' by postulating the existence of a scalar field (called the ``inflaton''). However, other less ad hoc options are possible. In the running vacuum model (RVM) framework, the vacuum energy density (VED) is a function of the Hubble rate $H$ and its time derivatives: $ρ_{\rm vac}=ρ_{\rm vac}(H, \dot{H},\ddot{H},\dots)$. In this context, the VED is dynamical (there is no rigid cosmological constant $Λ$). In the FLRW epoch, $ρ_{\rm vac}$ evolves very slowly with expansion, as befits the observed $Λ\simeq$const. behavior. In contrast, in the very early universe the vacuum fluctuations induce higher powers $H^N$ capable of unleashing fast inflation in a short period in which $H\simeq$ const. We call this mechanism `RVM-inflation'. It does not require an inflaton field since inflation is brought about by pure quantum field theory (QFT) effects on the dynamical background. It is different from Starobinsky's inflation, in which $H$ is never constant. In this work, we study a closely related scenario: the decay of the exact de Sitter vacuum into FLRW spacetime in its radiation epoch and the subsequent impact on the current universe, and compare with the RVM. We find that in both cases inflation is driven by $H^4$ powers together with subleading contributions of order $H^2$ that ease a graceful-exit transition into the radiation-dominated epoch, where the FLRW regime starts and ultimately develops a mildly evolving VED in the late universe: $δρ_{\rm vac}\sim {\cal O}(m_{\rm Pl} ^2 H^2)$. The outcome is an unified QFT approach to inflation and dark energy (conceived as dynamical vacuum energy) with potentially measurable phenomenological consequences in the present universe which can help to cure the cosmological tensions.
 2601.05190
2601.05190In this manuscript we generalize Ref. [1] and derive a complete set of local consistency conditions for bulk fields in braneworld scenarios with an arbitrary number of dimensions. This provides the first fully local and dimension-independent generalization of all known criteria for bulk fields. Within this framework, we show that a free scalar field is consistent and localized, whereas minimally and non-minimally coupled Maxwell fields violate the conditions, leading to a no-go theorem valid in any dimension. For nonlinear electrodynamics, we find that only the model $L(F)=b\sqrt{F}$ admits a consistent and normalizable zero mode, and that among p-forms, consistency occurs solely for the free 0-form. We also demonstrate that Dirac fermions, with or without Yukawa terms, are inconsistent within this framework and therefore cannot propagate in the bulk. Our local approach makes explicit that these conclusions do not depend on any particular internal geometry or warp factor: previously known results arise merely as special cases of a broader and strictly local structure, highlighting the universality of the constraints derived here.
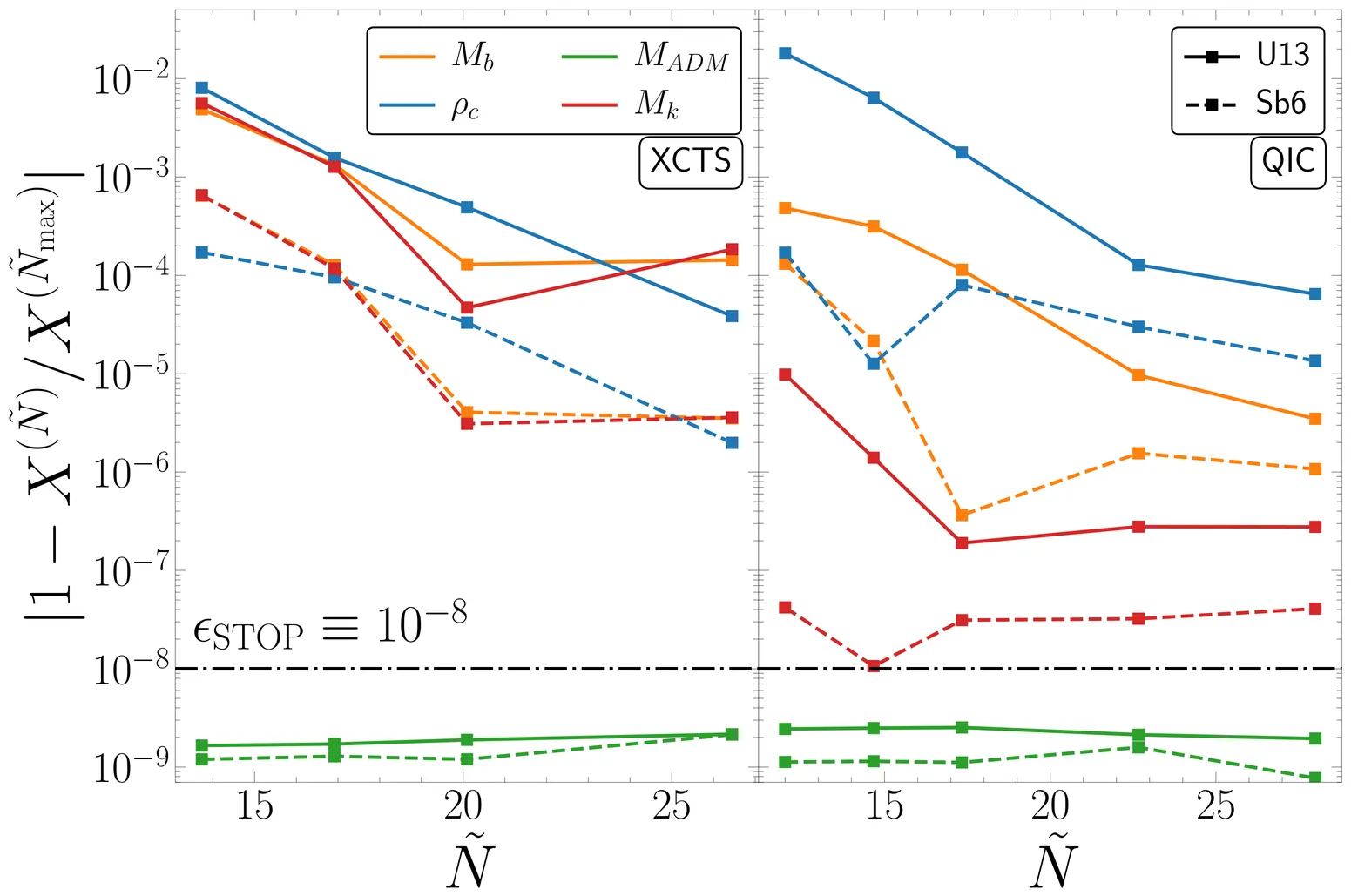
We present new initial data codes for constructing stationary, axisymmetric equilibrium models of differentially rotating neutron stars in full general relativity within the Frankfurt University/KADATH (FUKA) suite of initial data codes. FUKA leverages the KADATH spectral library to solve the Einstein equations under the assumption of an isentropic fluid without magnetic fields while incorporating GRHayLEOS to support 3D tabulated equations of state in \textit{stellar collapse} format. The two solvers explored in this work include one using quasi-isotropic coordinates (QIC) in Spherical coordinates while the other solves the eXtended Conformal Thin Sandwich (XCTS) decomposition in Cartesian coordinates, enabling the construction of equilibrium configurations with high accuracy and efficiency. In this work we adopt the Komatsu-Eriguchi-Hachisu differential rotation law, however, the code is designed to be extensible to other rotation laws, allowing for exploration of physically relevant sequences and critical rotation thresholds. Furthermore, we perform convergence tests demonstrating the exponential accuracy of the spectral approach, we validate QIC and XCTS solutions against models well-studied in the literature, and we also compare FUKA solutions against the well-known RNS code. Finally, we explore the impact that initial data resolution has on dynamical simulations and recover the convergence order of the evolution scheme, the dominate source of error in this study. The new FUKA codes and results presented here lay the foundation for future extensions to more general configurations, including magnetic fields, removal of isentropic assumptions, and binary systems, and have been made publicly available to support community efforts in modeling differentially rotating relativistic stars.
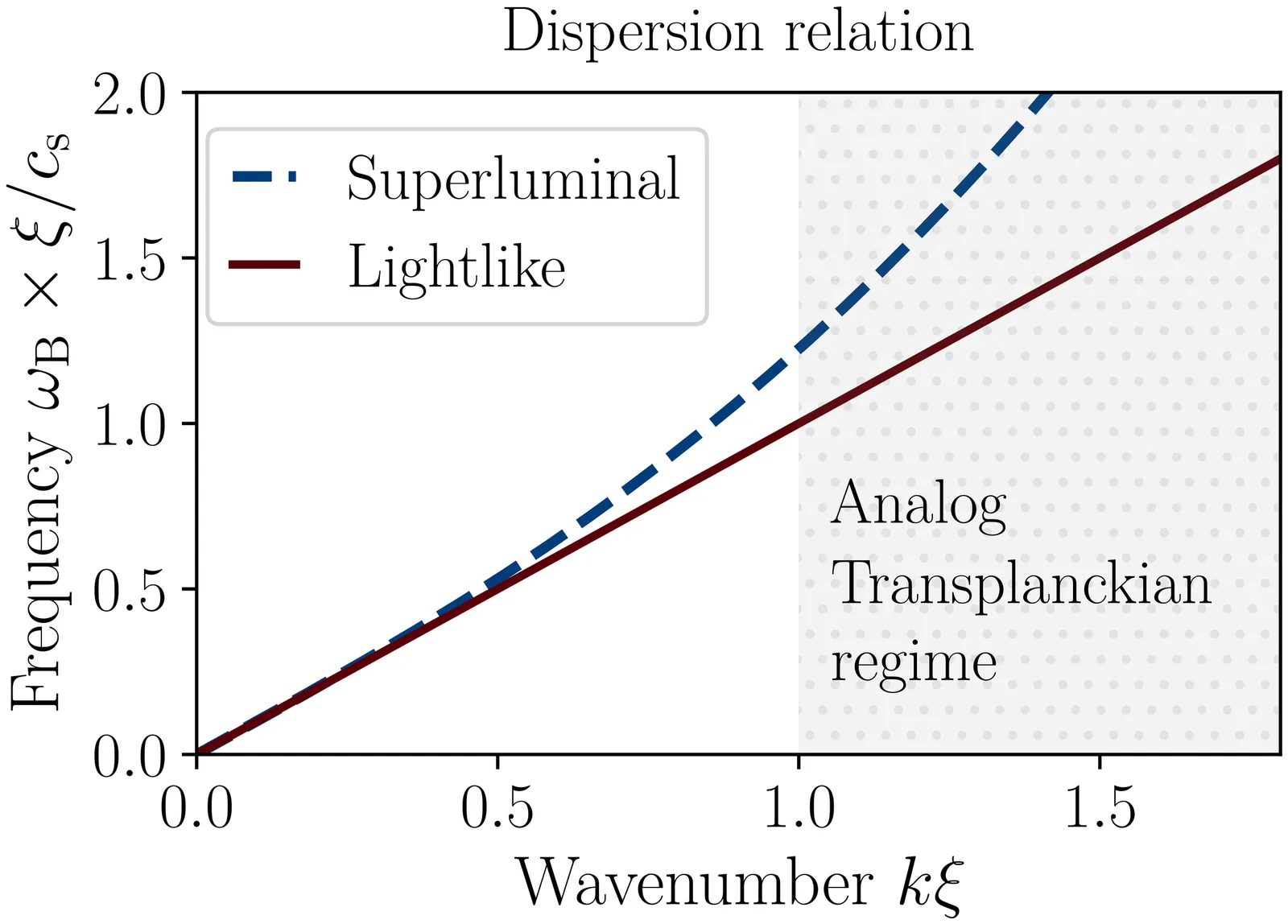
The quantum-field-theoretic description for the U(1)-Goldstone boson of a scalar Bose-Einstein condensate with time-dependent contact interactions is developed beyond the acoustic approximation in accordance with Bogoliubov theory. The resulting effective action is mapped to a relativistic quantum field theory on a dispersive (or rainbow) cosmological spacetime which has a superluminal Corley-Jacobson dispersion relation. Time-dependent changes of the s-wave scattering length to quantum-simulate cosmological particle production are accompanied by a time-dependent healing length that can be interpreted as an analog Planck length in the comoving frame. Non-adiabatic transitions acquire a dispersive character, which is thoroughly discussed. The framework is applied to exponentially expanding or power-law contracting $(2+1)$-dimensional spacetimes which are known to produce scale-invariant cosmological power spectra. The sensitivity of these scenarios to the time-dependence of the Bogoliubov dispersion is investigated: We find a violation of scale-invariance via analytically trackable Transplanckian damping effects if the cut-off scale is not well separated from the horizon-crossing scale. In case of the exponential expansion, these damping effects remarkably settle and converge to another scale-invariant plateau in the far ultraviolet regime where non-adiabatic transitions are suppressed by the high dispersion. The developed framework enables quantitative access to more drastic analog cosmological scenarios with improved predictability in the ultraviolet regime that ultimately may lead to the observation of a scale-invariant cosmological power spectrum in the laboratory.
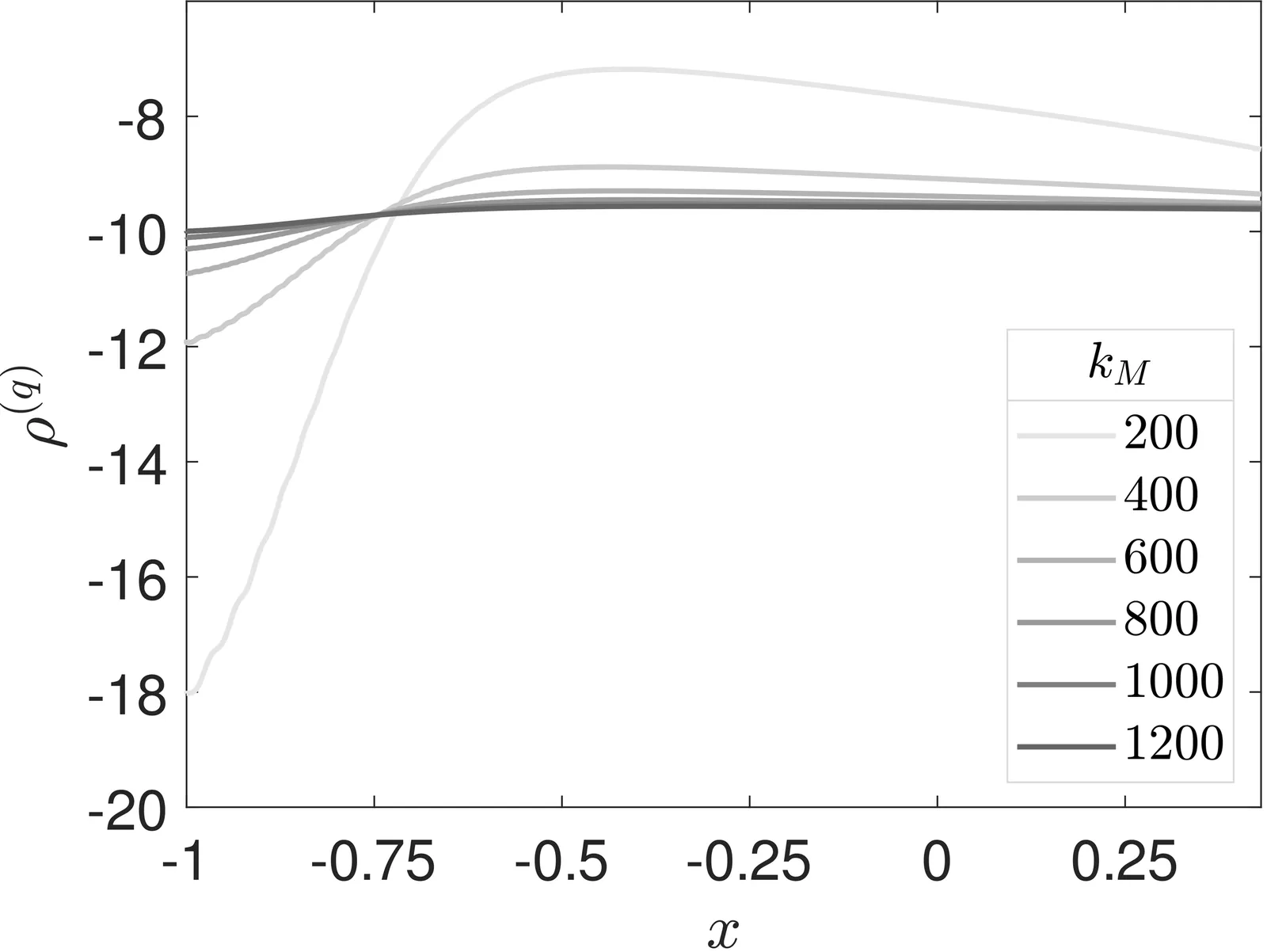
Boson stars have been extensively studied in classical gravity, but their quantum properties remain comparatively unexplored. In this paper, we compute the quantum scalar fields and stress tensor in boson star spacetimes within the framework of semiclassical gravity. Divergences are regularized using Pauli-Villars fields, and accurate numerical results are obtained through spectral methods. Employing coherent states enables a direct comparison between the classical part of the stress tensor and the quantum fluctuation. Our results indicate that strong spacetime curvature is the primary source of large quantum effects. The renormalized quantum energy density is mostly positive but the radial pressure is negative, suggesting that classical boson star solutions require modification once quantum effects are included. Moreover, in regimes of large curvature, the quantum fluctuations can constitute a significant fraction of the total stress tensor. The methods developed here can be generalized to other compact objects and used to study their response to quantum corrections.
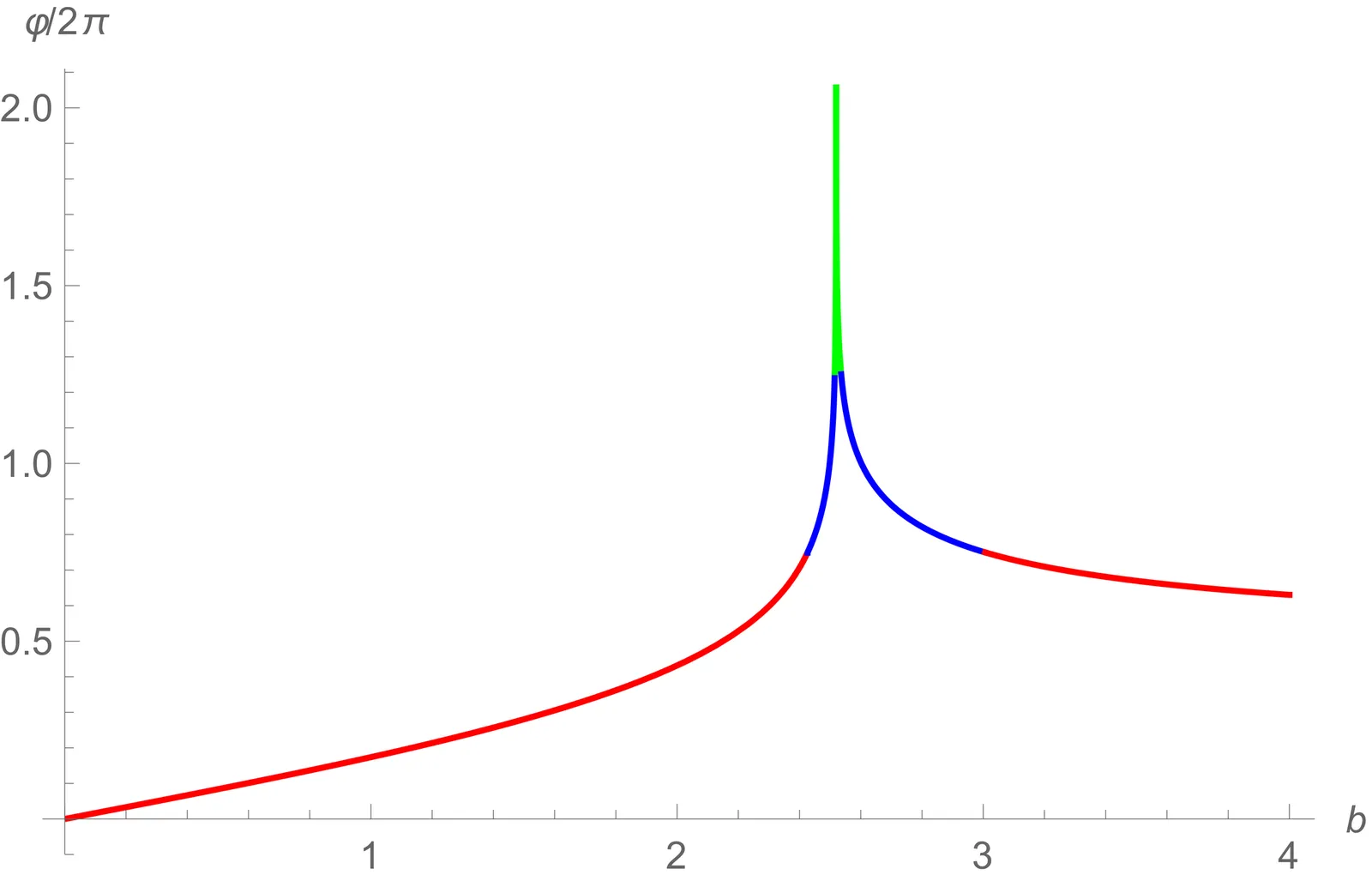
This work investigates the optical properties of a static, spherically symmetric, electrically charged black hole in f(R) gravity coupled to Euler-Heisenberg(EH) nonlinear electrodynamics(NLED). By analyzing photon trajectories in this background spacetime, we show how the model parameters affect light propagation, leading to wider ranges of lensed trajectories and photon rings. We identify regions of parameter space that admit physically consistent black hole shadows, characterized by the existence of a photon sphere located outside the event horizon and a shadow formed beyond it. These viable regions expand with increasing electric charge and increasing fR0, illustrating the interplay between gravitational and electromagnetic effects. By constraining the model using Event Horizon Telescope observations of M87*, we find that de Sitter black hole solutions remain compatible with the observational data, whereas anti-de Sitter solutions are disfavored for low electric charge and fR0 > -1. Finally, an analysis of the energy emission rate shows that higher electric charge enhances black hole evaporation, while stronger nonlinear electrodynamics effects and larger values of fR0 suppress it.
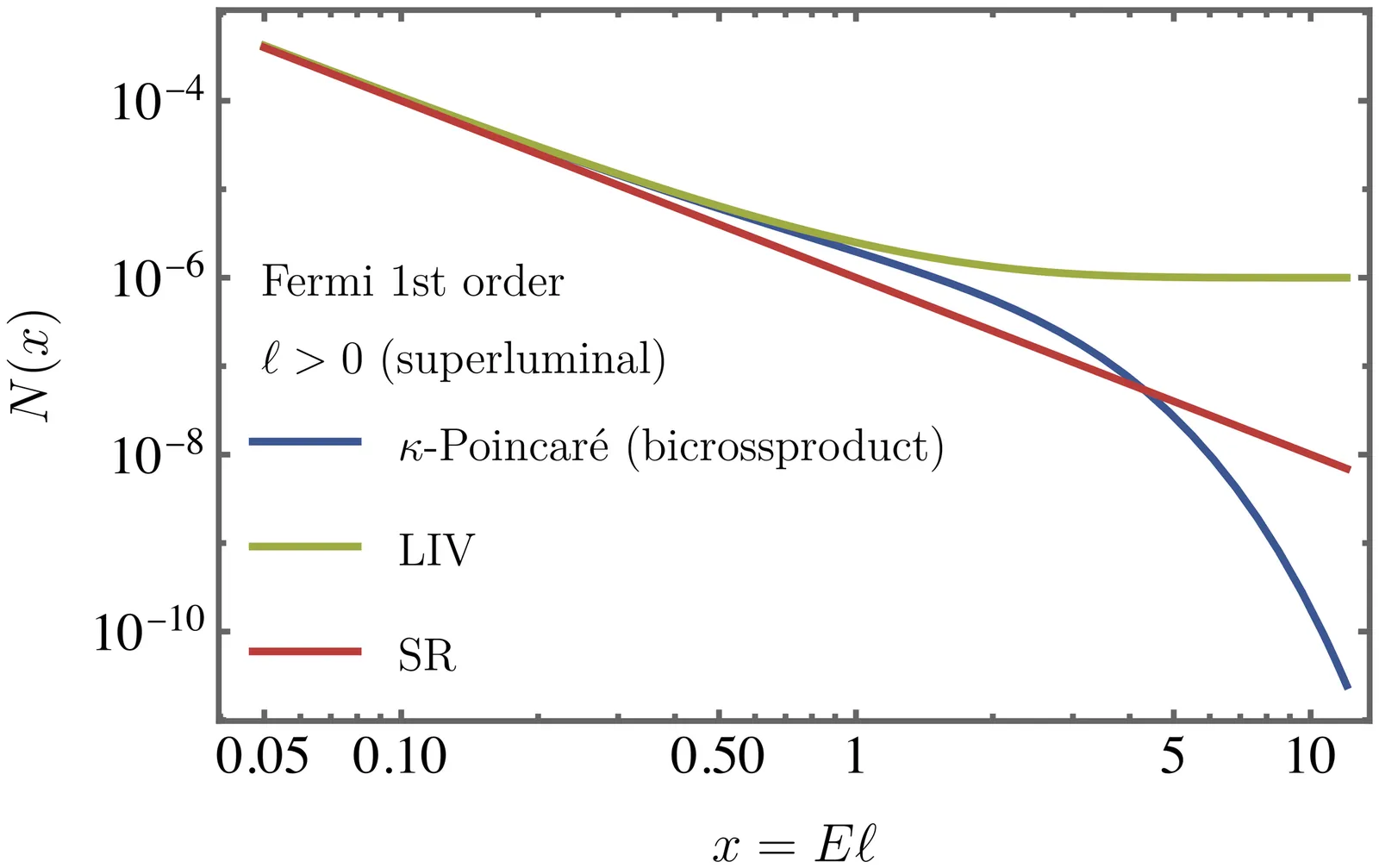
We construct models for first- and second-order Fermi acceleration of particles, incorporating generic frame transformations, dispersion relations, and conservation laws. Within this framework, we study deformations of Lorentz symmetry via the $κ$-Poincaré algebra in the bicrossproduct and classical bases, which respectively deform and preserve the relativistic dispersion relation. We also examine explicit Lorentz symmetry violation and compare the results with deformed relativity and special relativity.
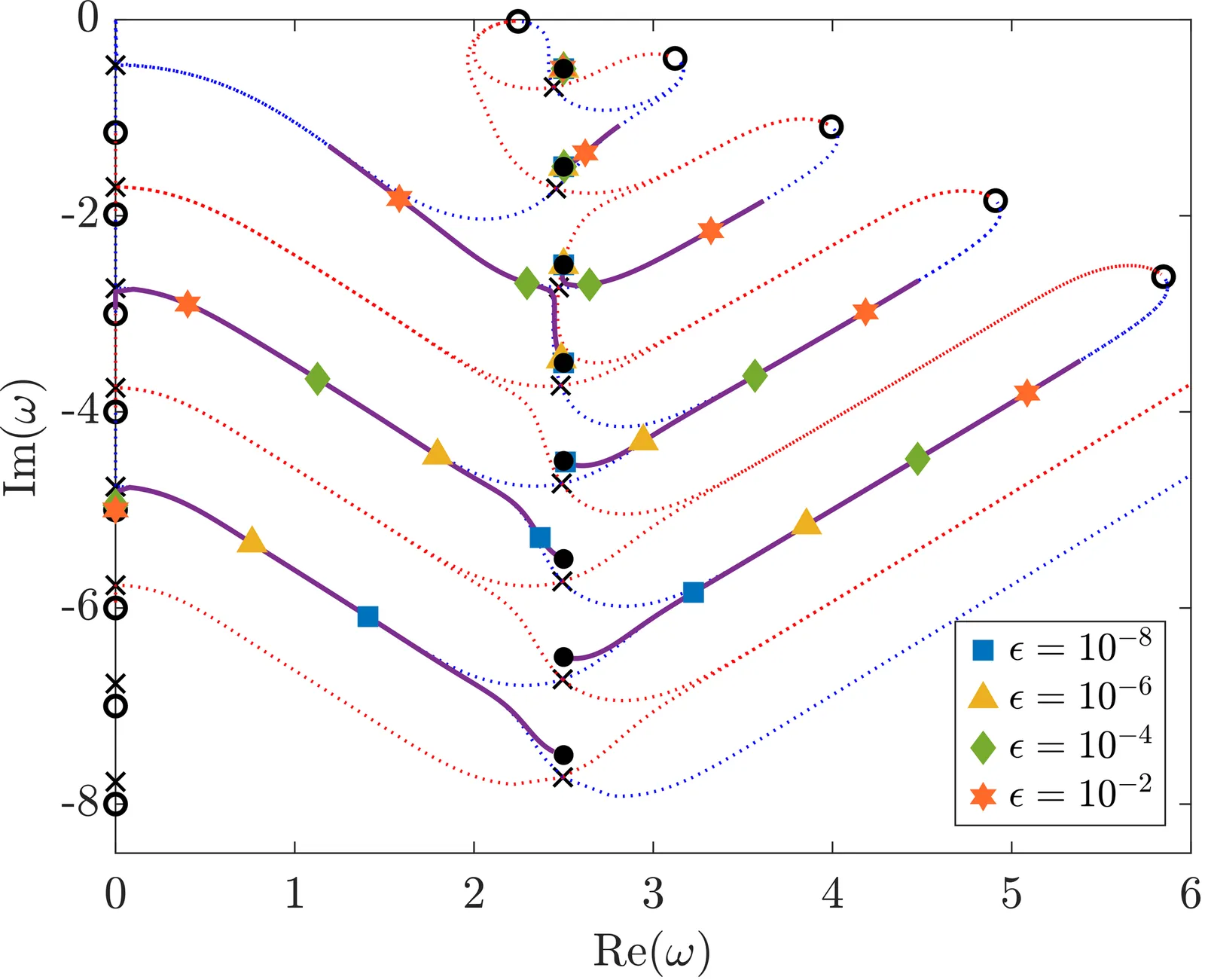
The aim of this work is to improve understanding of the resonant spectra of black holes under perturbations arising from e.g. compact objects or accretion disks in their vicinity. It is known that adding a weak perturbation to the radial potential can strongly disrupt the spectrum of quasinormal modes and Regge poles of a black hole spacetime. Here we examine the effect of (weak or strong) localised delta-function perturbations on the resonant spectra of spherically-symmetric systems, to address fundamental questions around linear and non-linear spectral stability. We examine two cases: the Nariai spacetime with a Poschl-Teller potential and the Schwarzschild spacetime. We show that, in either case, the spectrum deforms in a smooth and continuous manner as the position and strength of the perturbation is varied. As the strength of the perturbation is increased, resonances migrate along trajectories in the complex plane which ultimately tend towards attracting points determined by a hard-wall scenario. However, for weak perturbations the trajectory near the unperturbed resonance is typically strongly influenced by a set of repelling points which, for perturbations far from the system, lie very close to the unperturbed resonances; hence there arises a non-linear instability (i.e. the failure of a linearised approximation). Taking a dynamical systems perspective, the sets of attracting and repelling spectral points follow their own trajectories as the position of the perturbation is varied, and these are tracked and understood.
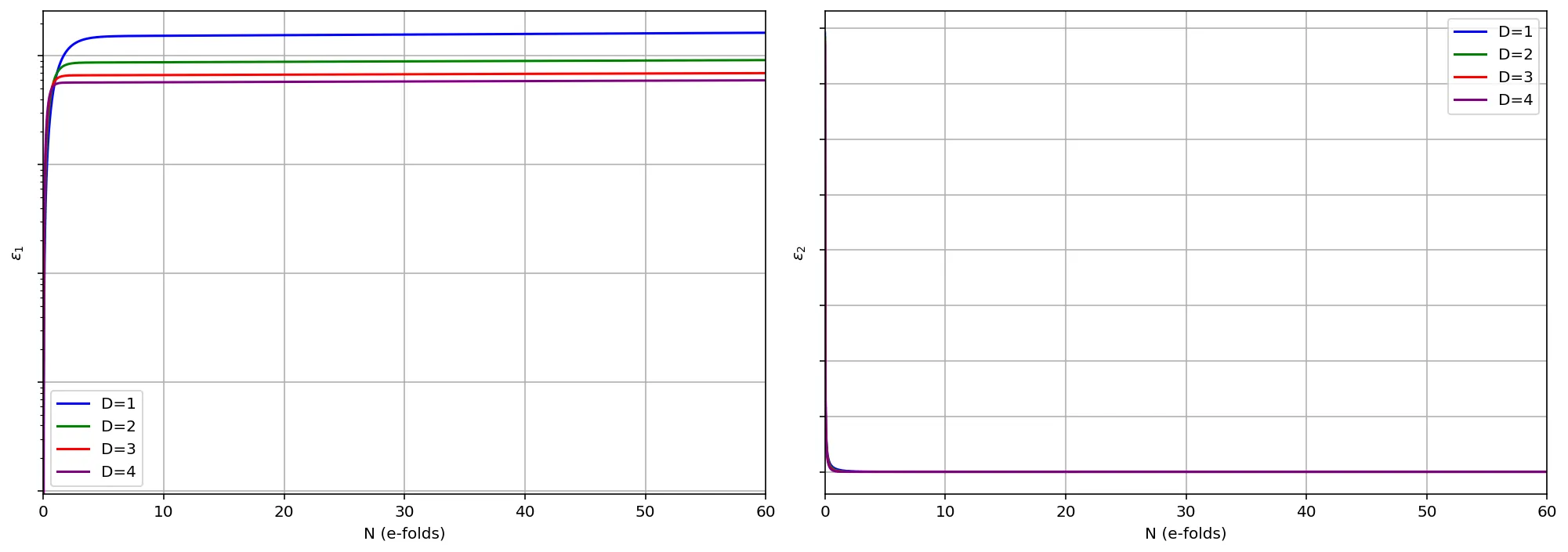
We study inflationary dynamics within the framework of fractal cosmology, where spacetime exhibits a non-integer effective dimension, sourced through a relaxation of the cosmological principle. Using Friedmann and continuity equations, modified by an effective fractal dimension $D$; we derive generalized slow-roll parameters and examine their evolution for cubic, Starobinsky and Natural inflationary potentials. We then formulate a fractal extension of the Mukhanov-Sasaki equation by introducing an effective momentum term $k_{\text{eff}}$, arising from the fractal decomposition of the spatial Laplacian, that captures the geometric influence of fractal cosmology on scalar perturbations. This leads to corrections in the power spectrum and a scalar spectral index $n_s$ that depends explicitly on both the fractal dimension $D$ and a fractional scale $L$, which controls the strength of the fractal deformation. Comparison with the Planck 2018 data ($n_s=0.9649\pm 0.0042$) constrains the allowed range of $D$ ($2.7\lesssim D\lesssim3$) depending on the cosmological and inflationary model assumed.
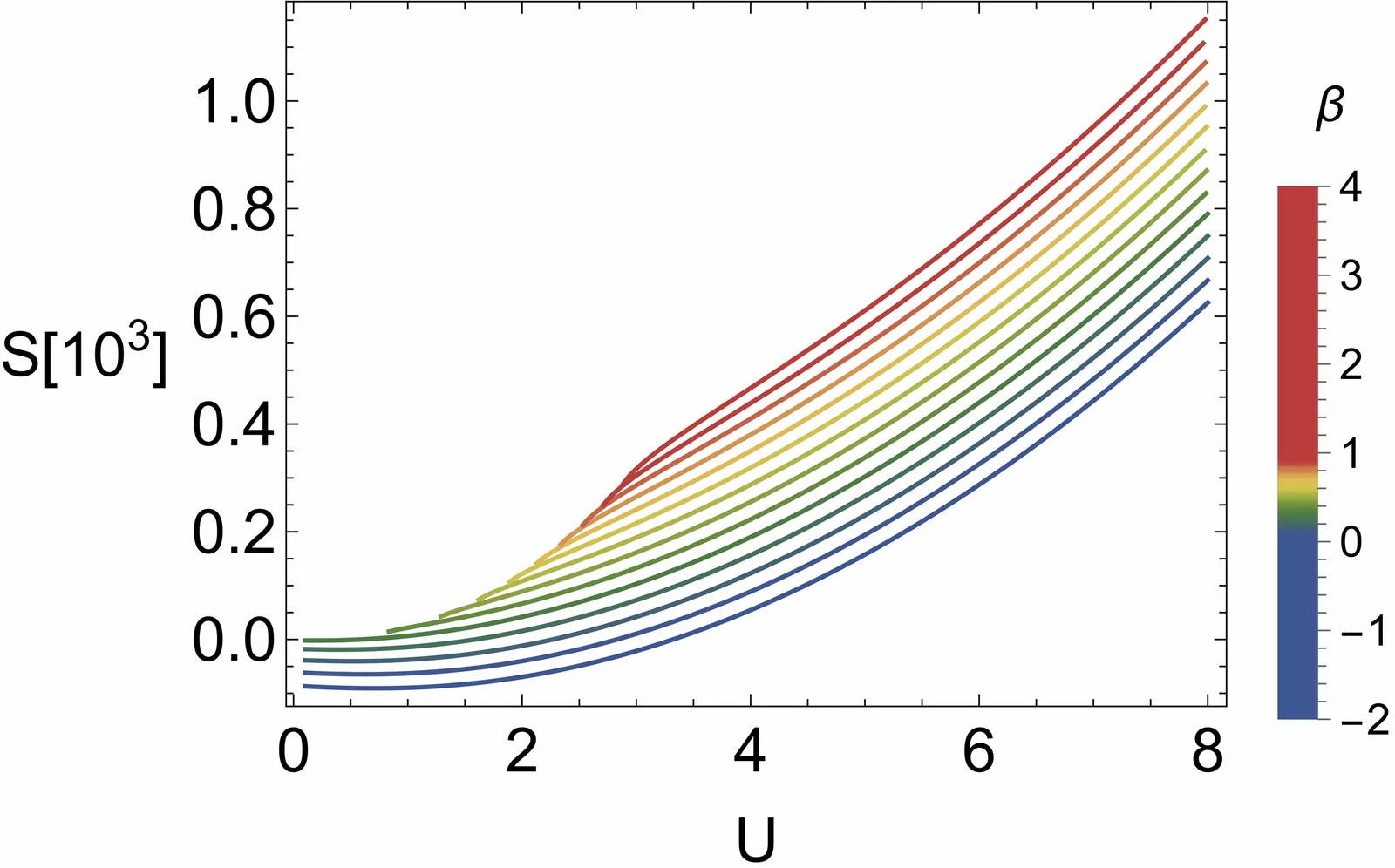
The analysis of phase transitions in cosmological spacetimes shows that their existence requires a time-dependent apparent horizon radius, which in turn implies an equation of state different from that of a dark energy fluid. This condition is not compatible with the simultaneous fulfillment of Hayward's unified gravitational first law and the fundamental thermodynamic equation of the apparent horizon. To solve this problem, we introduce an alternative formulation in which the cosmological horizon is modeled as a quasi-homogeneous thermodynamic system. We apply this approach to the Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker (FLRW) universe under quantum gravity corrections encoded by the Generalized Uncertainty Principle (GUP), promote the deformation parameter to a thermodynamic variable, and obtain a consistent thermodynamic description without relying on the usual pressure-volume interpretation. Using Geometrothermodynamics (GTD), we show that fluctuations of the GUP parameter can induce phase transitions closely resembling those of black hole configurations. Finally, we perform a numerical analysis of the behavior of the GTD scalar curvature near the phase transition point, where we find a scaling behavior characterized by the critical exponent close to 1, independently of the dimension of the equilibrium space. This reveals that quantum gravity corrections not only modify the thermodynamic consistency of cosmological models but also strengthen the notion of thermodynamic universality across gravitational systems. Our findings confirm GTD as a powerful geometric tool to unveil the emergent thermodynamic microstructure of spacetime.
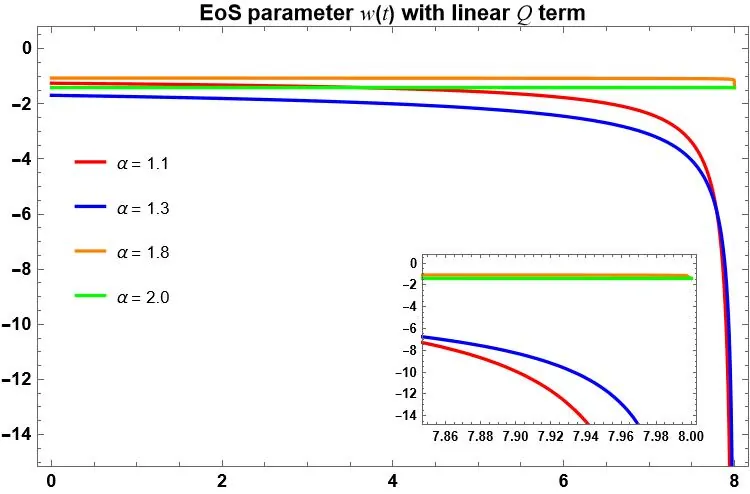
In this paper, we investigate the occurrence of late-time cosmological singularities, namely, the rip scenarios within the framework of interacting Fractional Holographic Dark Energy (FHDE). We start our investigation with the Granda-Oliveros (GO) cutoff, i.e., $L=(γH^{2}+δ\dot{H})^{-\frac{1}{2}}$, and highlight the range of allowed $α$ (Lévy's index) values for which big, little and pseudo rip can occur. In particular, we highlight the occurrence of a big rip for fractional values of the Lévy's index in the allowed range $1<α\leq2$. Moreover, we conclude that the occurrence of a pseudo-rip requires Lévy's index to be $α>2$. Therefore, we reject the possibility of pseudo-rip within the GO cutoff. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the occurrence of the little rip in FHDE equipped with a GO cutoff is rather contrived and requires a specific functional form of the IR cutoff $L\sim(γH^{2}+g(H))^{-\frac{1}{2}}$, which belongs to a larger class of Nojiri-Odintsov (NO) cutoffs. To extend our perspective beyond the GO cutoff, we investigate the interacting FHDE framework equipped with the Hubble cutoff, i.e., $L=H^{-1}$, in developing an ansatz-based approach to the little and pseudo-rip singularities as they fail to appear in the GO cutoff. Within this approach, we invoke the expression of the Hubble parameter, $H(t)$, which corresponds to the little and pseudo-rip, into the cosmological parameters such as the Equation of State (EoS) and Squared Sound Speed (SSS) as a function of cosmic time $t$. We produce numerical plots of these parameters in both linear and non-linear $Q$ regimes, which supplement our theoretical findings. In summary, our results highlight the occurrence of little and pseudo-rip singularities within a Hubble cutoff for a non-linear $Q$ term within the FHDE framework.
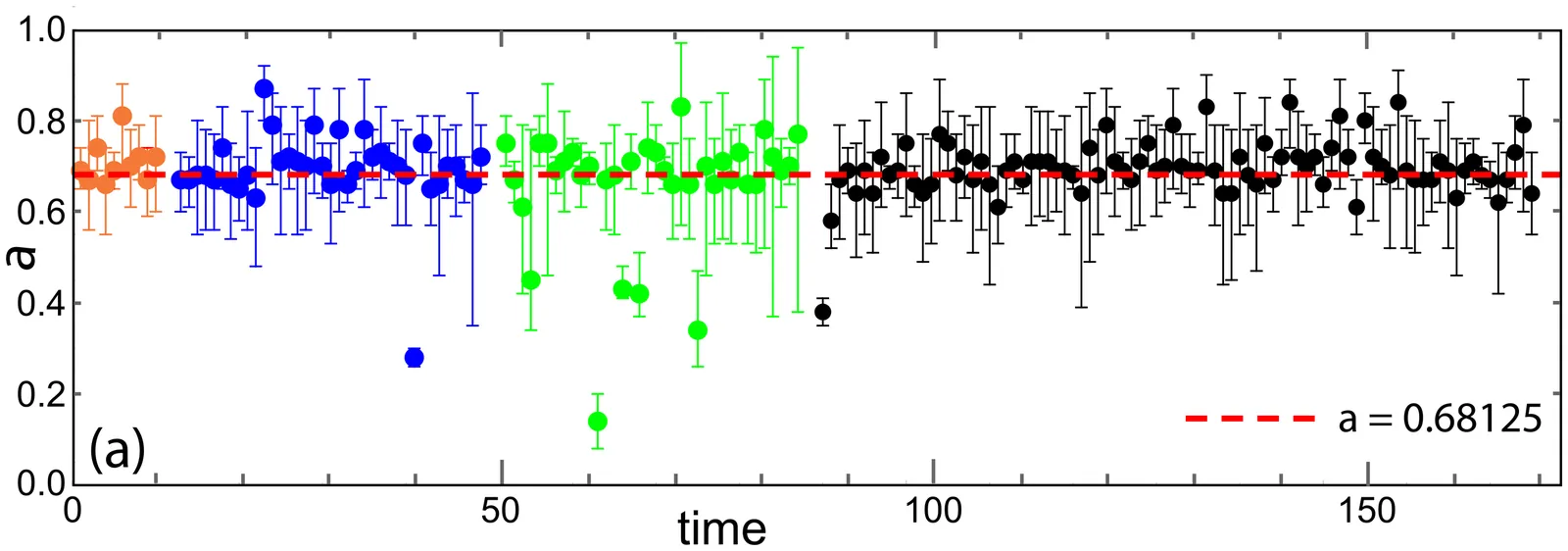
Gravitational waves from binary black hole mergers yield values for both the black hole remnant mass $M$ and it's spin $a$, with the $169$ $a$ values collected so far crowding significantly around their average $\bar{a}=0.6869\pm 0.087$. Could this crowding relate directly to the Davies phase transition point at $a=0.68125$ from black hole thermodynamics? I argue that a necessary challenge for such a connection requires a consistent application of the thermodynamic fluctuation theory that follows from black hole thermodynamics (BHT). Specifically, necessary are a correct choice of fluctuating variables, as well as thermal equilibrium between the event horizon at the Hawking temperature $\sim μK$ and the outside universe $\sim 3 K$. I show that the former requirement follows in straightforward fashion from the BHT of the Kerr model, while the later requires an accretion disk following the Novikov-Thorne accretion disk model. I construct a thermodynamic fluctuation theory meeting both these requirements. My results open the possibility that black hole mergers are based on some dynamical model (not known to me) with a limiting attractor state at the Davies point.
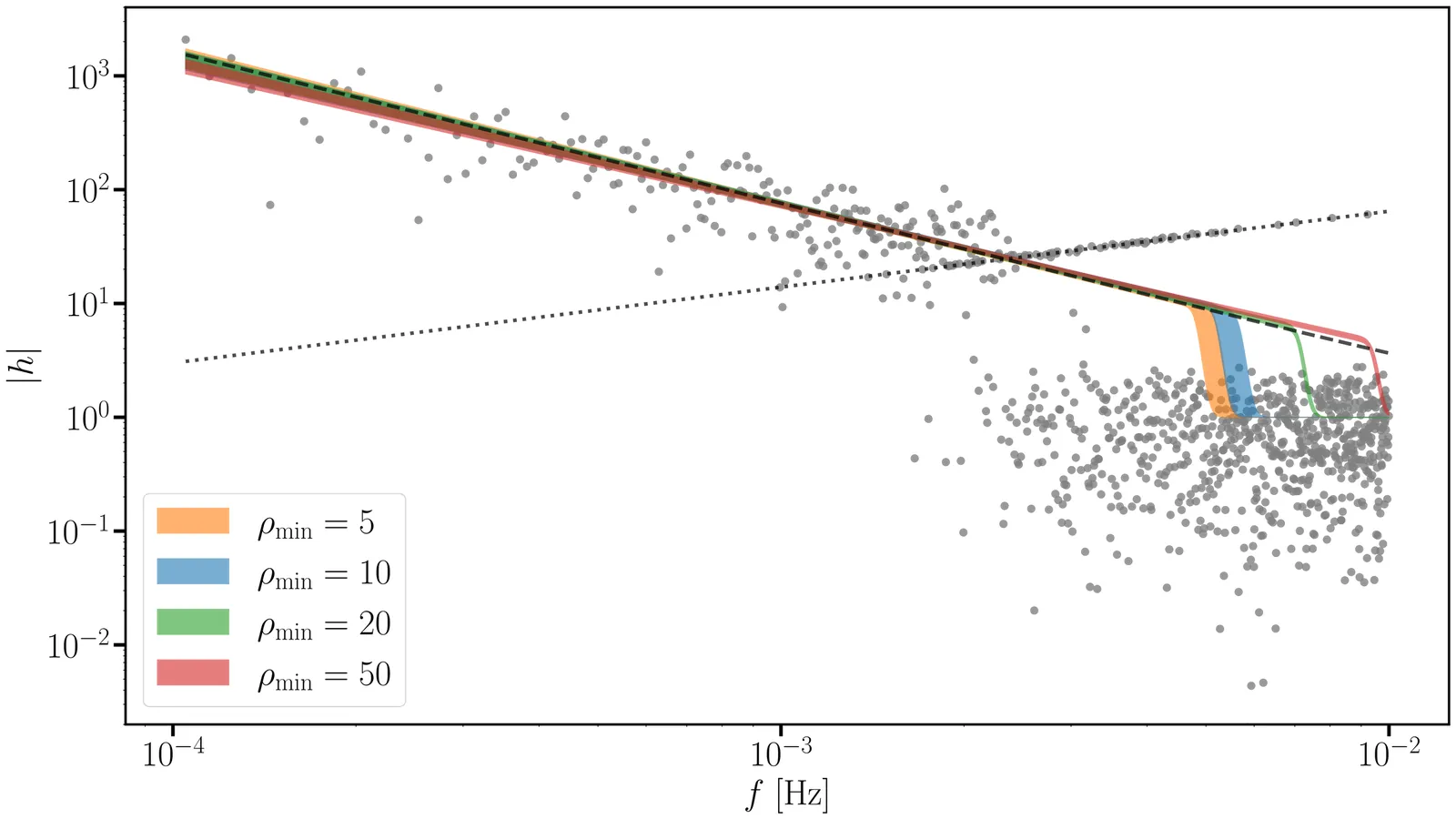
The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is expected to have a source rich data stream containing signals from large numbers of many different types of source. This will include both individually resolvable signals and overlapping stochastic backgrounds, a regime intermediate between current ground-based detectors and pulsar timing arrays. The resolved sources and backgrounds will be fitted together in a high dimensional Global Fit. To extract information about the astrophysical populations to which the sources belong, we need to decode the information in the Global Fit, which requires new methodology that has not been required for the analysis of current gravitational wave detectors. Here, we %start that development, presenting present a hierarchical Bayesian framework to infer the properties of astrophysical populations directly from the output of a LISA Global Fit, consistently accounting for information encoded in both the resolved sources and the unresolved background. Using a simplified model of the Global Fit, we illustrate how the interplay between resolved and unresolved components affects population inference and highlight the impact of data analysis choices, such as the signal-to-noise threshold for resolved sources, on the results. Our approach provides a practical foundation for population inference using LISA data.
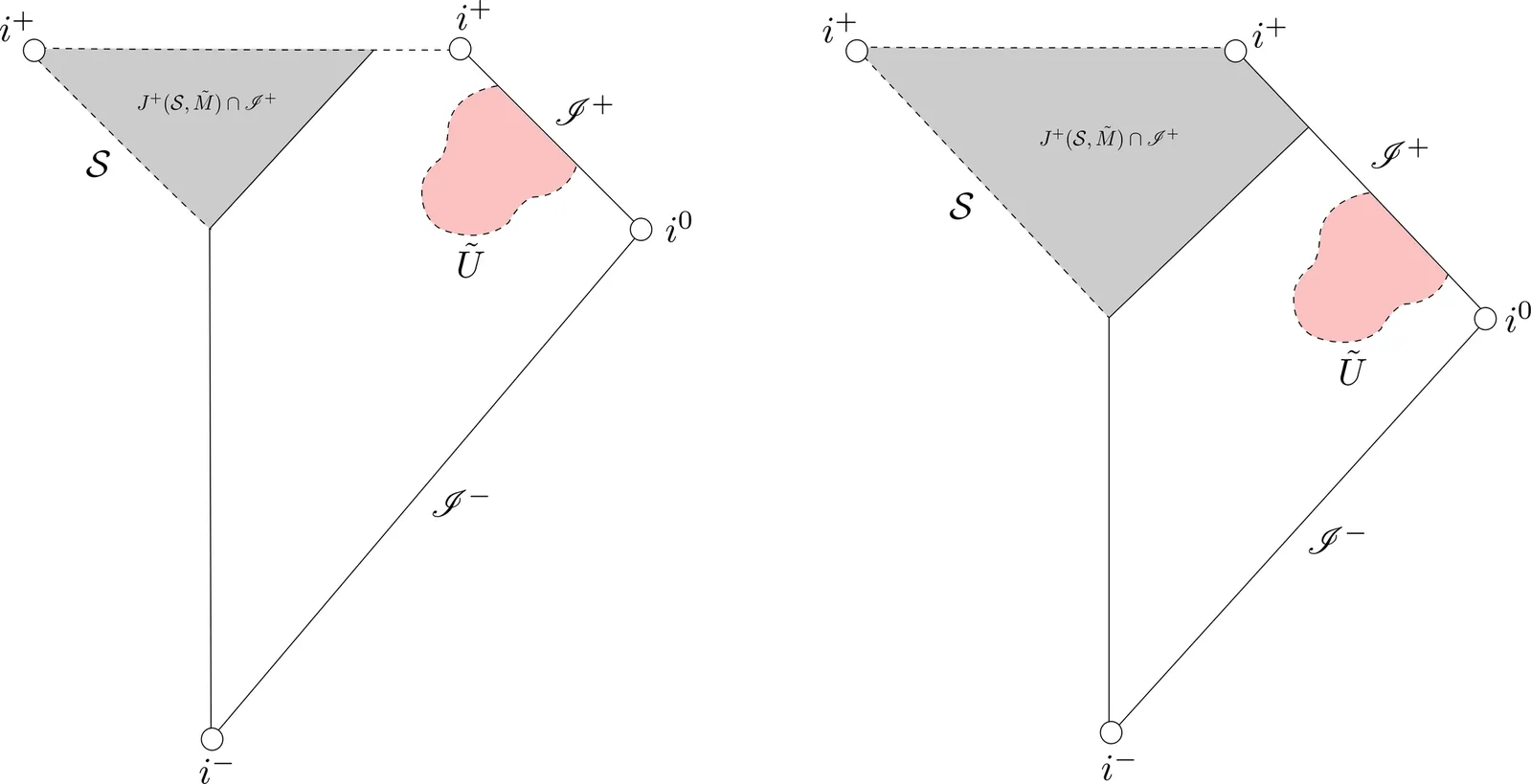
Consider an $(N+1)$-dimensional asymptotically flat spacetime and a future-directed, affinely parametrized outgoing null generator $γ$ of an achronal boundary $\partial J^+(S_\varepsilon)$, where $\{S_\varepsilon\}$ is a nested family of smooth compact codimension $2$ surfaces approaching a singular boundary set $S$ in the past. In the twist-free case and under the null energy condition, the Raychaudhuri equation on the $m:=N-1$ dimensional screen bundle reads, $$ θ'=-\frac1mθ^2-\|σ\|^2-\mathrm{Ric}(k,k), $$ where $k$ is the tangent to $γ$. This equation linearizes, via the rescaling $u:=A^{1/m}$ with $A := |\det D|$ the Jacobi-map $m$-volume, to the Sturm-type ODE $$ u''+\frac1m f\,u=0,\qquad f:=\|σ\|^2+\mathrm{Ric}(k,k)\ge 0. $$ We develop two purely generator-wise criteria forcing a first zero of $u$: (i) an exact Volterra identity combined with concavity leads to a barrier-weighted integral inequality, and (ii) Sturm comparison and a Prüfer-angle estimate yields failure of disconjugacy whenever $\int_c^d \sqrt{f/m}\,dλ>π$ on a subinterval. We prove that $u(λ_\ast)=0$ is equivalent to the existence of a focal (conjugate) point and implies $θ= m u'/u\to-\infty$ at $λ_\ast$. Using the standard structure of achronal boundaries, this yields a geodesic-wise obstruction: if every generator that could reach $\mathscr I^+$ satisfies one of the above conditions in the regular spacetime region, then $J^+(S_\varepsilon)\cap \mathscr I^+=\emptyset$, and hence $S$ is not globally visible. As an application, we illustrate one of these criteria in the Einstein-massless scalar field collapse model of Christodoulou.
We propose a mechanism for the generation of gravitationally bound dark photon halos during the matter-dominated era. Coupled to an ultralight axion field through a parity-violating Chern-Simons term, dark photons can be produced by the tachyonic instability of axion coherent oscillation. The dark photons with a net helicity lead to a metric vorticity and can generate chiral substructures. For axion masses in the range $10^{-28} \, \mathrm{eV} \lesssim m_a \lesssim 10^{-22} \, \mathrm{eV}$, the resulting inhomogeneities collapse to form halos with masses spanning $M_{\rm halo} \sim 10^5 \, M_{\odot}$ to $10^{11} \, M_{\odot}$, with halo sizes ranging from $O(1)$ to $O(10^{6}) \, \mathrm{pc}$. During halo collapse, the induced vorticity could mediate efficient angular-momentum transport, which enables monolithic collapse and provides primordial seeds for the early formation of supermassive black holes.
 2601.04144
2601.04144In cosmology, long-wavelength modes are related to large-gauge transformations (LGT), i.e. changes of coordinates that modify the physical geometry of the cosmological patch. These LGTs stand as bona-fide symmetries of cosmological perturbation theory with various applications, from consistency relations constraining cosmological correlators to non-linear conservation laws in the separate-universe approach. In this work, we revisit LGTs and derive two new results. First, we show that the global symmetries already identified in the literature can be extended to local infinite-dimensional symmetries. The associated generators depend on arbitrary functions of time, and generate low-multipole modes that modify the mean curvature energy and the angular momentum of the patch, demonstrating their physical nature. We propose to interpret these low-multipole soft modes as a new cosmological-frame ambiguity that needs to be fixed prior to evaluating cosmological observables. Second, we demonstrate that the adiabatic cosmological perturbations generated by LGTs deform but preserve all the explicit and hidden Killing symmetries of the background geometry. As such, long-wavelength modes stand as a concrete example of algebraically-special cosmological perturbations of Petrov-type O, and inherit the conformal group as isometries and a set of four deformed Killing-Yano tensors and their associated Killing tensors. This opens the possibility to study their effect on cosmological observables in a fully analytic manner.
 2601.04290
2601.04290We present a minimal relativistic completion of MOND in which (i) General Relativity is recovered exactly in the high-acceleration regime, while (ii) the Bekenstein--Milgrom (AQUAL) equation emerges in the low-acceleration regime, without introducing additional propagating fields beyond those already present in a right-handed gauge sector. The construction is motivated by an $E_6\times E_6$ framework in which $SU(3)_R\rightarrow SU(2)_R\times U(1)_{Y'}\rightarrow U(1)_{\rm dem}$, leaving a healthy repulsive $U(1)_{\rm dem}$ interaction whose charge is the square-root mass label. Gravity itself arises from the $SU(2)_R$ connection via a Plebanski/MacDowell--Mansouri mechanism, yielding an emergent tetrad and the Einstein--Hilbert action. MOND is implemented by an infrared (IR) metric deformation $ΔS_{\rm IR}[g]$ that is UV-vanishing (so GR is recovered) while its deep-MOND/static limit is fixed by a symmetry principle: in three spatial dimensions, the deep-MOND action is conformally invariant with a 10-parameter group isomorphic to $SO(4,1)$ (the de Sitter group). The single MOND acceleration scale is set by a de Sitter radius selected dynamically in the IR, $a_0=c^2/(ξ\,\ell_{\rm dS})$ with $ξ={ O}(1)$ fixed by matching to the static limit. MOND resides in perturbations and quasistatic systems; the homogeneous FRW background is controlled by the IR vacuum kinematics rather than an ad hoc cosmological constant.
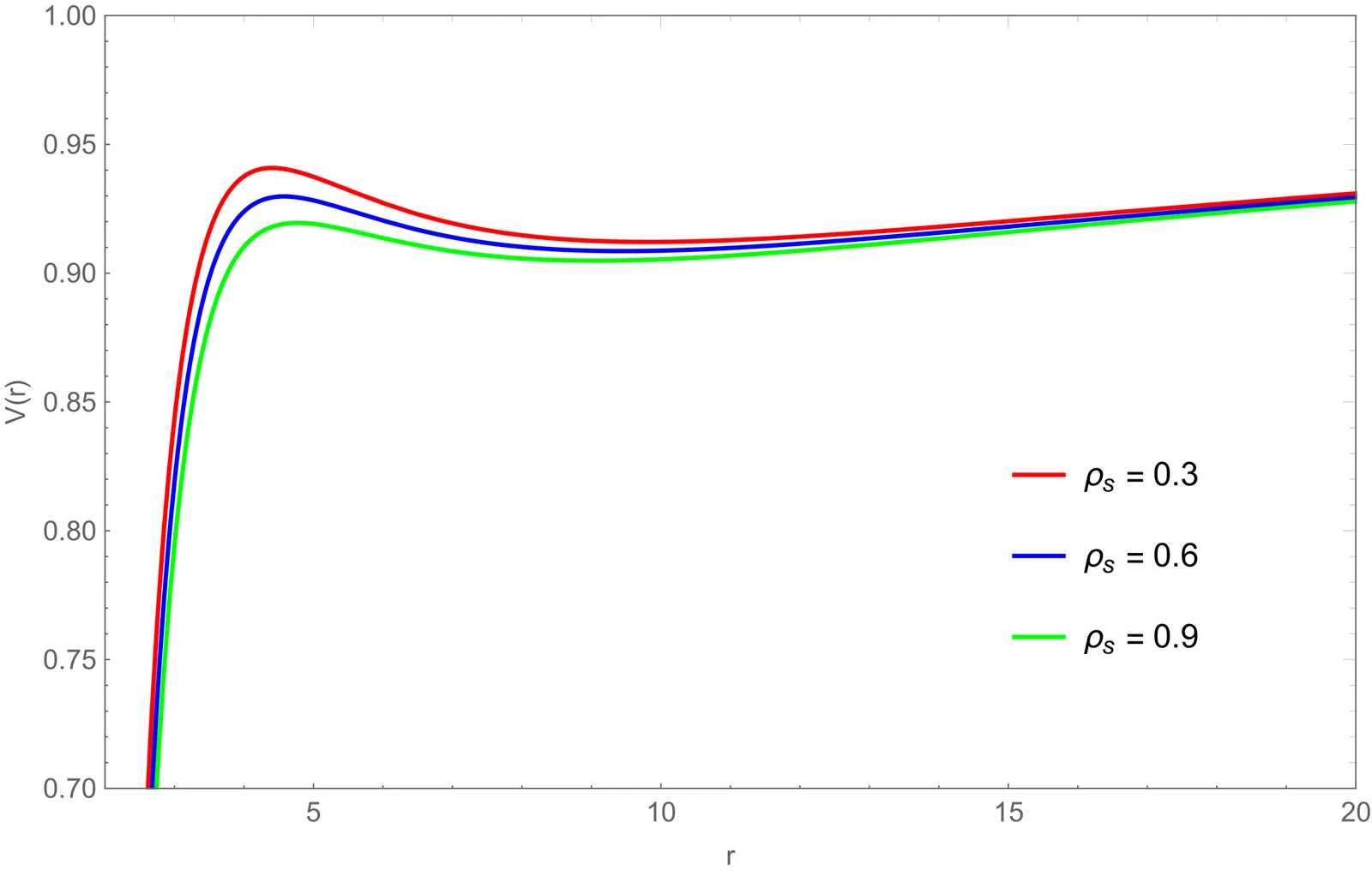
We investigate how a Hernquist type dark matter (DM) halo, parametrized by its core radius $r_{s}$ and central density $ρ_{s}$, influences both the gravitational wave (GW) emission from timelike periodic orbits and the electromagnetic appearance of a thin accretion disk around a Schwarzschild black hole (BH). By analyzing the effective potential for timelike geodesics, we show that the DM halo shifts the marginally bound orbit (MBO) and the innermost stable circular orbit (ISCO) outward, reflecting its modification of the spacetime geometry and the energy-angular momentum structure of particle motion. Employing a semi-analytical method, we compute orbital trajectories and the associated GW waveforms, revealing that the DM halo alters the characteristic zoom-whirl dynamics and induces measurable changes in waveform morphology. Furthermore, we generate direct and secondary images of the accretion disk across various observer inclinations and find that increasing $r_{s}$ or $ρ_{s}$ results in cooler, dimmer disks with modified flux distributions. Our results demonstrate that the presence of a DM halo imprints distinct signatures in both gravitational and electromagnetic observables, offering a multimessenger pathway to probe DM environments near BHs.
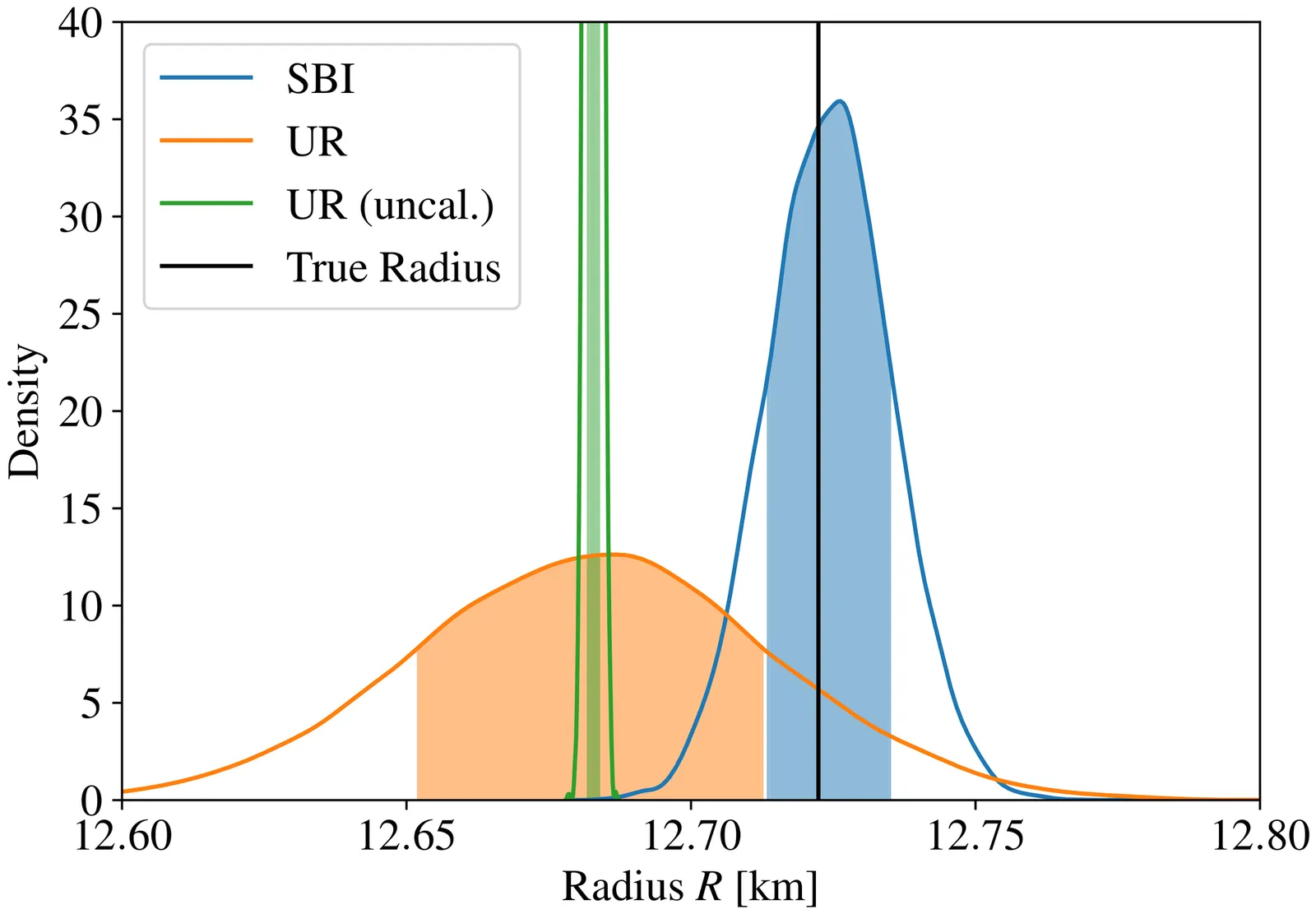
In this work, we propose a novel approach for identifying, constructing, and validating precise and accurate universal relations for neutron star bulk quantities. A central element is simulation-based inference (SBI), which we adopt to treat uncertainties due to the unknown nuclear equation of state (EOS) as intrinsic non-trivial noise. By assembling a large set of bulk properties of non-rotating neutron stars across multiple state-of-the-art EOS models, we are able to systematically explore universal relations in high-dimensional parameter spaces. Our framework further identifies the most promising parameter combinations, enabling a more focused and traditional construction of explicit universal relations. At the same time, SBI does not rely on explicit relations; instead, it directly provides predictive distributions together with a quantitative measure of systematic uncertainties, which are not captured by conventional approaches. As an example, we report a new universal relation that allows us to obtain the radius as a function of mass, fundamental mode, and one pressure mode. Our analysis shows that SBI can surpass the predictive power of this universal relation while also mitigating systematic errors. Finally, we demonstrate how universal relations can be further calibrated to mitigate systematic errors accurately.